Abstract
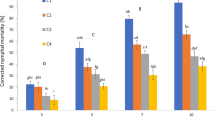
Thirty-five strains ofVerticillium lecanii which originated from different hosts and geographical locations were tested as potential biocontrol agents against silverleaf whitefly,Bemisia argentifolii Bellows & Perring. All strains were tested for their pathogenicity to third-instar nymphs. Several isolates which exhibited high pathogenicity to nymphs were also tested against eggs, pupae and adults ofB. argentifolii. Eggs were found to be immune to infection, but mortality of hatching nymphs reached 95–98%. The rate of hatching nymphs’ infection depended on the age at which the eggs were inoculated and the strain’s virulence. Mortality of nymphs recorded on day 4 after inoculation varied from 0.5±0.3% to 83±2.4%; that of the control ranged from 2.5% to 10.2%. The most virulent strains, with LT50 ranging between 3.2 and 3.8 days, were isolated from aphids in Israel and probably have a similar origin. The pathogenicity ofV. lecanii strains to pupae 6 days after inoculation varied between 59± 12.1 % and 72.5± 13.1 %, as compared with natural mortality of 13.5±4%. The maximum adult mortality caused byV. lecanii strains was between 34.1±5.1% and 52.6±3.8%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asiatic, J.M. and Zoebisch, T.G. (1992) Control of whiteflyBemisia tabaci (Gennadius) on tomato with biological and chemical insecticides.Manejo Integr. Plagas 24-25:1–7.
Ben-Ze’ev, I.S. (1993) Check-list of fungi pathogenic to insects and mites in Israel, updated through 1992.Phytoparasitica 21:213–237.
Byrne, D.N. and Bellows, T.S. Jr. (1991) Whitefly biology.Annu. Rev. Entomol 36:431–457.
Chandler, D., Heale, J.B. and Gillespie, A.T. (1993) Germination of the entomopathogenic fungusVerticillium lecanii on scales of the glasshouse whiteflyTrialeurodes vaporariorum.Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 3:161–164.
Ekbom, B.S. (1979) Investigations on the potential of a parasitic fungus (Verticillium lecanii) for biological control of the greenhouse whitefly (Trialeurodes).Swed. J. Agric. Res. 9:129–138.
Gindin, G., Barash, I., Raccah, B., Singer, S., Ben-Ze’ev, I. and Klein, M. (1996) The potential of some entomopathogenic fungi as biocontrol agents against the onion thrips,Thrips tabaci and the western flower thrips,Frankliniella occidentalis. Folia Entomol. Hung. LVII:37–42.
Hall, R.A. (1981) The fungusVerticillium lecanii as a microbial insecticide against aphids and scales.in: Burges, H.D. [Ed.] Microbial Control of Pests and Plant Diseases 1970-1980. pp. 483–498. Academic Press, New York, NY.
Hall, R.A. (1982) Control of whitefly,Trialeurodes vaporariorum and cotton aphid,Aphis gossypii in glasshouses by two isolates of the fungusVerticillium lecanii.Ann. Appl. Biol. 10:1–11.
Helyer, N. (1993)Verticillium lecanii for control of aphids and thrips on cucumber.IOBC/WPRS Bull. 16:63–66.
Hsiao, W.F., Bidochka, M.J. and Khachatourians, G.G. (1992) Effect of temperature and relative humidity on the virulence of the entomopathogenic fungus,Verticillium lecanii, towards the oat-bird berry aphid,Rhopalosiphum padi (Horn., Aphididae).J. Appl. Entomol. 114:484–490.
Hussey, N.W. (1958) Notes on a fungus parasitic on greenhouse whitefly.Plant Pathol. 7:71–72.
Lacey, L.A., Kirk, A.A. and Hennessey, R.D. (1993) Foreign exploration for natural enemies ofBemisia tabaci and implementation in integrated control programs in the United States.Proc. Third Int. Conf. on Pests in Agriculture. Vol. 1, 351–360.
Masuda, T. and Kikuchi, O. (1992) Pathogenicity ofVerticillium lecanii isolates to whitefly and aphids.Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 36:239–245.
Meade, D.L. and Byrne, D.N. (1991) The use ofVerticillium lecanii against subimaginal instars ofBemisia tabaci.J. Invertebr. Pathol. 57:296–298.
Mor, H., Gindin, G., Ben-Ze’ev, I.S., Raccah, B., Geschtovt, N.U., Ajtkhozina, N. and Barash, I. (1996) Diversity among isolates ofVerticillium lecanii as expressed by DNA polymorphism and virulence towardsBemisia tabaci.Phytoparasitica 24:111–118.
Nier, T., Rivera, F., Bermudez, J.C., Dominguez, Y, Benavides, C. and Ulloa, M. (1991) First report in Mexico on the isolation ofVerticillium lecanii from whitefly andin vitro pathogenicity tests on this insect.Rev. Mex. Micol. 7:149–156.
Osborne, L.S. and Landa, Z. (1992) Biological control of whiteflies with entomopathogenic fungi.Fla. Entomol. 75:456–471.
Perring, T.M., Cooper, A.D., Rodrigues, R.J., Farrar, C.A. and Bellows, T.S. Jr. (1993) Identification of a whitefly species by genomic and behavioral studies.Science 259:74–77.
Ravensberg, W.J., Malais, M. and van derSchaaf, D.A. (1990)Verticillium lecanii as a microbial insecticide against glasshouse whitefly.Proc. Brighton Crop Protection Conf. Pests and Diseases Vol. 1, pp. 265–268.
Saito, T. (1992) Control ofThrips palmi andBemisia tabaci by a mycoinsecticidal preparation ofVerticillium lecanii. Proc. Kanto Tosan Plant Protection Soc. (Shizuoka, Japan), pp. 209–210.
Saito, T. (1993) Control of two whitefly species,Bemisia tabaci andTrialeurodes vaporariorum, by a preparation ofVerticillium lecanii. Proc. Kanto Tosan Plant Protection Soc. (Shizuoka, Japan), pp. 221–222.
Smith, P. (1993) Control ofBemisia tabaci and the potential ofPaecilomyces fumosoroseus as a biopesticide.Biocontrol News Inf. 14:71N-78N.
Steenberg, T. and Humber, R. (1999) Entomopathogenic potential ofVerticillium lecanii andAcremonium species (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes).J. Invertebr. Pathol. 73:309–314.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gindin, G., Geschtovt, N.U., Raccah, B. et al. Pathogenicity ofVerticillium lecanii to different developmental stages of the silverleaf whitefly,Bemisia argentifolii . Phytoparasitica 28, 229–239 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02981801
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02981801