Abstract
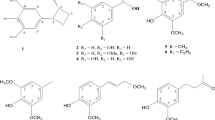
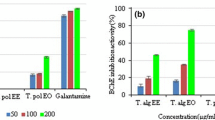
The methanolic extract of the twigs ofCeltis chinensis was found to show inhibitory activity on acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme that plays a role in the metabolic hydrolysis of ACh. Bioassay-guided fractionation of the methanolic extract resulted in the isolation ofN-p-coumaroyl tyramine, as an inhibitor on AChE. This compound inhibited AChE activity in a dose-dependent manner, and the IC50 value oftrans-N-p-coumaroyl tyramine was 34.5 μg/mL (122 μM).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartus, R. T., On neurodegenerative diseases, models, and treatment strategies: lessons learned and lessons forgotten a generation following the cholinergic hypothesis.Exp. Neurol., 163, 495–529 (2000).
Bartus, R. T., Dean, R. L., Beer, B., and Lippa, A. S., The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction.Science, 217, 408–414 (1982).
Broadwell, R. D. and Sofroniew, M. V., Serum proteins bypass the blood-brain fluid barriers for extracellular entry to the central nervous system.Exp. Neurol., 120, 245–263 (1993).
But, Paul R. H., Kimura, T., Guo, J. X., and Sung, C. K.,International collation of traditional and folk medicine: Part 2. World scientific, Singapore, pp. 22–23, (1997).
Chung, Y. K., Heo, H. J., Kim, E. K., Kim, H. K., Huh, T. L., Lim, Y., Kim, S. K., and Shin, D. H., Inhibitory effect of ursolic acid purified fromOriganum majorana L. on the acetylcholinesterse.Mol. Cells, 11, 137–143 (2001).
Dennis, T. V. and John, C. M., The diagnosis of Alzheimers disease.Alzheimers Disease Review, 3, 142–152 (1998).
Ellman, G. L., Courtney, D., Valentino, A., and Featherstone, R. M., A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity.Biochem. Pharmacol., 7, 88–95 (1961).
Hwang, S. Y., Chang, Y. P., Byun, S. J., Jeon, M. H., and Kim, Y. C., An acetylcholinesterase inhibitor isolated from Corydalis tuber and its mode of action.Kor. J. Pharmacogn., 27, 91–95 (1996).
Mortensen, S. R., Chanda, S. M., Hooper, M. J., and Padilla, S., Maturational differences in chlorpyrifos-oxonase activity may contribute to age-related sensitivity to chlorpyrifos.J. Biochem. Toxicol., 11, 279–287 (1996).
Numata, A., Katsuno, T., Yamamoto, K., Nishida, T., Takemura, T., and Seto, K., Plant constituents biologically active to insects. IV: antifeedants for the larvae of the yellow butterfly, Eurema hecabe mandarina, inArachniodes standishii.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 32, 325–331 (1984).
Okuyama, T., Shibata, S., Hoson, M., Kawada, T., Osada, H., and Noguchi., Effect of oriental plant drugs on platelet aggregation: III. Effect of Chinese drug “Xiebai” on human platelet aggregation.Plants Med., 171–175 (1986).
Park, C. H., Kim, S. H., Choi, W., Lee, Y. J., Kim, J. S., Kang, S. S., and Suh, Y. H., Novel anticholinesterase and antiamnesic activities of dehydroevodiamine, a constituent ofEvodia rutaecarpa.Planta Med., 62, 405–409 (1996).
Perry, E. K., The cholinergic hypothesis-ten years on.Br. Med. Bull., 42, 63–69 (1986).
Rhee, I. K., van de Meent, M., Ingkaninan, K., and Verpoorte, R., Screening for acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from Amaryllidaceae using silica gel thin-layer chromatography in combination with bioactivity staining.J. Chromatogr. A, 915, 217–223 (2001).
Riger, E., Shelanski, M. L., and Greene, L. A., The effects of nerve growh factor on acetylcholinesterase and its multiple forms in cultures of rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cells; increased total specific activity and appearance of the 16 S molecular form.Dev. Biol., 76, 238–243 (1980).
Yosihara, T., Takamatsu, S., and Sakamura, S., Three new phenolic amides from the roots of eggplants (Solarium melongena L).Agric. Biol. Chem., 42, 623–627 (1978).
Zhao, G., Hui, Y., Rupprecht, J. K., and Mclaughlin, J. L., Additional bioactive compounds and trilobacin, a novel highly cytotoxic acetogenin from the bark ofAsimina trilova.J. Nat. Prod., 55, 347–356 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D.K., Lee, K. Inhibitory effect ofTrans-N-p-coumaroyl tryamine from the twigs ofCeltis chinensis on the acetylcholinesterase. Arch Pharm Res 26, 735–738 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976684
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976684