Abstract
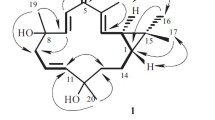
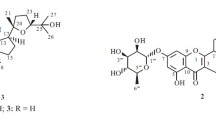
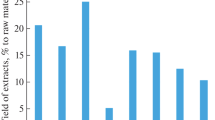
Activity-guided fractionation of the roots ofAnthriscus sylvestris resulted in the isolation and characterization of five cytotoxic compounds, deoxypodophyllotoxin (1), falcarindiol (2), and angeloyl podophyllotoxin (5) from the hexane soluble fraction and morelensin (3), bursehernin (4) from the chloroform soluble fraction. It is the first report of the occurrence of compound5 in nature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Ayres, D. C. and Loike, J. D.:Lignans-Chemical, biological and clinical properties. Cambridge Univ Press, Cambridge, 1990.
Boguchi, D. E. and Charlton, S. L.: An Asymmetric Synthesis of (-)-Deoxy podophyllotoxin,J. Org. Chem., 60, 588–593 (1995).
Brewer, C. F., Loike, J. D., Horwit, S. B., Sternlicht, H. and Gensler, W. J.: Conformational Analysis of Podophyllotoxin and its Congeners. Structure-Activity Relationship in Microtubule Assembly,J. Med. Chem., 22, 215–221 (1979)
Carmichael, J., Graffe, W. G., Gadzar, A. F., Minna, J. D. and Mitchel J. B.: Evaluation of tetrazolium based Semi-automated colorimetric assay: assessment of chemosensitivity testing,Cancer Res., 47, 936–941, (1987)
Jolad, S. D., Wiedhopf, R. M. and Cole, J. R.: Cytotxic Agents from Bursera morelensis (Burseraceae): Deoxypodophyllotoxin and a New Lignan, 5′-Desmethoxy deoxypodophyllotoxin,J. Pharm. Sci., 66, 892–893 (1977)
Kozawa, M., Morita, N. and Hata, K.: Structures of Anthriscusun, a New Phenylpropanoid Ester from the Roots ofAnthriscus sylvestris Hoffm.,Chem. Pharm. Bull., 26, 1337–1338 (1978a)
Kozawa, M., Morita, N. and Hata, K.: Chemial Components of the Roots ofAnthriscus sylvestris Hoffm. 1. Structures of an Acyloxycarboxylic Acid and a New Phenylpropanoid ester, Anthriscusin.,Yakugaku Zasshi, 98, 1486–1490 (1978b)
Kozawa, M., Baba, K., Matsuyama, Y., Kido, T., Sakai, M. and Takemoto, T.: Components of the Roots ofAnthriscus sylvestris Hoffm. II. Insecticidal Activity.,Chem. Pharm. Bull., 30 2885–2888 (1982)
Noguchi, T. and Kawanami, M.: Studies on the Constituents of Anthriscus sylvestris Hoffm.,Yakugaku Zasshi, 60, 629–636 (1940).
Villegas, M., Vargas, D., Msonthi, J. D., Marston, A. and Hostettmann, K.: Isolation of the Antifungal Compounds Falcarindiol and Sarisan fromHeteromorpha trifoliata., Planta Med., 54, 36–37 (1988)
Yamaguchi, H., Arimoto, M., Yamamoto, K. and Numata, A.: Studies on the Constituents of the Seeds of Hernandia ovigera L.,Yakugaku Zasshi, 99, 674–677 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, YH., Leem, MJ., Shin, DH. et al. Cytotoxic constituents from the roots ofAnthriscus sylvestris . Arch Pharm Res 22, 208–212 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976548
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976548