Abstract
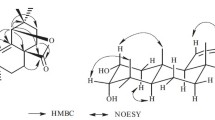
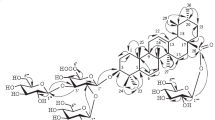
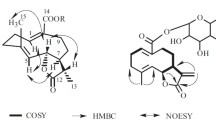
Four triterpenoids were isolated from the roots ofDipsacus asper. On the basis of chemical and spectral evidence, the structures of these compounds have been elucidated to be hederagenin (1), hederagenin 3-O-α-L-arabinoside (2). 3-O-α-L-arabinopyranosyl hederagenin 28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (3) and hederagenin 28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (4). The new glycoside,4, was named dipsacus saponin A.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Chandel, R. S. and Rastogi, R. P., Triterpenoid saponins and sapogenins: 1973–1978.Phytochemistry, 19, 1889 (1980).
Kizu, H., Kitayama, S., Nakatani, F., Tomimori, T. and Namba, T., Studies on nepalese crude drugs. III. On the saponins ofHedera nepalensis K. Koch.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 33, 3324 (1985a).
Kizu, H., Hirabayashi, S., Suzuki, M. and Tomimori, T., Studies on the constituents ofHedera rhombea Bean. IV. On the hederagenin glycosides. (2).Chem. Pharm. Bull., 33, 3473 (1985b).
Kang, S. S.,13C-NMR spectroscopy of amyrins.Kor. J. Pharmacogn., 18, 151 (1987).
Kouno, I., Tsuboi, A., Nanri, M. and Kawano, N., Acylated Triterpene glycoside from roots ofDipsacus asper.Phytochemistry, 29, 338 (1990).
Matsumoto, K., Kasai, R., Kanamaru, F., Kohda, H. and Tanaka, O., 3,4-secolupane type triterpene glycosyl esters from leaves ofAcanthopanax divaricatus SEEM.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 35, 413 (1987).
Mahato, S. B., Sarkar, S. K. and Poddar, G., Triterpenoid saponins.Phytochemistry, 27, 3037 (1988).
Mizui, F., Kasai, R., Ohtani, K. and Tanaka, O., Saponins from brans of quinoa,Chenopodium quinoa Willd. I.Chem., Pharm. Bull., 36, 1415 (1988).
Namba, T.,Coloured Illustrations of Wakan-Yaku (The Crude Drugs in Japan, China and Neighbouring Countries). Vol. I, Hoikusha Publishing Co., Osaka, 1986, p.187.
Shanghai Science and Technologic Publisher and Shougakukan,The Dictionary of Chinese Drugs. Vol. III, Shougakukan, Tokyo, 1985, p.1616.
Zhang, Y. W. and Xue, Z., New triterpenoid glycosides fromDipsacus asper Wall.Yaoxue Xuebao,26, 911 (1991b);Chem. Abstr. 117, 44545x (1992).
Zhang, Y. W. and Xue, Z., Chemical constituents ofDipsacus asper Wall.Yaoxue Xuebao, 26, 676 (1991a);Chem. Abstr., 116, 170117z (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, K.Y., Son, K.H. & Do, J.C. Triterpenoids from the roots ofDipsacus asper . Arch. Pharm. Res. 16, 32–35 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974125
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974125