Abstract
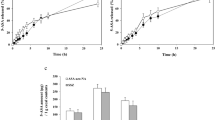
As a new colon-specific prodrug of 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), 5-aminosalicyl-glycine (5-ASA-Gly) was prepared by a simple synthetic route in good yield. Apparent partition coefficients of 5-ASA-Gly were lower than those of 5-ASA, which determined in CHCl3/pH 6.8 buffer or n-octanol/pH 6.8 buffer system. Stability of 5-ASA-Gly by peptidases was investigated by incubation of 5-ASA-Gly with the homogenates of tissue and contents of stomach, proximal small intestine or distal small intestine of rats at 37°C. 5-ASA was not detected, indicating that the prodrug was stable in the upper intestine. The amount of 5-ASA liberated from incubation of the prodrug in cecal or colonic contents of rats was about 65% or 27% in 8 hrs, respectively, which indicated that the prodrug activation took place more readily in the rat cecum whose bacterial counts are high like human colon. Results fromin vitro experiments suggested 5-ASA-Gly as a promising candidate of a colon-specific prodrug of 5-ASA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Brown, J. P., McGarraugh, G. V., Parkinson, T. M., Wingard, R. E., Onderdonk, A. B., A polymeric drug for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.J. Med. Chem., 26, 1300–1307 (1983).
Crotty, B. and Jewel, J. P., Drug therapy of ulcerative colitis.Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 34, 189–198 (1992).
Danel, K., Podolsky, M. D., Inflammatory bowel disease.The New England J. Med. 325, 928–937, 1008–1016, (1991).
Istran, C., Gabor, S. and Ferene, S., Glycosides of 5-aminosalicylic acid.Magy Kem FOLY., 97, 143–147 (1991).
Martin C. Carey and Michael J. Cahalane, Enterohepatic circulation inThe Liver, Biology and Pathobiology, 2nd ed., Irwin M. Arias, Hans Popper, David Schachter, and David, A. Shafritz Eds., Raven press, New York, (1988), chap. 33.
Mcleod, A. D. and Tozer, N. T., Kinetic perspectives in colonic drug delivery, inOral Colon Specific Drug Delivery, Friend, D. R. Ed., CRC press, Boca Raton, FL., 85–114, (1992)
Nakamura, J., Asai, K., Nishida, K. and Sasaki, H., A novel prodrug of salicylic acid, salicylic acid-glutamic acid conjugate utilizing hydrolysis in rabbit intestinal microorganisms.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 40, 2164–2168 (1992).
Novis, B. H., Korzets, J., Chen, P. and Bernheim, J., Nephrotic syndrome after treatment with 5-amino-salicylic acid.Br. Med. J., 296, 1442 (1988).
Ryde, E. M., Low-molecular-weight azo compounds, inOral Colon Specific Drug Delivery, Friend, D. R., Ed., CRC press, Boca Raton, FL., 143–152, (1992).
Saffran, M., Oral colon-specific drug delivery with emphasis on insulin: A critical review, inOral Colon Specific Drug Delivery, Friend, D. R., Ed., CRC press, Boca Raton, FL., 45–84, (1992)
Scheline, R. R., Metabolism of foreign compounds by gastrointestinal microorganisms.Pharmacological Review 25, 451–523 (1973)
Yamaguchi, T., Sasaki, K., Nakayama, T. and Kimura, T., Biopharmaceutical evaluation of salicylazosulfanilic acid as a novel colon-targeted prodrug of 5-aminosalicylic acid, 2, 123–131 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, Y.J., Lee, J.S., Kim, H.H. et al. Synthesis and evaluation of 5-aminosalicyl-glycine as a potential colon-specific prodrug of 5-aminosalicylic acid. Arch. Pharm. Res. 21, 174–178 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974024
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974024