Abstract
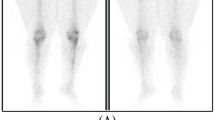
Articular involvement was reported to be present in approximately 5-76% of Behçet patients. Therefore, we need a useful non-invasive method to detect articular involvement early in Behçet patients with nonspecific complaints. We aimed to evaluate the usefulness of99mTc-methylene diphosphonate (Tc-99m-MDP) bone scintigraphy in the detection of the articular involvement of Behçet’s disease (BD). Bone scintigraphy with Tc-99m-MDP was performed in 32 (17 male, 15 female) consecutive patients with BD. The sacroiliac (SI) joints with SI index higher than 1.34 were diagnosed as having sacroiliitis. Although joint complaints were present in only 8 (25%) patients, we detected joint involvement by scintigraphy in 27/32 (84.4%) Behçet patients mostly affecting the knees (62.5%), ankles (59.4%), SI joints (25%), wrists (21.9%), shoulders (18.7%), elbows (12.5%) and hips (3.1%). The articular involvement was monoarticular in four cases (12.5%) and was oligoarticular in the remaining. There was no correlation between joint involvement and age, gender, disease duration, drug usage or other clinical manifestations. Despite the fact that our patients were clinically asymptomatic and had normal pelvis radiography, sacroiliitis was found in 8 patients (25%). Bone scintigraphy is sensitive in the diagnosis of joint involvement allowing earlier diagnosis and showing the presence of articular involvement, especially in SI joints.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jorizzo JL. Behçet’s Disease. In: Fitzpatrick TB, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, et al. eds.Dermatology in General Medicine 4th edn. New York; McGraw-Hill Inc., 1993: 2290–2294.
International Study Group for Behçet’s Disease. Evaluation of diagnostic (“classification”) criteria in Behçet’s Disease: towards internationally agreed criteria.Br J Rheumatol 1992;31:299–308.
Al-Mutawa SA, Hegab SM. Behçet’s disease.Clin Exp Med 2004; 4: 103–131.
Gharibdoost F, Davatchi F, Shahram F, et al. Clinical Manifestations of Behçet’s Disease in Iran Analysis of 2176 cases. In: Godeau P, Wechsler B, eds.Behçet’s Disease. Amsterdam; Elsevier Science Publishers, 1993: 153–158.
DilşFen N, Koniçe M, Aral O. et al. Risk factors for vital organ involvement in Behçet’s Disease. In: Godeau P, Wechsler B, eds.Behçet’s Disease. Amsterdam; Elsevier Science Publishers, 1993: 165–169.
Prokaeva T, Madanat W, Yermakova N, Alekberova Z. Sex dimorphism of Behçet’s Disease. In: Godeau P, Wechsler B, eds.Behçet’s Disease. Amsterdam; Elsevier Science Publishers, 1993:219–221.
Zouboulis CHC, Djawari D, Kirch W, et al. Adamantiades-Behçet’s Disease in Germany. In: Godeau P, Wechsler B, eds.Behçet’s Disease. Amsterdam; Elsevier Science Publishers, 1993: 193–196.
Yazici H, Tüzün Y, Pazarli H,et al. Influence of age of onset and patient’s sex on the prevalence and severity of manifestations of Behçet’s syndrome.Ann Rheum Dis 1984; 43: 783–789.
Yurdakul S, Yazici H, Tuzun Y, Pazarli H, Yalcin B, Altac M, et al. The arthritis of Behçet’s disease: a prospective study.Ann Rheum Dis 1983; 42: 505–115.
Kim HA, Choi KW, Song YW. Arthropathy in Behçet’s disease.Scand J Rheumatol 1997; 26: 125–129.
Kim HS, Lee J, Lee CH, Song JH, Bang DS, Lee SK. Heel pain in Behçet’s disease.J Korean Rheum Assoc 1995; 2: 151–156.
Yapar Z, Kibar M, Soy M, Ozbek S. Osteonecrosis in Behçet’s disease seen on bone scintigraphy.Clin Nucl Med 2001;26:267–268.
Tanaka E, Nishinarita M, Uesato M, Kamatani N. A case of intestinal Behcet’s disease with abnormal ossification complicated by myelodysplastic syndrome, symptoms revealed after the perforation of ileum ulcer.Ryumachi 2000; 40: 711–718.
Kane D, Balint PV, Wood F, Sturrock RD. Early diagnosis of pyomyositis using clinic-based ultrasonography in a patient receiving infliximab therapy for Behçet’s disease.Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003; 42: 1564–1565.
Davis MC, Turner DA, Charters JR, Golden HE, Ali A, Fordham EW. Quantitative sacroiliac scintigraphy. The effect of method of selection of region of interest.Clin Nucl Med 1984; 9: 334–340.
