Abstract
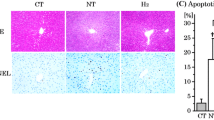
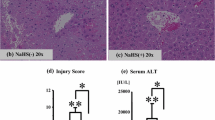
The mechanisms of liver injury from cold storage and reperfusion are not completely under-stood. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether the inactivation of Kupffer cells (KCs) by gadolinium chloride (GdCl3) modulates ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat liver. Hepatic function was assessed using an isolated perfused rat liver model. In livers subjected to cold storage at 4°C in University of Wisconsin solution for 24 hrs and to 20 min rewarm-ing ischemia, oxygen uptake was markedly decreased, Kupffer cell phagocytosis was stimulated, releases of purine nucleoside phosphorylase and lactate dehydrogenase were increased as compared with control livers. Pretreatment of rats with GdCl3, a selective KC toxicant, suppressed Kupffer cell activity, and reduced the grade of hepatic injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion. While the initial mixed function oxidation of 7-ethoxycoumarin was not different from that found in the control livers, the subsequent conjugation of its meta-bolite to sulfate and glucuronide esters was suppressed by ischemia-reperfusion. GdCl3, restored sulfation and glucuronidation capacities to the level of the control liver. Our findings suggest that Kupffer cells could play an important role in cold/warm ischemia-reperfusion hepatic injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brass, C. A. and Mody, M. G., Evaluation of purine nucleoside phosphorylase release as a measure of hepatic endothelial cell injury.Hepatology, 21, 174–179 (1995).
Caldwell-Kenkel, J. C., Currin, R. T., Tanaka, Y., Thurman, R. G. and Lemasters, J. J., Reperfusion injury to endothelial cells following cold ischemic storage of rat liver.Hepatology, 10, 292–299 (1989).
Caldwell-Kenkel, J. C., Currin, R. T., Tanaka, Y., Thurman, R. G. and Lemasters, J. J., Kupffer cell activation and endothelial cell damage after storage of rat livers: effects of reperfusion.Hepatology, 13, 83–95 (1991).
Carles, J., Fawaz, R., Hamoudi, N. E., Neaud, V., Balabaud, C. and Biolae-Sage, P., Preservation of human liver grafts in UW solution. Ultrastructural evidence for endothelial and Kupffer cell activation during cold ischemia and after ischemia-reperfusion.Liver, 14, 50–56 (1994).
Cha, Y. N., Dong, M. S. and Hong, S. S., Functional relationship between initial oxidation of 7-ethoxycoumarin and subsequent conjugation of 7-hydroxy-coumarin in isolated perfused rat livers.Chem. Biol. Interact., 61, 125–137 (1987).
Chun, K., Zhang, J., Biewer, J., Ferguson, D. and Clemens, M. G., Microcirculatory failure determines lethal hepatocyte injury in ischemic/reperfused rat livers.Shock, 1, 3–9 (1994).
Cowper, K. B., Currin, R. T., Dawson, T. L., Lindert, K. A., Lemasters, J. J. and Thurman, R. G., A new method to monitor Kupffer-cell function continuously in the perfused rat liver. Dissociation of glycogenolysis from particle phagocytosis.Biochem. J., 266, 141–147 (1990).
Griffeth, L. K., Rosen, G. M. and Rauchman, E. J., Effects of model traumatic injury on hepatic drug metabolism in the rat.Drug Metab. Dispos., 15, 749–759 (1987).
Hoffe, P. A., May, R. and Robertson, B. D., Purine nucleoside phosphorylase from Salmonella typhimurium and rat liver. In: Hoffee P, Jones MA, eds.Methods in enzymology, Vol 51. New York: Academic Press, pp. 517–524 (1978).
Huet, P. M. and Villenueve, J. P., Determinations of drug disposition in patients with cirrhosis.Hepatology, 3, 913–918 (1983).
Jaeschke, H. and Farhood, A., Neutrophil and Kupffer cell-induced oxidant stress and ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat liver.Am. J. Physiol., 260, G355-G362 (1991).
