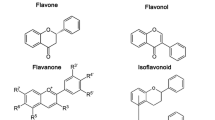
Abstract
Flavonoids, a group of low molecular weight phenylbenzopyrones, have various pharmacological properties including antioxidant, anticancer, bactericidal, and anti-inflammatory. We carried out anti-herpetic assays on 18 flavonoids in five classes and a virus-induced cytopathic effect (CPE) inhibitory assay, plaque reduction assay, and yield reduction assay were performed. When flavonoids were applied at various concentrations to Vero cells infected by HSV-1 and 2, most of the flavonoids showed inhibitory effects on virus-induced CPE. Among the flavonoids, EC, ECG (flavanols), genistein (isoflavone), naringenin (flavanone), and quercetin (flavonol) showed a high level of CPE inhibitory activity. The antiviral activity of flavonoids were also examined by a plaque reduction assay. EC, ECG., galangin, and kaempferol showed a strong antiviral activity, and catechin, EGC, EGCG., naringenin, chrysin, baicalin, fisetin, myricetin, quercetin, and genistein showed moderate inhibitory effects against HSV-1. In these experiments, flavanols and flavonols appeared to be more active than flavones. Furthermore, treatment of Vero cells with ECG and galangin (which previously showed strong antiviral activities) before virus adsorption led to a slight enhancement of inhibition as determined by a yield reduction assay, indicating that an intracellular effect may also be involved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Betancur-Galvis, L., Zuluaga, C., Arno, M., Gonzalez, M. A., and Zaragoza, R. J., Cytotoxic effect (on tumor cells) andin vitro antiviral activity againstherpes simplex virus of synthetic spongiane diterpenes.J. Nat. Prod, 65, 189–192 (2002).
Bourne, N., Stanberry, L. R., Kern, E. R., Holan, G., Matthews, B., and Bernstein, D. I., Dendrimers, a new class of candidate topical microbicides with activity againstHerpes Simplex virus infection.Antimicrob. Agents C.hemother., 44, 2471–2474 (2000).
Charles, E. I., Weimin, X., Raju, P., and Richard, K., Retinoic acid reduces the yield of herpes simplex virus in Vero cells and alters the N-glycosylation of viral envelope proteins.Antiviral Res., 47, 29–40 (2000).
Dargan, D. J. and Dargan, H., S. -S. J., The antiviral activity against Herpes simplex virus of the triterpenoid compounds carbenoxolone sodium and cicloxolone sodium.J. Antimicrob. Chemother, 18, 185–200 (1986).
Felser, J., Kichington, P. R., Inchauspe, G., Straus, S. E., and Ostrove, J. M., Cell line containing varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 62 and expressing the ’IE’ 175 protein complement ICP4 mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1.J. Virol., 62, 2076–2082 (1988).
Freshney, R. I., Culture of animal cells, a manual of basic technique, 3rd ed.Wiley-liss Inc, New York, pp. 331–332, (1994).
Gius, D. and Laimins, L. A., Activation of human papillomavirus type 18 gene expression by herpes simplex virus type 1 viral transactivators and phorbol ester.J. Virol., 63, 555–563 (1989).
Harbome, J. B., The Flavonoids. Advances in Research since 1986.Chapman and Hall, London, pp. 441–473, (1994).
Havsteen, B. H., The biochemistry and medical significance of the flavonoids.Pharmacol. Ther., 96, 67–202 (2002).
Hook, E. W. I., C.annon, R. O., and Nahmias, A. J., Herpes simplex virus infection as a risk factor for human immunodeficiency virus infection in hetera sexuals.J. Infect. Dis., 165, 251–255 (1992).
Hudson, J. Antiviral compounds from plants.CRC Press, Florida, pp. 119–131, (1990).
Kaul, T. N., Middleton, E., and Ogra, P. L, Antiviral effect of flavonoids on human viruses.J. Med. Virol., 15, 71–79 (1985).
