Abstract
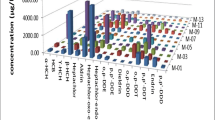
In order to investigate the residual amounts of organochlorines and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in Korean human tissues (blood, adipose tissue, liver, kidney cortex, and lung), the samples were collected from the autopsied cadavers of 40 men and 40 women (from teens to seventies of age) α-BHC, β-BHC, γ-BHC, σ-BHC,p,p′-DDT,p,p′-DDD,p,p′-DDE, endrin, dieldein, aldrin, and 7 marker PCBs (28, 52, 101, 118, 138, 153, and 180) were determined in human tissues. The levels of organochlorines and PCB congeners indicated that they have been widely distributed in Korean human body. Positive correlations in terms of age were observed for the following cases:p,p′-DDE,p,p′-DDT, θ-DDT, PCB 118, PCB 138, PCB 153, and θ-PCB in the adipose tissue, andp,p′-DDE in the lung. Concentration of these compounds showed a significant age-related increase. Accumulation of these compounds in aged people revealed that these compounds were more slowly eliminated in our environment and risk assessment was necessary for further proper action. Significant differences in the levels of PCBs between genders were found for PCB 118 in the adipose tissue and PCB 138 in the liver. Positive correlation coefficients between tissues were detected withp,p′-DDE and β-BHC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archibeque-Engle, S. L., Tessari, J. D., Winn, D. T., Keefe, T. J., Nett, T. M., and Zheng, T., Comparison of organochlorine pesticide and polychlorinated biphenyl residues in human breast adipose tissue and serum.J. Toxicol. Environ. Health, 52, 285–293 (1997).
Burgaz, S., Afkham, B. L., and Karakaya, A. E., Organochlorine pesticide contaminants in human adipose tissue collected in Tebriz(Iran).Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 54, 546–553 (1995).
Colborn, T., Vom Saal, F., and Soto, A. M., Developmental effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals in wildlife and humans.Environ. Health Perspect., 101, 378–384 (1993).
Dewailly, E., Dodin, S., Verreault, R., Ayotte, P., Sauve, L., Morin, J., and Brisson, J., High organochlorine body burden in women with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer.J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 86, 232–234 (1994).
Dewailly, E., Mulvad, G., Pedersen, H. S., Ayotte, P., Demers, A., Weber, J. P., and Hansen, J. C., Concentration of organochlorines in human brain, liver, and adipose tissue autopsy samples from Greenland.Environ. Health Perspect., 107, 823–828 (1999).
Gallelli, G., Mangini, S., and Gerbino, C., Organochlorine residues in human adipose and hepatic tissues from autopsy sources in northern Italy.J. Toxicol. Environ. Health, 46, 293–300 (1995).
Gomez-Catalan, J., Lezaun, M., To-Figueras, J., and Corbella, J., Organochlorine residues in the adipose tissue of the population of Navarra(Spain).Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 54, 534–540 (1995).
Hileman, B., Concerns broaden over chlorine and chlorinated hydrocarbons.Chem. Eng. News, 71, 11–20 (1993).
Jensen, G. E. and Clausen, J., Organochlorine compounds in adipose tissue of Greenlanders and southern Danes.J. Toxicol. Environ Health, 5, 617–629 (1979).
Kang, Y. S., Matsuda, M., Kawano, M., Wakimoto, T., and Min, B. Y., Organochlorine pesticides, polychlorinatedbiphenyls, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxines and dibenzofurans in human adipose tissue from western Kyungnam, Korea.Chemosphere, 35, 2107–2117 (1997).
Kutz, F. W., Wood, P. H., and Battimore, D. P., Organochlorine pesticide and polychlorinated biphenyls in human adipose tissue.Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 120, 71–82 (1991).
Nakamura, H., Matsuda, M., Quynh, H. T., Cau, H. D., Chi, H. T. K., and Wakimoto, T., Levels of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxines, dibenzofurans, PCBs, DDTs, and HCHs in human adipose tissue and breast milk from the south of Vietnam.Organohalogen compounds, 21, 71–76 (1994).
Pauwels, A., Covaci, A., Weyler, J., Delbeke, L., Dhont, M., De Sutter, P., D'Hooghe, T., and Schepens, P. J. C., Comparison of persistent pollutant residues in serum and adipose tissue in a female population in Belgium, 1996–1998.Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 39, 265–270 (2000).
Schecter, A., Fürst, P., Krüger, C., Meemken, H. A., Groebel, W., and Constable, J. D., Levels of polychlorinated dibenzofurans, dibenzodioxines, PCBs, DDT, and DDE, hexachlorobenzene, dieldrin, hexachlorocyclohexanes, and oxychlordane in human breast milk from the United States, Thailand, Vietnam, and Germany.Chemosphere, 18, 445–454 (1989).
Soto, A. M., Sonnenschein, C., Chung, K. L., Fernandez, M. F., Olea, N., and Serrano, F. O., The E-SCREEN assay as a tool to identify estrogens: An update on estrogenic environmental pollutants.Environ. Health Perspect., 103, 113–122 (1995).
Stellman, S. D., Djordjevic, M. V., Muscat, J. E., Gong, L., Bernstein, D., Citron, M. L., White, A., Kemeny, M., Busch, E., and Nafziger, A. N., Relative abundance of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in adipose tissue and serum of women in Long Island, New York [see comments].Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev., 7, 489–496 (1998).
Yoo, Y. C., Lee, S. K., Lee, S. Y., Yang, J. Y., In, S. W., Kim, K. W., and Chung, K. H., Distribution of Organochlorine Pesticides in Korean Human Tissues.Yakhak Hoeji, 45, 366–377 (2001).
Yoo, Y. C., Lee, S. K., Lee, Kim, K. W., Lee, S. Y., Yang, J. Y., Kim, Y. S., Oh, S. M., and Chung, K. H., Distribution of Organochlorins and PCB Congeners in Korean Adipose Tissue, Liver, and Whole Blood.Yakhak Hoeji, 46, 247–257 (2002).
Waliszewski, S. M., Aguirre, A. A., Infanzon, R. M., Benitez, A., and Rivera, J., Comparison of organochlorine pesticide levels in adipose tissue and human milk of mothers living in Veracruz, Mexico.Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 62, 685–690 (1999).
Weistrand, C. and Noren, K., Polychlorinated naphthalenes and other organochlorine contaminants in human adipose and liver tissue.J. Toxicol. Environ. Health, Part A, 53, 293–311 (1998).
WHO: Assessment of health risks in infants associated with exposure to PCBs, PCDDs, and PCDFs in breast milk.Environ. Health Series, 29 (1988).
Wolff, M. S., Fischbein, A., and Selikoff, I. J., Changes in PCB serum concentrations among capacitor manufacturing workers.Environ. Res., 59, 202–216 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, MJ., Lee, SK., Yang, JY. et al. Distribution of organochlorines and PCB congeners in Korean human tissues. Arch Pharm Res 28, 829–838 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977350
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977350