Abstract
Objective
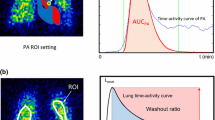
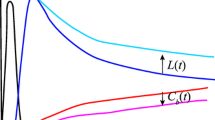
Arterial input function represents the delivery of intravascular tracer to the brain. The optimal setting of this function is essential for measuring regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) based on the microsphere model usingN-isopropyl-4-[123I]iodoamphetamine (123I-IMP), in which the arterial123I-IMP concentration (integral value) during the initial 5 min is usually applied. We developed a novel method in which the arterial123I-IMP concentration is estimated from that in venous blood samples.
Methods
Brain perfusion SPECT with123I-IMP was performed in 110 patients with disorders of the central nervous system. A causality analysis determined the relationship between various SPECT parameters and the ratio of the octanol-extracted arterial radioactivity concentration during the first 5 min (Caoct) to the octanol-extracted venous radioactivity concentration at 27 min after an intravenous injection of123I-IMP (Cvoct). The Caoct/Cvoct value was estimated using various SPECT parameters and compared with the directly measured value.
Results
The measured and estimated values of Caoct/ Cvoct (r = 0.856, n = 50) closely correlated when the following 7 parameters were included in the regression formula: radioactivity concentration in venous blood sampled at 27 min (Cv), Cvoct, Cvoct/Cv, and 4 parameters related to cerebral tissue accumulation that were measured using a four-head gamma camera 5 and 28 min after123I-IMP injection. Furthermore, the rCBF values obtained using the input function estimated by this method also closely correlated with the rCBF values measured using the continuous arterial blood sampling (r = 0.912, n = 180).
Conclusion
These results suggest that this method would serve as a convenient and less invasive method of rCBF measurement in the clinical setting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuhl DE, Barrio JR, Huang SC, Selin C, Ackermann RF, Lear JL, Quantifying local cerebral blood flow byN- isopropyl-p-[123I]iodoamphetamine (IMP) tomography.J Nucl Med 1982; 23: 196–203.
Matsuda H, Seki H, Sumiya H, Tsuji S, Tonami N, Hisada K, et al. Quantitative cerebral blood flow measurements usingN-isopropyl-(iodine 123)p-iodoamphetamine and single photon emission computed tomography with rotating gamma camera.Am J Physiol Imaging 1986; 1: 186–194.
Greenberg JH, Kushner M, Rango M, Alavi A, Reivich M. Validation studies of iodine-123-iodoamphetamine as a cerebral blood flow tracer using emission tomography.J Nucl Med 1990; 31: 1364–1369.
Murase K, Tanada S, Mogami H, Kawamura M, Miyagawa M, Yamada M, et al. Validity of microsphere model in cerebral blood flow measurement usingN-isopropyl-p-(I- 123)iodoamphetamine.MedPhys 1990; 17: 79–83.
Odano I, Ohkubo M, Takahashi N, Higuchi T. A new method of regional cerebral blood flow measurement using one-point arterial sampling based on the microsphere model with N-isopropyl-p-[123I]-iodoamphetamine SPECT.Nucl Med Commun 1994; 15: 560–564.
Ohkubo M, Odano I, Takahashi M. A comparative study of simple methods to measure regional cerebral blood flow using iodine-123-IMP SPECT.J NuclMed 1997; 38: 597–601.
Fujioka H, Murase K, Inoue T, Ishimaru Y, Akamune A, Yamamoto Y, et al. A method for estimating the integral of the input function for the quantification of cerebral blood flow with123I-IMP using one-point arterial blood sampling.Nucl Med Commun 1998; 19: 561–566.
Murase K, Inoue T, Fujioka H, Yamamoto Y, Ikezoe J. Double-injection method for sequentially measuring cerebral blood flow with N-isopropyl-(l23I)p-Modoamphetamine.Ann Nucl Med 2000; 14: 441–452.