Kennedy, T. P., Rao, N. V., Hopkins, C., Pennington, L., Tolley, E. and Hoidal, J. R., Role of reactive oxygen species in reperfusion injury of the rabbit lung.J. Clin. Invest., 83, 1326–1335 (1989).
Lee, S. M. and Clemens, M. G., Subacinar distribution of hepatocyte membrane potential response to stimulation of gluconeogenesis.Am. J. Physiol., 263, G319-G326 (1992).
Lee, S. M., Park, M. J., Cho, T. S. and Clemens, M. G., Hepatic injury and lipid peroxidation during ischemia and reperfuison.Shock, 13, 279–284 (2000).
Lemasters, J. J. and Thurman, R. G., Hypoxic, ischemic and preservation-induced injury in the liver. In: Ballet, F., Thurman, R. G., eds., Perfused liver:Clinical and basic applications. London: Libbey, pp. 99 (1991).
Marubayash, S., Takenaka, M., Mhi, K., Ezaki, H. and Kawasaki, T., Adenine nucleotide metabolism during hepatic ischemia and subsequent blood flow periods and its relation to organ viability.Transplantation, 30, 294–296 (1980).
Marzi, I., Cowper, K. B., Takei, Y., Lindert, K. A., Lemasters, J. J. and Thurman, R. G., Methyl palmitate prevents Kupffer cell activation and improves survival after orthotopic liver transplantation in the rat.Transplant. Int., 4, 215–220 (1991).
Marzi, I., Zhong, Z., Zimmermann, F. A., Lemasters, J. J. and Thurman, R. G., Xanthine and hypoxanthine accumulation during storage may contribute to reperfusion injury following liver transplantation in the rat.Transplant. Proc., 21, 1319–1320 (1989).
Nakagawa, I., Hishinuma, I., Hirota, K., Miyamoto, K., Yamanaka, T., Tsukidate, K., Katayama, K. and Yamatsu, I., Involvement of tumor necrosis-alpha in the pathogenesis of activated macrophage-mediated hepatitis in mice.Gastroenterology, 99, 758–765 (1990).
Pichlmayer, R., Ringe, B., Lauchart, W. and Wonigeit, K., Liver transplantation.Transplant. Proc., 19, 103–112 (1987).
Ploeg, R. J., DAlessandro, A. M., Knechtle, S. J., Stegall, M. D. and Kalayoglu M., Risk factors for primary dysfunction after liver transplantation-A multivariate analysis.Transplantation, 55, 807–813 (1993).
Rao, P. N., Liu, T., Snyder, J. T., Platt, J. L. and Starzl, T. E., Reperfusion injury following cold ischemia activated rat liver Kupffer cells.Transplant. Proc., 23, 666–669 (1991).
Rao, P. N., Walsh, T. R. and Makowka, L., Purine nucleoside phosphorylase: A new marker for free oxygen radical injury to the endothelial cell.Hepatology, 11, 193–198 (1990).
Shiratori, Y., Kiriyama, H., Fukushi, Y., Nagura, T., Takada, H., Hai, K. and Kamii, K., Modulation of ischemia-reperfusion-induced hepatic injury by Kupffer cells.Dig. Dis. Sci., 39, 1265–1272 (1994).
Takei, Y., Marzi, I., Gao, W., Cores, G. J., Lemasters, J. J. and Thurman, R. G., Leukocyte adhesion and cell death following orthotopic liver transplantation in the rat.Transplantation, 50, 959–965 (1991).
Thurman, R. G., Marzi, I., Seitz, G., Thies, J., Lemasters, J. J. and Zimmerman, F., Hepatic reperfusion injury following orthotopic liver transplantation in the rat.Transplantation, 46, 502–506 (1988).
Yang, C. M. and Carlson, G. P., Glucuronidation and sulfation in subcellular fractions and in the isolated perfused rabbit lung: influence of ethanol.Pharmacology, 42, 28–35 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YG., Lee, SH. & Lee, SM. Role of kupffer cells in cold/warm ischemia-reperfusion injury of rat liver. Arch Pharm Res 23, 620–625 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02975251
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02975251