Abstract
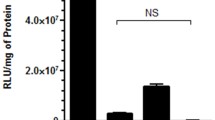
LPD vectors are non-viral vehicles for gene delivery comprised of polycation-condensed plasmid DNA and liposomes. Here, we described a novel anionic LPD formulation containing protamine-DNA complexes and pH sensitive liposomes composed of DOPE and cholesteryl hemisuccinate (Chems). Central composite design (CCD) was employed to optimize stable LPD formulation with small particle size. A three factor, five-level CCD design was used for the optimization procedure, with the weight ratio of protamine/DNA (X1), the weight ratio of Chems/ DNA (X2) and the molar ratio of Chems/DOPE in the anionic liposomes (X3) as the independent variables. LPD size (Y1) and LPD protection efficiency against nuclease (Y2) were response variables. Zeta potential determination was utilized to define the experimental design region. Based on experimental design, responses for the 15 formulations were obtained. Mathematical equations and response surface plots were used to relate the dependent and independent variables. The mathematical model predicted optimized X1-X3 levels that achieve the desired particle size and the protection efficiency against nuclease. According to these levels, an optimized LPD formulation was prepared, resulting in a particle size of 185.3 nm and protection efficiency of 80.22%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arangoa, M. A., Dzgnes, N., and llarduya, C. T., Increased receptor-mediated gene delivery to the liver by protamine-enhanced-asialofetuin-lipoplexes.Gene Therapy, 10, 5–14 (2003).
Audouy, S. A. L., Lou, F. M. H., Leij, H., and Molema, G.,In vivo characteristics of cationic liposomes as delivery vectors for gene therapy.Pharm. Res., 19, 1599–1605 (2002).
Cherng, J. Y., Schuurmans-Nieuwenbroek, N. M., Jiskoot, W., Talsma, H., Zuidam, N. J., Hennink, W. E., and Crommelin, D. J., Effect of DNA topology on the transfection efficiency of poly((2-dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate)-plasmid complexes.J. Control Release, 60, 343–353 (1999).
Corsi, K., Chellat, F., Hocine, Y. L., and Fernandes, J. C., Mesenchymal stem cells, MG63 and HEK293 transfection using chitosan-DNA nanoparticles.Bbmaterials, 24, 1255–1264 (2003).
Guo, W. and Lee, R. J., Efficient gene delivery using anionic liposome-complexed polyplexes (LPD).Bioscience Reports, 20, 419–432 (2000).
Guo, W., Gosselin, M. A., and Lee, R. J., Characterization of novel diolein-based LPD vector for gene delivery.J. Control. Release, 83, 121–132 (2002).
Jeannette, T. T., Kevin, J. F., Michnick, T., Sloane, D. L., and Paul, R. W., Quantitative physical characterization of lipidpolycation-DNA lipopolyplexes.Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem., 36, 13–20 (2002).
Kabanov, A. V. and Kabanov, V. A., DNA complexes with polycations for the delivery of genetic material into cells.Bioconjug. Chem., 6, 7–20 (1995).
Kim, Y. J., Kim, T. W., Chung, H., Kwon, I. C., Sung, H. C., and Jeong, S. Y., The effects of serum on the stability and the transfection activity of the cationic lipid emulsion various oils.Inter. J. Pharm., 252, 241–252 (2003).
Koppelhus, U. and Nielsen, P. E., Cellular delivery of peptide nucleic acid (PNA).Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 55, 267–280 (2003).
Kreiss, P., Cameron, B., Rangara, R., Mailhe, P., Aguerre-Charriol, O., Airiau, M., Scherman, D., Crouzet, J., and Pitard, B., Plasmid DNA size does not affect the physicochemical properties of lipoplexes but modulates gene transfer efficiency.Nucleic Acids Res., 27, 3792–3798 (1999).
Lee, R. J. and Huang, L., Folate-targeted, anionic liposomeentrapped polylysine-condensed DNA for tumor cell-specific gene transfer.J. Biol. Chem., 271, 8481–8487 (1996).
Liu, G., Molas, M., Grossmann, G. A., Pasumarthy, M., Perales, J. C., Cooper, M. J., and Hanson, R. W., Biological Properties of Poly-L-lysine-DNA complexes generated by cooperative binding of the polycation.J. Biol. Chem., 276, 34379–34387 (2001).
Mastrobattista, E., Kapel, R. H. G., Eggenhuisen, M. H., Roholl, P. J. M., Crommelin, D. J. A., Hennink, W. E., and Storm, G., Lipid-coated polyplexes for targeted gene delivery to ovarian carcinoma cells.Cancer Gene Therapy, 8, 405–413 (2001).
Moret, I., Peris, J. E., Guillem, V. M., Benet, M., Revert, F., Das, F., Crespo, A., and Alio, S. F., Stability of PEI-DNA and DOTAP-DNA complexes: effect of alkaline PH, heparin and serum.J. Contrl. Release, 76, 169–181 (2001).
Stuart, D. D. and Allen, T. M., A new liposomal formulation for antisense oligodeoxynucleotides with small size, high incorporation efficiency and good stability.Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1463, 219–229 (2000).
Trubetskoy, V. S., Loomis, A., Hagstrom, J. E., Budker, V. G., and Wolff, J. A., Layer-by-layer deposition of oppositely charged polyelectrolytes on the surface of condensed DNA particles.Nucleic Acids Res., 27, 3090–3095 (1999).
Ueno, N. T., Bartholomeusz, C., Xia, W., Anklesaria, P., Bruckheimer, E. M., Mebel, E., Paul, R., Li, S., Yo, G. H., Huang, L., and Hung, M. C., Systemic gene therapy in human xenograft tumor models by liposomal delivery of theBIR gene.Cancer Res., 62, 6712–6716 (2002).
Vinogradov, S. V., Bronich T. K., and Kabanov, A. V., Nanosized cationic hydrogels for drug delivery: preparation.properties and interaction with cells.Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 54, 135–147 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Zhang, Z. Optimizing the novel formulation of liposome-polycation-dna complexes (lpd) by central composite design. Arch Pharm Res 27, 797–805 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980151
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980151