Abstract
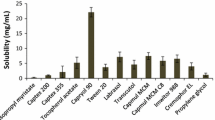
The absorption profile of phenytoin Na emulsion were examined compared to that of phenytoin suspension after oral administration in the rat. The corn oil-in-water emulsion, particle size of 184±57.8 nm, was prepared using a microfludizer, and phenytoin Na added by shaft homogenizer. The phenytoin emulsion or suspension, 100 mg/kg, were intubated intragastrically using oral dosing needle and blood samples were withdrawn via an indwelling cannula from the conscious rat. Plasma concentrations of phenytoin were measured with HPLC using phenacetin as an internal standard. The plasma concentration versus time data were fitted to a one compartment open model and the pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated using the computer program, Boomer. The phenytoin plasma concentrations from the emulsion at each observed time were about 1.5–2 times higher than those from the suspension, significantly at time of 5, 6 and 7 hr after administration. The absorption (ka) and elimination rate constant (ke) were not altered significantly, however the AUC increased from 65.6 to 106.7 μg·hr/ml after phenytoin suspension or emulsion oral administration, respectively. From an equilibrium dialysis study, the diffusion rate constant (kIE) was considerably higher from the phenytoin Na emulsion (0.0439 hr−1) than phenytoin suspension (0.0014 hr−1).
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Alvarez, F. J. and Stella, V., Pancreatic lipase-catalyzed hydrolysis of esters of hydroxymethyl phenytoin.J. Pharm. Res., 6, 555–563 (1989).
Bates, T. R., Pieniaszek, H. J., Sequeira, J. A. L. and Rasmussen, J. E., Gastrointestinal absorption of griseofulvin from corn oil-in-water emulsions.Arch. Dermatol., 113, 302–306 (1977).
Borel, P., Armand, M., Pasquier, M., Senft, M., Dutot, G., Melin, C., Lafont, H., and Lairon, D., Digestion and absorption of tube-feeding emulsions with different droplet sizes and compositions in the rat.J. Parent. Enteral Nutri., 18, 534–543 (1994).
Bourne, D. W. A., Boomer, a simulation and modeling program for pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data analysis.Computer Methods Programs in Biomed., 29, 191–195 (1989).
Carrigan, P. J. and Bates, T. R., Biopharmaceutics of drugs administered in lipid-containing dosage forms l: Gl absorption of griseofulvin from an oil-in-water emulsion in the rat.J. Pharm. Sci., 62, 1476–1478 (1973).
Chakrabarti, S. and Belpaire, F. M., Bioavailability of phenytoin in lipid containing dosage forms in rats.J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 30, 330–334 (1978).
Corvari, S. J., Hollenbeck, R. G., Leslie, J., Plaisance, K. I. and Young, D., Absorption and disposition of colloidal drug delivery systems. I. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of a cyclosporin emulsion.Pharm. Res., 8, 40–46 (1991).
DiPiro, J. T., Blouin, R. A., Pruemer, J. M. and Spruill, W. J.,Concepts in clinical pharmacokinetics, American society of hospital pharmacists, Betheda, 1988.
Gibaldi, M. and Perrier, D.,Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed. Dekker, New York, 1982.
Kararli, T. T., Needham, T. E. and Alcorn, L., Oral delivery of renin inhibitor compound using emulsion formulations.Pharm. Res., 9, 888–893 (1992).
Khalil, A. T. and Al-khamis, I., Phenytoin-bupropion interaction: Effect on plasma phenytoin in the rat.J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 42, 799–801 (1990).
Kirsh, R., Goldstein, R., Tarioff, J., Paris, D., Hook, J., Hanna, N., Bugelski, P. and Poste, G., An emulsion formulation of amphotericin B improved the therapeutic index when treating systemic murine candidiasis.J. Infec. Diseas., 158, 1066–1070 (1988).
Macheras, P., Ismailos, G. and Reppas, C., Bioavailability study of a freeze-dried sodium phenytoin-milk formulation.Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 12, 687–695 (1991).
Physicians GenR. The complete drug references. Mosby, Baltimore, 1996.
Neuvonen, P. J., Bioavailability of phenytoin; Clinical pharmacokinetic and therapeutic implications.Clin. Pharmacokin., 4, 91–103 (1979).
Perucca, E., Pharmacokinetic interactions with antiepileptic drugs. Clin.Pharmacokin., 7, 57–84 (1982).
Savio, E. O., Fagiolino, P., Jelen, M. and Leon, A. S., Influence of the emulsion sign in phenytoin bioavailability.Boll. Chim. Farmaceutico-Anno, 133, 239–245 (1994).
Savio, E. O., Fagiolino, P., Solana, G., Parente, E. and Leon, A., Development of water/oil phenytoin emulsion bioavailability in rats.S.T.P. Pharma Sci., 1, 379–385 (1991).
Shargel, L. and Yu, A. B.,Applied biopharmaceutics and pharmacokinetics, 3rd ed. Appleton & Lange, Norwalk, 1993.
Splinter, M. Y., Seifert, C. F., Bradberry, J. C. and Allen, L. V., Effect of pH on the equilibrium dialysis of phenytoin suspension with and without enteral feeding formula.J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr., 14, 275–278 (1990).
Stout, S. A. and DeVane, C. L., Tissue assay of phenobarbital, phenytoin and p-hydroxyphenytoin by high-performance liquid chromatography.J. Chromatogr, 285, 500–508 (1984).
Vila, M. R., Sidney, A. T. and Ponzo, J. L., An HPLC assay for phenytoin in serum with an improved sample preparation technique.Clin. Chem., 31, 1932–1935 (1985).
Wieland, K. K. and Ciranowicz, M.,Physician's drug handbook 6th ed. Spring House, Pennsylvania, 1995.
Young, L. Y. and Koda-kimble, M. A.,Applied therapeuticc: The clinical use of drugs, 6th ed., vancouver, 1996.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, Ki., Bourne, D.W.A. Gastrointestinal absorption of phenytoin from an oil-in-water microemulsion. Arch. Pharm. Res. 20, 480–485 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02973944
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02973944