Abstract
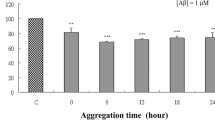
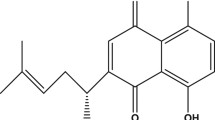
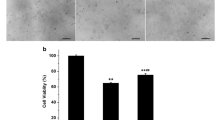
The present study investigated the effects of gossypin, 3,3′,4′,5,7,8-hexahydroxyflavone 8-glu-coside, on the toxicity induced by oxidative stress or β-amyloid (Aβ) in primary cultured rat cortical cells. The antioxidant properties of gossypin were also evaluated by cell-free assays. Gossypin was found to inhibit the oxidative neuronal damage induced by xanthine/xanthine oxidase or by a glutathione depleting agent, D,L-buthionine (S,R)-sulfoximine. In addition, gossypin significantly attenuated the neurotoxicity induced by Aβ(25–35). Furthermore, gossypin dramatically inhibited lipid peroxidation initiated by Fe2+ and ascorbic acid in rat brain homogenates. It also exhibited potent radical scavenging activity generated from 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl. These results indicate that gossypin exerts neuroprotective effects in the cultured cortical cells by inhibiting oxidative stress- and Aβ-induced toxicity, and that the antioxidant properties of gossypin may contribute to its neuroprotective actions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bains, J. S. and Shaw, C. A., Neurodegenerative disorders in humans: the role of glutathione in oxidative stress-mediated neuronal death.Brain Res. Rev., 25, 335–358 (1997).
Behl, C., Davis, J. B., Lesley, R., and Schubert, D., Hydrogen peroxide mediates amyloid-beta protein toxicity.Cell, 77, 817–827 (1994).
Behl, C. and Moosmann, B., Causes and consequences of oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease.Free Rad. Biol. Med., 33, 182–191 (2002).
Cho, J., Joo, N. E., Kong, J.-Y., Jeong, D.-Y., Lee, K. D., and Kang, B.-S., Inhibition of excitotoxic neuronal death by methanol extract of Acori graminei rhizoma in cultured rat cortical neurons.J. Ethnopharmacol., 73, 31–37 (2000).
Cho, J., Kong, J.-Y., Jeong, D.-Y., Lee, K. D., Lee, D. U., and Kang, B.-S., NMDA receptor-mediated neuroprotection by essential oils from rhizomes ofAcorus gramineus.Life Sci., 68, 1567–1573 (2001).
Cho, J., Kim, Y. H., Kong, J.-Y., Yang, C.-H., and Park, C.-G., Protection of cultured rat cortical neurons from excitotoxicity by asarone, a major essential oil component in the rhizomes ofAcorus gramineus.Life Sci., 71, 591–599 (2002).
Cho, J. and Lee, H.-K., Wogonin inhibits excitotoxic and oxidative neuronal damage in primary cultured rat cortical cells.Eur. J. Pharmacol., 485, 105–110 (2004).
Dok-Go, H., Lee, K. H., Kim, H. J., Lee, E. H., Lee, J., Song, Y. S., Lee, Y. H., Jin, C., Lee, Y. S., and Cho, J., Neuroprotective effects of antioxidative flavonoids, quercetin, (+)-dihydroquercetin and quercetin 3-methyl ether, isolated fromOpuntia ficus-indica var.saboten. Brain Res., 965, 130–136 (2003).
Dyrks, T., Dyrks, E., Harmann, R., Masters, C., and Beyreuther, K., Amyloidogenecity of pA4 and βA4-bearing amyloid protein precursor fragments by metal-catalyzed oxidation.J. Biol. Chem., 267, 18210–18217 (1992).
Ferrandiz, M. L. and Alcaraz, M. J., Anti-inflammatory activity and inhibition of arachidonic acid metabolism by flavonoids.Agents Actions, 32, 283–288 (1991).
