Abstract
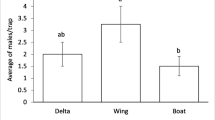
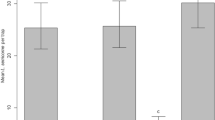
The effects of ratio between sex pheromone components, pheromone dose in the dispenser, aging of dispenser in the field, and trap type on trapping efficiency of males of the peach twig borer,Anarsia lineatella Zeller (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae), were investigated. To attract males, the optimal ratio between pheromonal components in a binary blend containing (E)-5-decenyl acetate (E5-10:Ac): (E)-5-decenol (E5-10:OH) was 72:28 or 83:17. Dosages of 7 or 0.7 mg of the binary blend containing E5-10:Ac: E5-10:OH (72:28) were equally effective in attracting males. The effect of aging of dispenser (Israeli dispensers, loaded with 7 mg pheromone) in the field on trapping efficiency was moderate. Captures in traps baited with 4-week-old septa did not differ from those in traps baited with 1-week-old septa. The fairly slow loss of attractancy exhibited by rubber septa indicates that septa may be used for at least 4–5 weeks. At high population levels, the nonsticky IPS trap was significantly more effective in capturing males than the sticky Pherocon 1C trap; at low populations, however, the Pherocon 1C trap was better.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anshelevich, L., Kehat, M., Dunkelblum, E. and Greenberg, S. (1993) Sex pheromone traps for monitoring the honeydew moth,Cryptoblabes gnidiella: Effect of pheromone compounds, pheromone dose, field aging of dispenser, and type of trap on male captures.Phytoparasitica 21: 189–198.
Anshelevich, L., Kehat, M., Dunkelblum, E. and Greenberg, S. (1994) Sex pheromone traps for monitoring the European vine moth,Lobesia botrana: Effect of dispenser type, pheromone dose, field aging of dispenser, and type of trap on male captures.Phytoparasitica 22: 281–290.
Anthon, E., Smith, L.O. and Garret, S.D. (1971) Artificial diet and pheromone studies with peach twig borer.J. Econ. Entomol. 64: 259–262.
Avidov, Z. and Harpaz, I. (1969) Plant Pests of Israel. Israel Universities Press, Jerusalem.
Barnett, W.W. and Hendricks, L.C. (1992) Comparison of pheromone trap catches to adult emergence and oviposition of peach twig borer,Anarsia lineatella Zeller, in California almond orchards.Acta Phytopathol. Entomol. Hung. 27: 85–88.
Hathaway, D.O. (1981) Peach twig borer: Field evaluations of concentrations of pheromone and monitoring of populations.J. Econ. Entomol. 74: 344–345.
Kehat, M., Anshelevich, L., Dunkelblum, E., Fraishtat, P. and Greenberg, S. (1994) Sex pheromone traps for monitoring the codling moth: Effect of dispenser type, field aging of dispenser, pheromone dose, and type of trap on male captures.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 70: 55–62.
Millar, J.G. and Rice, R.E. (1992) Reexamination of the female sex pheromone of the peach twig borer: Field screening of minor constituents of pheromone gland extracts and pheromone analogs.J. Econ. Entomol. 85: 1709–1716.
Reil, W.O., Johnson, T.W., Profita, J.C., Davis, C.S., Hendricks, L.C. and Rough, D. (1981) Monitoring peach twig borer in almonds with sex pheromone traps.Calif. Agric. 35: 19–21.
Rice, R.E. and Jones, R.A. (1975) Peach twig borer: Field use of a synthetic sex pheromone.J. Econ. Entomol. 8: 358–360.
Rice, R.E. and Jones, R.A. (1988) Timing post-bloom sprays for peach twig borer (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) and San Jose scale (Homoptera: Diaspididae).J. Econ. Entomol. 81: 293–299.
Roelofs, W.L., Kochansky, J., Anthon, E., Rice, R.E. and Carde, R. (1975) Sex pheromone of the peach twig borer (Anarsia lineatella).Environ. Entomol. 4: 580–582.
Steel, R.G.D. and Torrie, J.H. (1960) Principles and Procedures of Statistics. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY.
Youngman, R.R. and Barnes, M.M. (1985) The longevity of attractiveness of the commercially available pheromone septa of the peach twig borer (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae).J. Econ. Entomol. 78: 110–112.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kehat, M., Anshelevich, L., Dunkelblum, E. et al. Sex Pheromone Traps for Monitoring the Peach Twig Borer,Anarsia lineatella Zeller: Effect of Pheromone Components, Pheromone Dose, Field Aging of Dispenser, and Type of Trap on Male Captures. Phytoparasitica 22, 291–298 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980530
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980530