Abstract
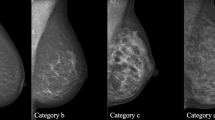
Objective: To determine whether the categories defined in the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) are useful predictors of malignancy. Methods: A total of 348 cases with benign and malignant breast diseases were collected. Mammographic and pathologic findings were reviewed. Mammograms of 348 cases were characterized according to BI-RADS descriptors and were categorized by the final assessment categories. Results: Of the all 348 patients, 232 (67%) were carcinomas. Significantly more masses with calcification and speculation were found in breast cancers than in benign breast diseases. BI-RADS final assessment categories were category 2 and 3 in 106 cases, in which 75% (79/106) were benign; category 4 and 5 in 242 cases, in which 85% (205/242) were carcinomas. BI-RADS categories 4 and 5 are useful predictors of relative likelihood of malignancy. The features with higher positive predictive values for carcinomas were irregular shape, indistinct or speculated margins, fine or linear calcification morphology, and regional calcification distribution. Conclusion: BI-RADS lexicon is successful in providing a standardized language for physicians to describe lesion morphology. BI-RADS category is useful for predicting the presence of malignancy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American College of Radiology (ACR). Breast imaging reporting and data system (BI-RADS) [M]. 3rd ed. Reston, VA: American College of Radiology, 1998.
Laura L, Andrea FA, Fredric BS, et al. The breast imaging reporting and data system: positive predictive value of mammographic features and final assessment categories [J]. AJR 1998; 171:35.
Susan GO, Nicole K, Carol R, et al. BI-RADS categorization as a predictor of malignancy [J]. Radiology 1999; 211:845.
Jay AB, Phyllis JK, Carey EF. Breast imaging reporting and data system standardized mammography lexicon: observer variability in lesion description [J]. AJR 1996; 166:773.
Berg WA, Campassi, Sexton MJ, et al. Analysis of sources of variation in mammographic interpretation [J]. Radiology 1997; 205:447.
Daniel BK. Standardized mammography reporting [J]. Radiologic Clinics of North America 1992; 30:257.
Jay AB, Phyllis JK, Joseph YL, et al. Breast cancer: prediction with artificial neural network based on BI-RADS standardized lexicon [J]. Radiology 1995; 196:817.
Berube M, Curpen B, Ugolini P, et al. Level of suspicion of a mammographic lesion: use of features defined by BI-RADS lexicon and correlation with large core breast biopsy [J]. Can Assoc Radiol J 1998; 49:223.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: This work was supported by a grant from ICRETT Foundation of UICC (No. 706).
Biography: TANG Rui-ying (1955-), associate professor, Beijing Cancer Hospital, majors in breast imaging diagnosis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Ry., Gao, W., Ma, Lh. et al. Bi-rads categorization and positive predictive value of mammographic features. Chin J Cancer Res 13, 202–205 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02983885
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02983885