Abstract
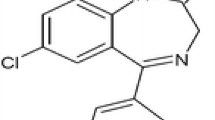
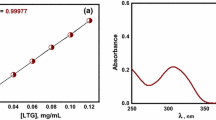
Aim of this work is to prepare poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) nanoparticles by dialysis method without surfactant and to investigate drug loading capacity and drug release. The size of PLGA nanoparticles was 269.9±118.7 nm in intensity average and the morphology of PLGA nanoparticles was spherical shape from the observation of SEM and TEM. In the effect of drug loading contents on the particle size distribution, PLGA nanoparticles were monomodal pattern with narrow size distribution in the empty and lower drug loading nanoparticles whereas bi- or trimodal pattern was showed in the higher drug loading ones. Release of clonazepam from PLGA nanoparticles with higher drug loading contents was slower than that with lower loading contents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Alleman, E., Gurny, R. and Doelker, E., Drug-loaded nanoparticles-preparation methods and drug targeting issues.Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 39, 173–191 (1993).
Cho, C. S., Na, J. W., Jeong, Y. I., Kim, S. H., Lee, Y. M. and Sung, Y. K., Micelle formation of the hexablock copolymer consisting of poly((γ-benzyl L-glutamate) as the hydrophobic part and poly(ethylene oxide) as the hydrophilic part.Polymer (Korea), 19, 926–931 (1995).
Ciftci, K., Suheyla Kas, H., Atilla Hincal, A., Meral Ercan, T., Guven, O. and Ruacan, S.,In vitro and in vivo evaluation of PLGA (50/50) microspheres containing 5-fluorouracil prepared by a solvent evaporation method.Int. J. Pharm., 131, 73–82 (1996).
Couvreur, P., Fattal, E. and Andremont, A., Liposomes and nanoparticles in the treatment of intracellular bacterial infections.Pharm. Res., 8, 1079–1086 (1991).
Couvreur, P., Fattal, E. and Alphandary, H., Puisieux, F. and Andremont, A., Intracellular targeting of antibiotics by means of biodegradable nanoparticles.J. Control. Release. 19, 259–268 (1992).
Davis, S. S., Illum, L., Moghimi, S. M., Davies, M. C., Porter, C. J. H., Muir, I. S., Brindley, A., Christy, N. M., Norman, M. E., Williams, P. and Dunn, S. E., Microspheres for targeting drugs to specific body sites.J. Control. Release, 24, 157–163 (1993).
Davis, S. S., Colloids as drug-delivery systems.Pharmaceut. Technol., 5, 71–88 (1981).
Dunn, S. E., Brindley, A., Davis, S. S., Davies, M. C. and Illum, L., Polystyrene-poly(ethylene glycol) (PSPEG 2000) particles as model systems for site specific drug delivery. 2. The effect of PEG surface density on thein vitro cell characterization andin vivo biodistribution.Pharm. Res., 11, 1016–1022 (1994).
Gref, R., Minamitake, Y., Peracchia, M. T., Trubetskoy, V., Torchilin, V., Langer, R., Biodegradable long-circulating polymeric nanospheres.Science, 263, 1600–1603 (1994).
Illum, L., Davis, S. S., Wilson, C. G., Frier, M., Hardy, J. G., Thomas, N. W., Blood clearance and organ deposition of intravenously administered colloidal particles: the effects of particle size, nature and shape.Int. J. Pharm., 12, 135–146 (1982).
Illum, L., Hunneyball, I. M., Davis, S. S., The effect of hydrophilic coatings on the uptake of colloidal particles by the liver and by peritoneal macrophages.Int. J. Pharm., 29, 53–65 (1986).
Jeffery, H., Davis, S. S., O'Hagan, D. T., The preparation and characterization of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microparticles. I. Oil-in water emulsion solvent evaporation.Int. J. Pharm., 77, 169–175 (1991).
Jeong, Y. I., Cheon, J. B., Kim, S. H., Nah, J. W., Lee, Y. M., Sung, Y. K., Akaike, T., Cho, C. S., Clonazepam release from core-shell type nanoparticlesin vitro.J. Control. Release, 51, 169–178 (1998).
Juliene, M. C., Alonso, M. J., Gomez Amoza, J. L., Benoit, J. P., Preparation of poly(dl-lactide/glycolide) nanoparticles of controlled particle size distribution: application of experimental design.Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 18, 1063–1077 (1992).