Yokoi T, Iida H, Itoh H, Kanno I. A new graphic plot analysis for cerebral blood flow and partition coefficient with iodine-123-iodoamphetamine and dynamic SPECT validation studies using oxygen-15-water and PET.J Nucl Med 1993; 34: 498–505.
Iida H, Itoh H, Bloomfield PM, Munaka M, Higano S, Murakami M, et al. A method to quantitate cerebral blood flow using a rotating gamma camera and iodine-123 iodoamphetamine with one blood sampling.Eur J Nucl Med 1994; 21: 1072–1084.
Iida H, Itoh H, Nakazawa M, Hatazawa J, Nishimura H, Onishi Y, et al. Quantitative mapping of regional cerebral blood flow using iodine-123-IMP and SPECT.J Nucl Med 1994; 35: 2019–2030.
Ito H, Ishii K, Atsumi H, Inukai Y, Abe S, Sato M, et al. Error analysis of autoradiography method for measurement of cerebral blood flow by123I-IMP brain SPECT: a comparison study with table look-up method and microsphere model method.Ann Nucl Med 1995; 9: 185–190.
Iida H, Akutsu T, Endo K, Fukuda H, Inoue T, Ito H, et al. A multicenter validation of regional cerebral blood flow quantitation using [123I]iodoamphetamine and single photon emission computed tomography.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1996; 16:781–793.
Odano I, Ohkubo M, Takahashi M. Quantification of cerebral blood flow and partition coefficient using iodine-123- iodoamphetamine.J Nucl Med 1997; 38: 1248–1253.
Inoue K, Ito H, Nakagawa M, Goto R, Yamazaki T, Fukuda H. Regional differences in distribution volume of 1–123 IMP in the human brain: effect on CBF calculated by ARG method.Ann Nucl Med 2002; 16: 311–316.
Matsuda H, Higashi S, Tsuji S, Seki H, Sumiya H, Fujii H, et al. A new noninvasive quantitative assessment of cerebral blood flow usingN-isopropyl-(iodine 123)p-iodoamphet- amine.Am J Physiol Imaging 1987; 2: 49–55.
Mimura H, Ono S, Fukunaga M, Monta K, Nagai K, Otsuka N, et al. The quantitative analysis of regional cerebral blood flow by peripheral venous sampling in single photon emission computed tomography using N-isopropyl-p-[l23I]iodoamphetamine: comparison with peripheral arterial sampling.KAKU IGAKU (Jpn J Nucl Med) 1989; 26: 1327–1334.
Moriwaki H, Matsumoto M, Hashikawa K, Oku N, Okazaki Y, Handa N, et al. Quantitative assessment of cerebral blood flow by123I-IMP SPECT: venous sampling method with hand warming in the water bath.KAKU IGAKU (Jpn J Nucl Med) 1993; 30: 481–488.
Ito H, Koyama M, Goto R, Kawashima R, Ono S, Atsumi H, et al. Cerebral blood flow measurement with iodine-123- IMP SPECT, calibrated standard input function and venous blood sampling.J Nucl Med 1995; 36: 2339–2342.
Fujioka H, Murase K, Inoue T, Ishimaru Y, Ebara H, Akamune A, et al. Estimation of integral of input function for quantification of cerebral blood flow with N-isopropyl- p-[123I]iodoamphetamine using one-point venous blood sampling.KAKU IGAKU (Jpn J Nucl Med) 1999; 36: 801–807.
Takahashi Y, Sone T, Mimura H, Yoshioka K, Murase K, Matsuda H. Analysis on time-series and causality of input and output signals using incomplete data: causality model for the quantification of rCBF with venous values.KAKU IGAKU (Jpn J Nucl Med) 2004; 41: 371–372.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mimura, H., Sone, T., Takahashi, Y. et al. Measurement of regional cerebral blood flow with123I-IMP using one-point venous blood sampling and causality analysis: Evaluation by comparison with conventional continuous arterial blood sampling. Ann Nucl Med 20, 589–595 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02984656
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02984656