Prakash S, Gopinath PG, Bhargava S, Mehra NK, Malaviya AN. Evaluation of quantitative sacroiliac scintigraphy for the early detection of sacroiliitis.Eur J Nucl Med 1983; 8: 531–534.
Lee SK, Lee J. Behçet’s disease—a rheumatologic perspective.Yonsei Medical Journal 1997; 38: 395–400.
Tursen U, Gurler A, Boyvat A. Evaluation of clinical findings according to sex in 2313 Turkish patients with Behçet’s disease.Int J Dermatol 2003; 42: 346–351.
Kim NH, Yang IH, Kim SM, Bang DS. Behçet’s arthritis.J Korean Orthop Assoc 1993; 28: 1890–1897.
Kastner DL. Intermittent and Periodic Arthritic Syndromes: Behcet’s Disease. In: Koopman WJ, ed.Arthritis and Allied Conditions. 13th ed. Baltimore, Md; Williams & Wilkins Co., 1997: 1291–1297.
Takeuchi A, Mori M, Hashimoto A. Radiographic abnormalities in patients with Behcet’s disease.Clin Exp Rheumatol 1984; 3: 59–62.
Duzgun N, Ates A. Erosive arthritis in a patient with Behcet’s disease.Rheumatol Int 2003; 5: 265–267.
Bernard TN, Cassidy JD. The sacroiliac joint syndrome. In: Frymoyer JW (ed).The adult spine. New York; Raven, 1991: 2107–2130.
Rosenthall L. Nuclear medicine techniques in arthritis.Rheum Dis Clin North Am 1991; 17: 585–597.
Ryan PJ, Fogelman I. The bone scan: where are we now?Semin Nucl Med 1995; 25: 76–91.
Silberstein EB, Elgazzar AH, Fernandez-Ulloa M, Nishiyama H. Skeletal scintigraphy in non-neoplastic osseous disorders. In: Henkin RE (ed).Nuclear Medicine. New York; Mosby, 1996.
Yildiz M, Tunc SE, Sahin M, Okudan B, Aydin O, Suslu H, et al.. Evaluation of joints using Tc 99m-MDP bone scintigraphy in patients with familial Mediterranean fever: should bone scans be used for diagnosis and follow-up?Rheumatol Int 2006; 3: 220–223.
Krause L, Leibovici L, Guedj D, Molad Y, Weinberger A. Disease patterns of patients with Behçet’s disease demonstrated by factor analysis.Clin Exp Rheumatol 1999; 17: 347–350.
Dilsen N, Konice M, Aral O. Why Behcet’s disease should be accepted as a seronegative arthritis. In: Lehner T, Barnes CG, eds.Recent advances in Behcet’s disease. London; Royal Society of Medicine Services, 1986: 281–284.
Olivieri I, Salvarani C, Cantini F. Is Behcet’s disease part of the Spondarthritis complex?J Rheumatol 1997; 24: 1870- 1872.
Chamberlain MA, Robertson RJH. A controlled study of sacroiliitis in Behcet’s disease.Br J Rheumatol 1993; 32: 693–698.
Maghraoui AE, Tabache F, Bezza A, Abouzahir A, Ghafir D, Ohayon V, et al. A controlled study of sacroiliitis in Behcet’s disease.Clin Rheumatol 2001; 20: 189–191.
Chang HK, Cho EH, Kim JU, Herr H. A case of coexisting Behcet’s disease and ankylosing Spondylitis.Korean J Intern Med 2000; 15: 93–95.
Miron SD, Khan MA, Wiesen EJ, Kushner I, Bellon EM. The value of quantitative sacroiliac scintigraphy in detection of sacroiliitis.Clin Rheumatol 1983; 2: 407–414.
Kacar G, Kacar C, Karayalcin B, Gungor F, Tuncer T, Erkilic M. Quantitative sacroiliac joint scintigraphy in normal subjects and patients with sacroiliitis.Ann Nucl Med 1998; 12: 169–173.
Inanc N, Atagunduz P, Sen F, Biren T, Turoğlu HT, Direskeneli H. The investigation of sacroiliitis with different imaging techniques in spondyloarthropathies.Rheumatol Int 2005; 25: 591–594.
Esdaile JM, Rosenthall L, Terkeltaub R, Kloiber R. Prospective evaluation of sacroiliac scintigraphy in chronic inflammatory back pain.Arthritis Rheum 1980; 23: 998–1003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ahin, M., Tunc, S.E., Yildiz, M. et al. The usefulness of Tc-99m-MDP bone scintigraphy in detection of articular involvement of Behçet’s disease. Ann Nucl Med 20, 649–653 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02984675
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02984675