Abstract
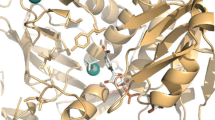
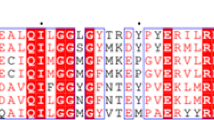
Gly-224 residue of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase was mutated by site-directed mutagenesis to isoleucine, which is the corresponding amino acid residue of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase. The mutated gene on M13 vector was subcloned in YEp13 and used to transformSaccharomyces cerevisiae 302-21 #2 strain, and the expressed protein was purified. The turnover numbers of mutant enzyme for ethanol and acetaldehyde were decreased compared to wild-type enzyme. The results of product inhibition studies indicated that the reaction mechanism was changed to Iso Theorell-Chance from Ordered Bi Bi. We supposed that Gly-224 was related to the enzyme reaction mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Bennetzen, J. and Hall, B. D., The primary structure of theSaccharomyces cerevisiae and gene for alcohol dehydrogenase I.J. Biol. Chem., 257, 3018–3025 (1982).
Branden, C. I., Jornvall, H., Eklund, H. and Furugren, B., Alcohol dehydrogenase: InEnzymes (3rd Ed.), 11, 1975, pp. 103–190.
Cleland, W. W., Statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data.Methods Enzymol., 63, 103–138 (1979).
Cornell, N. W., Properties of alcohol dehydrogenase and ethanol oxidation in vivo and in hepatocytes.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 18, Suppl. 1, 215–221 (1983).
Eklund, H., and Brändén, C. I.,Active Sites of Enzymes, Jurnak, F. A. and McPherson, A. (Eds), Wiley, New York, 1987, pp. 73–142.
Eklund, H., Plapp, B. V., Samama, J. P. and Brändén, C. I., Binding of substrate in a ternary complex of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase.J. Biol. Chem., 257, 14349–14358 (1982).
Ganzhorn, A. J., Green, D. W., Hershey, A. D., Gould, R. M. and Plapp, B. V., Kinetic characterization of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase.J. Biol. Chem., 262, 3754–3761 (1987).
Ganzhorn, A. J. and Plapp, B. V., Carboxyl groups near the active site zinc contribute to catalysis in yeast alcohol dehydrogenase, J. Biol. Chem., 263, 5446–5454 (1988).
Gould, R. M., Plapp, B. V., Substitution of arginine for histidine-47 in the coenzyme binding site of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase I.Biochemistry, 29, 5463–5468 (1990).
Hayes, J. E., Jr., and Velick, S. F., Yeast alcohol dehydrogenase; Molecular weight, coenzyme binding and reaction equilibria, J. Biol. Chem., 207, 225–244 (1954).
Ito, H., Fukuda, Y., Murata, K. and Kimura, A., Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations.J. Bacteriol., 153, 163–168 (1983).
Jornvall, H., Eklund, H. and Branden, C. I., Subunit conformation of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase.J. Biol. Chem., 253, 8414–8419 (1978).
Klinman, J. P., Probes of mechanism and transition state structure in alcohol dehydrogenase reaction.Crit. Rev. Biochem., 10, 37–78 (1981).
Kunkel, T. A., Roberts, J. D. and Zakour, R. A., Rapid and efficient site-directed mutagenesis without phenotypic selection.Methods Enzymol., 154, 367–382 (1987).
Laemmli, U. K., Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.Nature, 227, 680–685 (1970).
Laidler, R. J. and Bunting, P. S.,The Chemical Kinetics of Enzyme Action (2nd Ed.), Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1973.
Park, D. H. and Plapp, B. V., Isozymes of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase active on ethanol and steroids; cDNA cloning, expression and comparison of active sites.J. Biol. Chem., 266, 13296–13302 (1991).
Plapp, B. V., Ganzhorn, A. J., Gould, R. G., Green, D. W. and Hershey, A. D., Aldehyde dehydrogenase, aldo-keto reductase and alcohol dehydrogenase, In Weiner, H. and Flynn, T. G., (Eds.),Enzymology and Molecular Biology of Carbonyl Metabolism 3, Progress in Clinical and Biological Research, Alan R. Liss, New York, 1987, Vol. 232, pp. 227–236.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F. and Maniatis, T., Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Mannual, CSH, New York, 1989, p4.31.
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. and Coulson, A. R., DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 74, 5463–5467 (1977).
Zoller, M. J. and Smith, M., Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis; A simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template.Methods Enzymol., 154, 329–350 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, K.M., Ryu, J.W. Substitution of Gly-224 residue to ile in yeast alcohol dehydrogenase and enzyme reaction mechamism. Arch. Pharm. Res. 16, 231–236 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974488
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974488