Formica, J. V. and Regelson, W., Review of the biology of quercetin and related bioflavonoids.Food Chem. Toxicol., 33, 1061–1080 (1995).
Griffith, O. W. and Meister, A., Potent and specific inhibition of glutathione synthesis by buthionine sulfoximine (S-n-butyl homocysteine sulfoximine).J. Biol. Chem., 254, 7558–7560 (1979).
Halliwell, B., Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system.J. Neurochem., 59, 1609–1623 (1992).
Harkany, T., Hortobagyi, T., Sasvari, M., Konya, C., Penke, B., Luiten, P. G. M., and Nyakas, C., Neuroprotective approaches in experimental models of β-amyloid neurotoxicity: relevance to Alzheimer’s disease.Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 23, 963–1008 (1999).
Harris, M. E., Hensley, K., Butterfield, D. A., Leedle, A., and Caney, J. M., Direct evidence of oxidative injury produced by the Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid peptide (1–40) in cultured hippocampal neurons.Exp. Neurol., 131, 193–202 (1995).
Hensley, K., Carney, J. M., Mattson, M. P., Aksenova, M., Harris, M., Wu, J. F., Floyd, R. A., and Butterfield, D. A., A model for beta-amyloid aggregation and neurotoxicity based on free radical generation by the peptide: relevance to Alzheimer disease.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 3270–3274 (1994).
Ishige, K., Schubert, D., and Sagara, Y., Flavonoids protect neuronal cells from oxidative stress by three distinct mechanisms.Free Rad. Biol. Med., 30, 433–446 (2001).
Johnson, M. K. and Loo, G., Effects of epigallocatechin gallate and quercetin on oxidative damage to cellular DNA.Mutat. Res., 459, 211–218 (2000).
Jung, Y.-S., Kang, T.-S., Yoon, J.-H., Joe, B.-Y., Lim, H.-J., Seong, C.-M., Park, W. K., Kong, J. Y., Cho, J., and Park, N. S., Synthesis and evaluation of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid amides and 4-hydroxycinnamamides as antioxidants.Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 12, 2599–2602 (2002).
Li, Y., Maher, P., and Schubert, D., A role for 12-lipoxygenase in nerve cell death caused by glutathione depletion.Neuron, 19, 453–463 (1997).
Muller, W. E., Romero, F. J., Perovic, S., Pergande, G., and Pialoglou, P., Protection of flupirtine on beta-amyloid-induced apoptosis in neuronal cellsin vitro: prevention of amyloid-induced glutathione depletion.J. Neurochem., 68, 2371–2377 (1997).
Reiter, R. J., Oxidative processes and antioxidative defense mechanism in the aging brain.FASEB J., 9, 526–533 (1995).
Simonian, N. A. and Coyle, J. T., Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases.Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 36, 83–106 (1996).
Smith, M. A., Perry, G., Richey, P. L., Sayre, L. M., Anderson, V. E., Beal, M. F., and Kowall, N., Oxidative damage in Alzheimer’s disease.Nature, 382, 120–121 (1996).
Viswanathan, S., Sambantham, P. T., Reddy, K., and Kameswaran, L., Gossypin-induced analgesia in mice.Eur. J. Pharmacol., 98, 289–291 (1984).
Viswanathan, S., Thirugnanasambantham, P., Ramaswamy, S., and Bapna, J. S., A study on the role of cholinergic and gamma amino butyric acid systems in the anti-nociceptive effect of gossypin.Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol., 20, 193–196 (1993).
Zhang, L., Zhao, B., Yew, D. T., Kusiak, J. W., and Roth, G. S., Processing of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein during H2O2-induced apoptosis in human neuronal cells.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 235, 845–848 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, I., Lee, K.H. & Cho, J. Gossypin protects primary cultured rat cortical cells from oxidative stress- and β-amyloid-lnduced toxicity. Arch Pharm Res 27, 454–459 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980089
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980089