Abstract
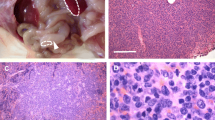
Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) is recognized as a unique lymphoma entity, which occurs exclusively in body cavities as a serous lymphomatous effusion without tumor formation or organ infiltration. We established a cell line of B-cell origin from a pericardial effusion of a 63-year-old Japanese PEL patient who did not have human immunodeficiency virus infection. This PEL cell line had human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection. We named this cell line RM-P1. This cell line showed complex chromosomal abnormalities that could not be identified by G-banding. However, spectral karyotyping analysis determined the origin and organization of all unidentified chromosomal abnormalities. When inoculated into the peritoneal cavity of 8 severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice depleted of natural killer cells, RM-P1 cells induced solid tumor with ascites in all animals tested. These tumor and ascitic cells had the same immunogenotypic features as those of the original RM-P1. These 2 types of cells were positive for both HHV-8 and EBV as demonstrated using polymerase chain reaction. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting analyses showed that neither tumors nor ascitic cells grown in SCID mice expressed leukocyte function-associated antigen (LFA)-1α (CD11a), LFA-1β (CD18), LFA-2 (CD2), LFA-3 (CD58), intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 (CD54), ICAM-2 (CD102), ICAM-3 (CD50), or leukocyte endothelial adhesion molecule (LECAM)-1 (CD62L), suggesting that these cytoadhesion molecules are not involved in tumor formation of RM-P1 cells in vivo. The establishment of the RM-P1 cell line and the animal model of PEL may provide insights for understanding the relationship between these viruses and PEL and for understand the mechanism for PEL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nador RG, Cesarman E, Chadburn A, et al. Primary effusion lymphoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity associated with the Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpes virus.Blood. 1996;88:645–656.
Jaffe ES. Primary body cavity-based AIDS-related lymphomas: evolution of a new disease entity.Am J Clin Pathol. 1996;105: 141–143.
Carbone A, Gaidano G. HHV-8-positive body-cavity-based lymphoma: a novel lymphoma entity.Br J Haematol. 1997;97:515–522.
Karcher DS, Alkan S. Human herpesvirus-8-associated body cavity-based lymphoma in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients: a unique B cell neoplasm.Hum Pathol. 1997;28:801–808.
Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Diebold J, et al. The World Health Organization classification of hematological malignancies report of the Clinical Advisory Committee Meeting, Airlie House, Virginia, November 1997.Mod Pathol. 2000;13:193–207.
Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore PS, Said JW, Knowles DM. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas.N Engl J Med. 1995;332: 1186–1191.
Cesarman E, Nador RG, Aozasa K, Delsol G, Said JW, Knowles DM. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus in non-AIDS-related lymphomas occurring in body cavities.Am J Pathol. 1996; 149:53–57.
Gaidano G, Pastore C, Gloghini A, et al. Distribution of human herpesvirus-8 sequences throughout the spectrum of AIDS-related neoplasia.AIDS. 1996;10:941–949.
Otsuki T, Kumar S, Ensoli B, et al. Detection of HHV-8/KSHV DNA sequences in AIDS-associated extranodal lymphoid malignancies.Leukemia. 1996;10:1358–1362.
Uphoff CC, Habig S, Carbone A, Gaidano G, Drexler HG. HHV-8 infection is specific for cell lines derived from primary effusion (body cavity-based) lymphomas.Leukemia. 1998;12:1806–1809.
Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, et al. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma.Science. 1994;266:1865–1869.
Moore PS, Boshoff C, Weiss RA, Chang Y. Molecular mimicry of human cytokine and cytokine response pathway genes by KSHV.Science. 1996;274:1739–1744.
Russo JJ, Bohenzky RA, Chien MC, et al. Nucleotide sequence of the Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (HHV8).Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:14862–14867.
Kiyuna M, Toda T, Higa K, Shiroma M. A case report of anaplastic large cell lymphoma arising as primary effusion lymphoma.J Jpn Soc Clin Cytol. 2001;40:281–285.
Kakazu N, Taniwaki M, Horiike S, et al. Combined spectral karyotyping and DAPI banding analysis of chromosome abnormalities in myelodysplastic syndrome.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1999; 26:336–345.
Tanaka T, Kitamura F, Nagasaka Y, Kuida K, Suwa H, Miyasaka M. Selective long-term elimination of natural killer cells in vivo by an anti-interleukin 2 receptor β chain monoclonal antibody in mice.J Exp Med. 1993;178:1103–1107.
Imai S, Usui N, Sugiura M, et al. Epstein-Barr virus genomic sequences and specific antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid in children with neurologic complications of acute and reactivated EBV infections.J Med Virol. 1993;40:278–284.
Cesarman E, Moore PS, Rao PH, Inghirami G, Knowles DM, Chang Y. In vitro establishment and characterization of two acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related lymphoma cell lines (BC-1 and BC-2) containing Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like (KSHV) DNA sequences.Blood. 1995;86:2708–2714.
Arvanitakis L, Mesri EA, Nador RG, et al. Establishment and characterization of a primary effusion (body cavity-based) lymphoma cell line (BC-3) harboring Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) in the absence of Epstein-Barr virus.Blood. 1996;88:2648–2654.
Gaidano G, Cechova K, Chang Y, Moore PS, Knowles DM, Dalla-Favera R. Establishment of AIDS-related lymphoma cell lines from lymphomatous effusions.Leukemia. 1996;10:1237–1240.