Lapucci, A., Macchia, M., and Parkin, A., Antiherpes virus agents: a review.Farmaco., 48, 871–895 (1993).
Manthey, J. A., Grohmann, K., and Guthrie, N., Biological properties of citrus flavonoids pertaining to cancer and inflammation.Med. Chem., 8, 135–153 (2001).
Middleton Jr., E., Kandaswami, C., and Theoharides, T. C., The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer.Curr. Med. Chem., 8, 135–153 (2001).
Mucsi, I., Beladi, I., Pusztai, R., Bakay, M., and Gabor, M., Proceedings5th Hungarian bioflavonoids symposium.In Farkas, L., Gabor, M., and Kallay, F. (Eds.).Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 401–409, (1977).
Mucsi, I. and Pragai, B. M., Inhibition of virus multiplication and alteration of cyclic AMP level in cell cultures by flavonoids.Experientia, 41, 930 (1985).
Ostrove, J. M., Leonard, J., Weck, E., Radson, A. B., and Gendelman, H. E., Activation of the human immunodeficiency virus by herpes simplex virus type 1.J. Virol., 61, 3726–3732 (1987).
Park, N. H., Park, J., Min, M., and Cherrick, H. M., Combined synergistic antiherpetic effect of acyclovir and Chlorhexidinein vitro.Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol., 71, 193–196 (1991).
Sarisky, R. T., C.rosson, P., Cano, R., Quail, M. R., Nguyen, T. T., Wittrock, R. J., Bacon, T. H., Sacks, S. L., Caspers-Velu, L., Hodinka, R. L., and Leary, J. J., Comparison of methods for identifying resistantherpes simplex virus and measuring antiviral susceptibility.J. Clin. Virol., 23, 191–200 (2002).
Selway, J. W. T., Plant flavonoids in biology and medicine. Biochemical, pharmacological, and structure-activity relation ships.In Cody, V., Middleton, E., and Arborne, J. B.(Eds.).Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. A. R. Liss, New York, pp. 521–536, (1986).
Serkedjieva, J. and Ivancheva, S., Antiherpes virus activity of extracts from the medicinal plantGeranium sanguineum L.J. Ethnopharmacol., 64, 59–68 (1999).
Shen, S., Lee, W. R., Lin, H. Y., Huang, H. C., Ko, C. H., Yang, L. L., and Chen, Y. C.,In vitro andin vivo inhibitory activities of rutin, wogonin, and quercetin on lipopolysac- charide-induced nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 production.Eur. J. Pharmacol., 446, 187–194 (2002).
Tsuchiya, Y., Shimizu, M., Hiyama, Y., Itoh, K., Hashimoto, Y., Nakayama, M., Horie, T., and Morita, N., Antiviral activity of natural occurring flavonoidsin vitro.Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo), 33, 3881–3886 (1985).
Vlietinck, A. J., Vanden Berghe, D. A., and Haemers, A., Plant flavonoids in biology and medicine. Biochemical, pharmacological, and structure-activity relationships.In Cody, V., Middleton, E., and Harborne, J. (Eds.).Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. A. R. Liss, New York, pp. 283–299, (1986).
Vrijsen, R., Everaert, L., and Boeye, A., Antiviral activity of flavones and potentiation by ascorbate.J. Gen. Virol., 69, 1749–1751 (1988).
Whitley, R. J., Herpes simplex viruses. Fields, B. N., and Knipe, D. M. (Eds.),In Fields Virology, 4th ed. Raven Press, New York, pp. 2461–2509, (2001).
Wleklik, M., Luczak, M., Panasiak, W., Kobus, M., and Lammer-Zarawska, E., Structural basis for antiviral activity of flavonoids- naturally occurring compounds.Acta Virol., 32, 522–525 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyu, S.Y., Rhim, J.Y. & Park, W.B. Antiherpetic activities of flavonoids against herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2)in vitro . Arch Pharm Res 28, 1293–1301 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02978215
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02978215