Kataoka, K., Kwon, G. S., Yokoyama, M., Okano, T., Sakurai, Y., Block copolymer micelles as vehicles for drug delivery.J. Control. Release, 24, 119–132 (1993).
Kim, H. J., Jeong, Y. I., Kim, S. H., Lee, Y. M., Cho, C. S., Clonazepam release from core-shell type nanoparticlesin vitro.Arch. Pharm. Res., 20, 324–329 (1997).
Kreuter, J., Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems.J. Control. Release, 16, 169–176 (1993).
Kwon, G. S., Naito, M., Yokoyama, M., Okano, T., Sakurai, Y., Kataoka, K., Physical entrapment of adriamycin in AB block copolymer micelles.Pharm. Res., 12, 192–195 (1995).
La, S. B., Okano, T., Kataoka, K. Preparation and characterization of the micelle-forming polymeric drug indomethacin-incorporated poly(ethylene oxide)-poly((-benzyl L-aspartate) block copolymer micelles.J. Pharm. Sci., 85, 85–90 (1996).
Lasic, D. D., Mixed micelles in drug delivery.Nature, 355, 279–280 (1992).
Leroux, J. C., Allemann, E., Jaeghere, F. D., Doelker, E., Gurny, R., Biodegradable nanoparticles-From sustained release formulations to improved site specific drug delivery.J. Control. Release, 39, 339–350 (1996).
Muller, R. H., Wallis, K. H., Troster, S. D., Kreuter, J.,In vitro characterization of poly(methyl-methacrylate) nanoparticles and correlation to theirin vivo fate.J. Control. Release, 20, 237–246 (1992).
Mura, P., Liguori, A., Bramanti, G., Corti, P., Murratzu, C., Celesti, L.,In vitro study of clonazepam diffusion kinetics from solutions or hydrophilic gel.Pharm. Acta Helv., 65, 298–303 (1990).
Nah, J. W., Jeong, Y. I., Cho, C. S., Clonazepam release from core-shell type nanoparticles composed of poly((-benzyl L-glutamate) as the hydrophobic part and poly(ethylene oxide) as the hydrophilic part.J. Polym. Sci. B: Polym. Phys., 36, 415–423 (1998).
Scholes, P. D., Coombes, A. G. A., Illum, L., Davis, S. S., Vert, M., Davies, M. C., The preparation of sub-200 nm poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres for site-specific drug delivery.J. Control. Release, 25, 145–153 (1993).
Seijo, B., Fattal, E., Roblot-Treupel, L., Couvreur, P., Design of nanoparticles of less than 50 nm diameter: preparation, characterization and drug loading.Int. J. Pharm., 62, 1–7 (1990).
Sjostrom, B., Kronberg, Br., Carlfors, J., A method for the preparation of submicron particles of sparingly water-soluble drugs by precifitation in oil-in water emulsions, I. Influence of emulsification and surfactant concentration.J. Pharm. Sci., 82, 579–583 (1993a).
Sjostrom, B., Bergenstahl, B., Kronberg, B., A method for the preparation of submicron particles of sparingly water-soluble drugs by precipitation in oil-in water emulsions. II: Influence of the emulsifier, the solvent, and the drug substance.J. Pharm. Sci., 82, 585–589 (1993b).
Sjostrom, B., Kaplun, A., Talmon, Y., Cabane, B., Structure of nanoparticles prepared from oil-in water emulsions.Pharm. Res., 12, 39–48 (1995).
Venier-Julienne, M. C., Benoit, J. P., Preparation, purification and morphology of polymeric nanoparticles as drug carriers.Pharm. Acta Helv., 71, 121–128 (1996).
Witschi, C., Doelker, E., Residual solvents in pharmaceutical products: acceptable limits, influences on physicochemical properties, analytical methods and documented values.Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 43, 215–242 (1997).
White, H. S. Antiepileptic drugs, in: A. R. Gennaro (Eds.),Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy, 19th Edition, Vol. 2, Mack Publishing Company, Easton, Pennsylvania, USA, pp. 1173–1174, 1995.
Yoshioka, T., Hashida, M., Muranishi, S., Sezaki, H., Specific delivery of mitomycin C to the liver, spleen and lung: nano- and microspherical carriers of gelatin.Int. J. Pharm., 81, 131–141 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nah, JW., Paek, YW., Jeong, YI. et al. Clonazepam release from poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles prepared by dialysis method. Arch. Pharm. Res. 21, 418–422 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974636
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974636