Abstract
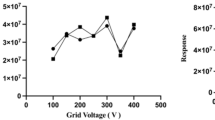
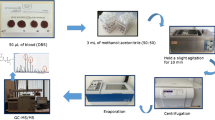
The most important step for Paraquat analysis in post-mortem human blood (PMB) is its extraction from the specimens, as Paraquat is insoluble in organic solvents due to its ionic form. The most common extraction method, solid phase extraction (SPE), has been used for the extraction of Paraquat from PMB. However, SPE procedures are somewhat time-consuming, and resulted in unsatisfactory recovery in our laboratory. Therefore, SPE procedures, with five extraction solvents for the liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) of paraquat in PMB, were compared using HPLC, and the chloroform-ethanol (7:3, v/v) solvent mixture was found to be the most effective. The recoveries of Paraquat using the 7:3 solvent mixture in human whole blood samples, which were already spiked with paraquat standards (1.05, 2.10 and 4.21 μg/mL) averaged 98.20, 105.71 and 99.40%, but the recoveries from the SPE were about 74.29, 78.50 and 80.10%, respectively. Linearity was obtained for the range of Paraquat standards, with a correlation coefficient; r2>0.999. The limit of detection (LOD, with S/N≥3) and limit of quantitation (LOQ, with S/N≥10) were 0.01 and 0.05 μg/mL, respectively. The extraction method was successfully applied to seven real post-mortem cases involving paraquat poisoning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baselt, R. C, Paraquat,Disposition of toxic drugs and chemicals in man. 5th edition. Chemical toxicology institute. Foster City, California, pp. 654–655, (2000)
Bowles, M. R., Eyles, D. W., Hampson, E. C, and Pond, S. M., Quantitation of paraquat in biological samples by radioim-munoassay using a monoclonal antibody,Fundamental & applied technologies, 19, 375–379 (1992)
Brown, P., Charlton, A., Cuthbert, M., Barnett, L, Ross, L, Green, M., Gillies, L, Shaw, L, and Fletcher, M., Identification of pesticide poisoning in wild life.Journal of chromatography A., 754, 430–478(1996)
Cross, K., Martens, F., and Desmet, K., Quantitation of Paraquat in serum by HPLC.Journal of analytical Toxicology, 17, 310–312(1993)
Fuke, C, Ameno, K., Shirakawa, Y, Ameno, S., Kiriu, T., Shinoharu, T., and Ijiri, I., Simultaneous determination of paraquat and diaquat in biological materials using high performance liquid chromatography and its application to poisoned patients,Japanese Journal of Toxicology 5, 387–393(1992)
Gill, R., Qua, S. C, and Moffat, A. C, High performance liquid chromatography of paraquat and diaquat in urine with rapid sample preparation involving ion-pair extraction on disposable cartridges of octadecyl-silica,Journal of Chromatography, 225,483–490(1983)
Ito, S., Nagata, T., Kudo, K., and Kimura, K., Simultaneous determination of paraquat and diaquat in human tissues by high performance liquid chromatography,Journal of Chromatography, 617, 119–123 (1993)
Jarvie, D. R., Fell, A. F., and Stewart, M. J., A rapid method for the emergency analysis of paraquat in plasma using a second derivative spectroscopy,Clinical Chimica Acta, 117, 153–165(1981)
Kawase, S., Kanno, S., and Ukai, S., Determination of the herbicides Paraquat and diaquat in blood and urine by gas chromatography.Journal of Chromatography, I 238, 231–240 (1984)
Maria, T. C. and Giuseppe, N., Determination of paraquat in rat brain by HPLC.Journal of Chromatography, 643, 419–425 (1993)
Maruyama, H. and Ide, M., Paraquat extraction from plasma or serum without sample deproteinization,Journal of Analytical Toxicology, 12, 33–3 (1989)
Matsuoka, T. and Okuda, J., Extraction and quantitation of paraquat and diaquat from blood,Forensic Science International, 62, 179–186(1993).
O’Neil, M. J., Smith, A., and Heckelman, P. E., The Merck Index, Merck & Co., Inc., 13th edition, pp. 1259-1260 (2001)
Tomlin, C. D. S., Paraquat, The pesticide manual, The British crop protection council. 12th edition, pp. 705-706, (2000)
Vinner, E., Stievenart, M., Humbert, L, Mathieu, D., and Lhermette, M., Separation and quantification of paraquat and diaquat in serum and urine by capillary electrophoresis,Biomedical Chromatography, 15, 342–347 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baeck, S.K., Shin, Y.S., Chung, H.S. et al. Comparison study of the extraction methods of paraquat in post-mortem human blood samples. Arch Pharm Res 30, 235–239 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977699
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977699