Abstract
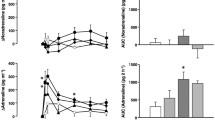
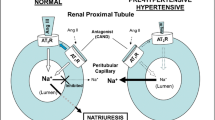
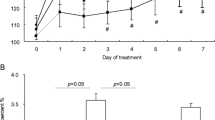
The changes in blood pressure may relate to the alterations of the responsiveness to vasoconstrictors and vasodilators, and these alterations can arise the modifications in the properties of angiotensin II (AII) receptor. In order to examine the changes of AII receptor in the hypertensive mechanism of renin-dependent hypertensive rats (RHRs; two-kidney, one-ligated type), we compared the equilibrium binding characteristics of [3H]All in adrenal cortex and medulla from RHRs and normotensive rats. The dissociation constants of All binding in both tissues of RHRs were very similar to those in the respective tissue of normotensive rats. However, the maximum binding was increased from 805 to 1050 fmole/mg protein in the adrenal cortex of RHRs, and decreased from 172 to 126 fmole/mg protein in the adrenal medulla of RHRs. These results imply that the up- and down-regulation of the All receptor population on the cell surface of adrenal glands from RHRs are consorted with the elevation of blood pressure and the activation of renin-angiotensin system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Cangiano, J., Rodriguez-Sargent, C. and Martinez-Maldonado, M., Effects of antihypertensive treatment on systolic blood pressure and renin in experimental hypertension in rats.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 208, 310–313 (1979).
Chiu, A. T., McCall, D. E., Price, W. A., Wong, P. C., Carini, D. J., Duncia, J. V., Wexler, R. R., Yoo, S. E., Johnson, A. L. and Timmermans, P. B. M. W. M., Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. VII. Cellular and biochemical pharmacology of DuP 753, an orally active antihypertensive agent.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 252, 711–718 (1990).
Devynck, M. A. and Meyer, P., Angiotensin receptors.Biochem. Pharmacol., 27, 1–5 (1978).
Douglas, J. G., Angiotensin receptor subtypes of the kidney cortex.Am. J. Physiol., 253, F1-F7 (1987).
Fernandes, M., Onesti, G., Weder, A., Oykyj, R., Gould, A. B., Kim, K. E. and Swartz, C., Experimental model of severe renal hypertension.J. Lab. Clin. Med., 87, 561–567 (1976).
Haber, E., Koerner, T., Page, L. B., Kliman B. and Purnode, A., Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects.J. Clin. Endocrinol., 29, 1349–1355 (1969).
Lee, B. H. and Shin, H. S., In vivo pharmacological evaluation of newly synthesized nonpeptidic AT, receptor antagonist in rats.Arch. Pharm. Res. 17, 263–268 (1994).
Lee, S., Lee, B., Shin, H. and Kong, J., Rat liver AT1 receptor binding analysis for drug screening.J. Appl. Pharmacol. 3, 21–27 (1995).
Munson, P. J. and Rodbard, D., Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems.Anal. Biochem., 107, 220–239 (1980).
Peach, M. J. and Ackerly, J. A., Angiotensin antagonists and the adrenal cortex and medulla.Fed. Proc., 35, 2502–2507 (1976).
Peach, M. J., Renin-angiotensin system: biochemistry and mechanisms of action.Physiol. Rev., 57, 313–370 (1977).
Timmermans, P. B. M. W. M., Wong, P. C., Chiu, A. T., Herblin, W. F., Benfield, P., Carini, D. J., Lee, R. J., Wexler, R. R., Saye, J. A. M. and Smith, R. D., Angiotensin II receptors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists.Pharmacol. Rev., 45, 205–251 (1993).
Wiest, S. A., Rampersaud, A., Zimmerman, K. and Steinberg, M. I., Characterization of distinct angiotensin II binding sites in rat adrenal gland and bovine cerebellum using selective nonpeptide antagonists.J. Cardiovas. Pharmacol., 17, 177–184 (1991).
Wong, P. C., Price, W. A., Chiu, A. T., Duncia, J. V., Carini, D. J., Wexler, R. R., Johnson, A. L. and Timmermans, P. B.-M. W. M., Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. IX. Antihypertensive activity in rats of DuP 753, an orally active antihypertensive agent.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 252, 726–732 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Lee, B. & Shin, H. Changes in adrenal angiotensin II receptors in renindependent hypertensive rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 18, 169–172 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02979190
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02979190