Abstract
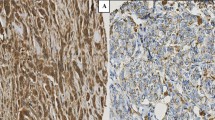
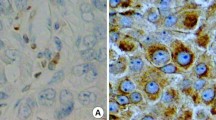
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate Cathepsin-D (Cath-D) expression in different location and its relationship with prognosis in the axillary lymph nodes negative (ANN) breast cancer patients. Methods: Cath-D expression in 192 cases of breast carcinoma were examined by immunohistochemistry. Depending on different parts of expression, three evaluating methods were used, compared and analysed. Results: The positive rate of Cath-D expression in ANN breast cancer with poor prognosis group and axillary nodes positive (ANP) group were significantly higher than that in ANN breast cancer with good prognosis group (x 2=23.20,P<0.01), while there was no significant difference between ANP group and ANN with poor prognosis group (x 2=0.19,P>0.05). Cath-D expression in stromal cells had no statistical difference among the three groups (x}2=1.56,P>0.05). When the Cath-D expression in cancer and stromal cells were counted into the positive rate, it was near the same (u 1=0.47,u 2=1.41,P>0.05). Conclusion: These results suggest that Cath-D expression is one of the powerful prognostic markers in ANN breast cancer. It’s a reliable, practical, and convenient method to observe and evaluate Cath-D expression in cancer cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia M, Platet N, Liaudet Estradiol, et al. Biological and clinical significance of cathepsin D in breast cancer metastasis [J]. Stem Cells 1996; 14:642.
Johnson MD, Torri JA, Lippman ME, et al. The role of cathepsin D in the invasiveness of human breast cancer cells [J]. Cancer Res 1993; 53: 873.
Duffy MJ. Proteases as prognostic markers in cancer [J]. Clin Cancer Res 1996; 2:613.
Westley BR, May FE. Cathepsin D and breast cancer [J]. Eur J Cancer 1996; 32A:7.
Riley LB, Lange MK, Browne RJ, et al. Analysis of cathepsin D in human breast cancer: usefulness of the processed 31 kDa active form of the enzyme as a prognostic indicator in node-negative and node-positive patients [J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2000; 60:173.
Fu XL. Histopathologic diagnosis. Chinese Common Malignant Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment Rule. Breast Carcinoma Volume [M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Beijing Medical University and Chinese Xiehe Medical University Union Publisher, 1999; 23.
Yang SQ. Health Statistics [M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: People Health Publisher, 1998; 131.
Bittl A, Nap M, Jager W, et al. Immuno-histochemical detection of P-glycoprotein on frozen and paraffin-embedded tissue sections of normal and malignant tissues [J]. Anticancer Res 1995; 15:1007.
Isola J, Weitz S, Visakorpi T, et al. Cathepsin D expression detected by immunohistochemistry has independent prognostic value in axillary node-negative breast cancer [J]. J Clin Oncol 1993; 11:36.
Castiglioni T, Merino MJ, Eisner B, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of cathepsins D, B, and L in human breast cancer [J]. Hum Pathol 1994; 25:857.
Montcourrier P, Mangeat PH, Valembois C, et al. Characterization of very acidic phagosomes in breast cancer cells and their association with invasion [J]. J Cell Sci 1994; 107:2381.
Foekens JA, Look MP, Bolt de Vries J, et al. Cathepsin-D in primary breast cancer: prognostic evaluation involving 2810 patients [J]. Br J Cancer 1999; 79:300.
Jahkola T, Toivonen T, von Smitten K, et al. Cathepsin-D, urokinase plasminogen activator and type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in early breast cancer: an immunohistochemical study of prognostic value and relations to tenascin-C and other factors [J]. Br J Cancer 1999; 80:167.
Thomssen C, Janicke F. Do we need better prognostic factors in node-negative breast cancer [J]? Eur J Cancer 2000; 36:293.
Kute TE, Grondahl Hansen J, Shao SM, et al. Low cathepsin D and low plasminogen activator type 1 inhibitor in tumor cytosols defines a group of node negative breast cancer patients with low risk of recurrence [J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1998; 47:9.
Charpin C, Garcia S, Bouvier C, et al. Cathepsin D detected by automated and quantitative immunohistochemistry in breast carcinomas: correlation with overall and disease free survival [J]. J Clin Pathol 1997; 50:586.
Roger P, Montcourrier P, Maudelonde T, et al. Cathepsin D immunostaining in paraffin-embedded breast cancer cells and macrophages: correlation with cytosolic assay [J]. Hum Pathol 1994; 25:847.
Escot C, Zhao Y, Puech C, et al. Cellular localisation byin situ hybridisation of cathepsin D, stromelysin 3, and urokinase plasminogen activator RNAs in breast cancer [J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1996; 38:217.
O’Donoghue AE, Poller DN, Bell JA, et al. Cathepsin D in primary breast carcinoma: adverse prognosis is associated with expression of cathepsin D in stromal cells [J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1995; 33:137.
Bittl A, Nap M, Jager W, et al. Immunohistochemical detection of P-glycoprotein on frozen and paraffin-embedded tissue sections of normal and malignant tissues [J]. Anticancer Res 1995; 15:1007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Biography: NIU Yun (1958-), associate professor, Tianjin Tumor Hospital, majors in breast cancer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, Y., Fu, Xl. & LÜ, Aj. The prognosis significance of cathepsin-d expression in the different locations in axillary nodes negative carcinoma. Chin J Cancer Res 13, 212–216 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02983888
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02983888
Key words
- Axillary lymph node negative breast carcinoma
- Cathepsin-D
- Expression location
- Prognosis
- Comparative study