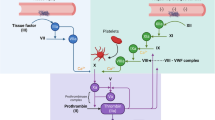
Abstract
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) plays a crucial role in hemostasis and thrombosis, and its receptors are potential targets for antithrombotic drugs. Two G-protein—coupled P2 receptors contribute to platelet aggregation: the P2Y1 receptor initiates aggregation through mobilization of calcium stores, whereas the P2Y12 receptor coupled to adenylyl cyclase inhibition is essential for a full aggregation response to ADP and the stabilization of aggregates. The latter is defective in certain patients with a selective congenital deficiency of aggregation to ADP. It is also the target of the antithrombotic drug clopidogrel and of adenosine triphosphate analogues and other compounds currently under evaluation. In addition, the P2X1 ionotropic receptor is present in platelets, but its role is not yet completely known. Studies in P2Y1-knockout mice and experimental thrombosis models using selective P2Y1 antagonists have shown that the P2Y1 receptor, like the P2Y12 receptor, is a potential target for new antithrombotic drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Gachet, C. Identification, Characterization, and Inhibition of the Platelet ADP Receptors. Int J Hematol 74, 375–381 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02982079
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02982079