Carbone A, Cilia AM, Gloghini A, et al. Establishment of HHV-8-positive and HHV-8-negative lymphoma cell lines from primary lymphomatous effusions.Int J Cancer. 1997;73:562–569.
Boshoff C, Gao SJ, Healy LE, et al. Establishing a KSHV+ cell line (BCP-1) from peripheral blood and characterizing its growth in Nod/SCID mice.Blood. 1998;91:1671–1679.
Carbone A, Cilia AM, Gloghini A, et al. Establishment and characterization of EBV-positive and EBV-negative primary effusion lymphoma cell lines harbouring human herpesvirus type-8.Br J Haematol. 1998;102:1081–1089.
Katano H, Hoshino Y, Morishita Y, et al. Establishing and characterizing a CD30-positive cell line harboring HHV-8 from a primary effusion lymphoma.J Med Virol. 1999;58:394–401.
Drexler HG, Uphoff CC, Gaidano G, Carbone A. Lymphoma cell lines: in vitro models for the study of HHV-8+ primary effusion lymphomas (body cavity-based lymphomas).Leukemia. 1998;12: 1507–1517.
Boshoff C, Whitby D, Hatziioannou T, et al. Kaposi’s-sarcoma-associated herpesvirus in HIV-negative Kaposi’s sarcoma.Lancet. 1995;345:1043–1044.
Boshoff C, Weiss RA. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.Adv Cancer Res. 1998;75:57–86.
Schulz TF. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human her-pesvirus-8).J Gen Virol. 1998;79:1573–1591.
Dupin N, Gorin I, Deleuze J, Agut H, Huraux JM, Escande J P. Herpes-like DNA sequences, AIDS-related tumors, and Castleman’s disease.N Engl J Med. 1995;333:798–799.
Soulier J, Grollet L, Oksenhendler E, et al. Molecular analysis of clonality in Castleman’s disease.Blood. 1995;86:1131–1138.
Soulier J, Grollet L, Oksenhendler E, et al. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman’s disease.Blood. 1995;86:1276–1280.
Gessain A, Sudaka A, Briére J, et al. Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpes-like virus (human herpesvirus type 8) DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman’s disease: is there any relevant association in non-human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients?Blood. 1996;87:414–416.
Kamada Y, Iwamasa T, Miyazato M, Sunagawa K, Kunishima N. Kaposi sarcoma in Okinawa.Cancer. 1992;70:861–868.
Gaidano G, Capello D, Cilia AM, et al. Genetic characterization of HHV-8/KSHV-positive primary effusion lymphoma reveals frequent mutations of BCL6: implications for disease pathogenesis and histogenesis.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1999;24:16–23.
Wilson KS, McKenna RW, Kroft SH, Dawson DB, Ansari Q, Schneider NR. Primary effusion lymphomas exhibit complex and recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities.Br J Haematol. 2002;116: 113–121.
Horenstein MG, Nador RG, Chadburn A, et al. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in primary effusion lymphomas containing Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus-8.Blood. 1997;90:1186–1191.
Szekely L, Chen F, Teramoto N, et al. Restricted expression of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded, growth transformation-associated antigens in an EBV- and human herpesvirus type 8-carrying body cavity lymphoma line.J Gen Virol. 1998;79: 1445–1452.
Bosma GC, Custer RP, Bosma MJ. A severe combined immunodeficiency mutant in the mouse.Nature. 1983;301:527–530.
McCune JM, Namikawa R, Kaneshima H, Shultz LD, Lieberman M, Weissman IL. The SCID-hu mouse: murine model for the analysis of human hematolymphoid differentiation and function.Science. 1988;241:1632–1639.
Mosier DE, Gulizia RJ, Baird SM, Wilson DB. Transfer of a functional human immune system to mice with severe combined immunodeficiency.Nature. 1988;335:256–259.
Kamel-Reid S, Letarte M, Sirard C, et al. A model of human acute lymphoblastic leukemia in immune-deficient SCID mice.Science. 1989;246:1597–1600.
Namikawa R, Ueda R, Kyoizumi S. Growth of human myeloid leukemias in the human marrow environment of SCID-hu mice.Blood. 1993;82:2526–2536.
Hamann A, Thiele HG. Molecules and regulation in lymphocyte.Immunol Rev. 1989;108:19–44.
Okada T, Katano H, Tsutsumi H, et al. Body-cavity-based lymphoma in an elderly AIDS-unrelated male.Int J Hematol. 1998;67: 417–422.
Chang Y, Moore PS, Talbot SJ, et al. Cyclin encoded by KS herpesvirus.Nature. 1996;382:410.
Davis MA, Stürzl M, Blasig C, et al. Expression of human herpesvirus 8-encoded cyclin D in Kaposi’s sarcoma spindle cells.J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997;89:1868–1874.
Neipel F, Albrecht JC, Fleckenstein B. Cell-homologous genes in the Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated rhadinovirus human her-pesvirus 8: determinants of its pathogenicity?J Virol. 1997;71: 4187–4192.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Miyagi, Ji., Masuda, M., Takasu, N. et al. Establishment of a Primary Effusion Lymphoma Cell Line (RM-P1) and In Vivo Growth System Using SCID Mice. Int J Hematol 76, 165–172 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02982580
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02982580