Abstract
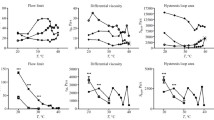
There are a wide variety of semi-solid ointments used for healing the skin diseases, whose therapeutic and skin penetration abilities may greatly differ from one another depending on the compositions of ointment vehicles. A computer optimization technique was applied to obtain the optimum formula of o/w type ointment giving the in vitro maximum absorption rate through hairless rat skin membrane. Some of the formulations were selected to find out a relationship between skin penetration of ointment and its rheological characteristics. The experimental value of absorption rate obtained from the ointment by optimum formula agreed well with the theoretical value obtained from a polynomial regression analysis. Three kinds of ointments selected among 15 formulations were obtained with a concentric cylinder type rheometer (Model; Rheolab SM-HM Physica, Germany) at 20, 30, 40 and 50°C for rheograms of rhelolgical properties of o/w type ointments. As the temperature was raised, all products showed a decrease in both shear stress and yield values. The higher skin penetration, the lower shear stress showed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Barry, B. W., Dermatological formulations; Percutaneous absorption. Marcel Dekker, INC. New York, NY 10016, pp. 127–340 (1983).
Chien, Y. W., Transdermal controlled systemic medications. Marcel Dekker, INC, New York, NY 10016, pp 1–21 (1987).
Hadgraft, J. Transdermal drug delivery. Marcel Dekker, INC., New York, N. Y. 10016, pp. 59–77 (1989).
Henderson, N. L., Meer, P. M. and Kostenbauder, H. B., Approximate rates of shear encountered in some pharmaceutical processes.J. Pharm. Sci., 50, 788 (1961).
Kydonieus, A. F. and Berner, B.,Transdermal delivery of drugs. Vol. 1, CRC press, INC. Boca Raton, Florida 33431, pp. 3–16 (1987).
Lee, C. H. and Shin, Y. H., Studies on computer optimization techniques for hydrophilic vehicle compositions.Arch. Pharm. Res., 11(3), 185–196 (1988).
Lund, W.,The pharmaceutical codex.12 ed., London, The Pharm. Press, pp. 153 (1994).
Montgomery, D. C.,Design and analysis of experiments. John Wiley & Sons, INC., New York, pp. 355 (1976).
Schwartz, J. B., Flamholz, J. R., and Press, R. H.; Computer optimization of pharmaceutical formulations I: General procedure.J. Pharm. Sci., 62, 1165 (1973).
Schwartz, J. B., Optimization techniques in product formulation.J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 32, 1536 (1985).
Shaw, J. E., Chandrasekaran, S. K. and Compbell, P., Percutaneous absorption: controlled drug delivery for topical or systemic therapy.J. Invest. Dermatol., 67, 677 (1976).
Shaw, J. E. and Chandrasekaran, S. K., Controlled topical delivery of drug for systemic action.Drug Metab. Rev., 8, 223 (1978).
Takayama, K., Imaizumi, H., Nambu, N. and Nagai, T., Mathematical optimization of formulation of indomethacin / polyvinyl polypyrrolidone / methy cellulose solid dispersions by the sequential unconstrained minimization technique.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 33, 292 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shon, SG., Lee, CH. A study on flow properties of semisolid dosage forms. Arch. Pharm. Res. 19, 183–190 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976887
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976887