Abstract
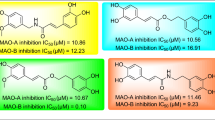
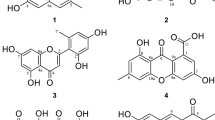
The methanol extract from the aerial parts ofDictamnus albus was active in inhibiting monoamine oxidase (MAO) from the mouse brain. Activity-guided fractionation led to the isolation of four known coumarins, 7-(6′R-hydroxy-3′, 7′-dimethyl-2′E, 7′-octadienyloxy) coumarin (1), auraptene (2), umbelliferone (3), and xanthotoxin (4), as active compounds along with an inactive alkaloid, skimmianine (5). Compounds1 and2 inhibited MAO activity in a concentration-dependent manner with IC50 values of 0.7 and 1.7 μM, respectively. Compounds1 and2 showed a slight and potently selective inhibitory effect against MAO-B (IC50 0.5 and 0.6 μM, respectively) compared to MAO-A (IC50 1.3 and 34.6 μM, respectively). According to kinetic analyses derived by Lineweaver-Burk reciprocal plots, compounds1 and2 exhibited a competitive inhibition to MAO-B.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benedetti, M. S. and Dostert, P., Monoamine oxidase: from physiology and pathophysiology to the design and clinical application of reversible inhibitors. In Testa, B. (Eds.) Advances in Drug Research, Vol. 23. Adademic Press, New York, pp. 65–125 (1992).
Bruhlmann, C., Ooms, F., Carrupt, P. A., Testa, B., Catto, M., Leonetti, F., Altomare, C., and Carotti, A., Coumarins derivatives as dual inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase and monoamine oxidase.J. Med. Chem., 44, 3195–3198 (2001).
Carotti, A., Altomare, C., Catto, M., Gnerre, C., Summo, L., De Marco, A., Rose, S., Jenner, P., and Testa, B., Lipophilicity plays a major role in modulating the inhibition of monoamine oxidase B by 7-substituted coumarins.Chem. Biodivers., 3, 134–149 (2006).
Carotti, A., Carrieri, A., Chimichi, S., Boccalini, M., Cosimelli, B., Gnerre, C., Carotti, A., Carrupt, P. A., and Testa, B., Natural and synthetic geiparvarins are strong and selective MAO-B inhibitors. Synthesis and SAR studies.Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 12, 3551–3555 (2002).
Catto, M., Nicolotti, O., Leonetti, F., Carotti, A., Favia, A. D., Soto-Otero, R., Mendez-Alvarez, E., and Carotti, A., Structural insights into monoamine oxidase inhibitory potency and selectivity of 7-substituted coumarins from ligand- and target-based approaches.J. Med. Chem., 49, 4912–4925 (2006).
Chakravarty, A. K., Sarkar, T., Masuda, K., and Shiojima, K., Carbazole alkaloids from roots ofGlycosmis arborea.Phytochemistry, 50, 1263–1266 (1999).
Chang, J., Xuan, L. J., Xu, Y. M., and Zhang, J. S., Cytotoxic terpenoid and immunosuppressive phenolic glycosides from the root bark ofDictamnus dasycarpus.Planta Med., 68, 425–429 (2002).
Chang, J., Xuan, L. J., Xu, Y. M., and Zhang, J. S., Seven new sesquiterpene glycosides from the root bark ofDictamnus dasycarpus.J. Nat. Prod., 64, 935–938 (2001).
Gnerre, C., Catto, M., Leonetti, F., Weber, P., Carrupt, P. A., Altomare, C., Carotti, A., and Testa, B., Inhibition of monoamine oxidases by functionalized coumarin derivatives: biological activities, QSARs, and 3D-QSARs.J. Med. Chem., 43, 4747–4758 (2000).
Huong, D. T., Choi, H. C., Rho, T. C., Lee, H. S., Lee, M. K., and Kim, Y. H.: Inhibitory activity of monoamine oxidase by coumarins fromPeucedanum japonicum.Arch. Pharm. Res., 22, 324–326 (1999).
Ishii, H., Ishikawa, T., Mihara, M., and Akaike, M., Studies on the chemical constituents of Rutaceous plants. XLVIII. The chemical constituents ofXanthoxylum ailanthoides [Fagara ailanthoides]. (3) Isolation of the chemical constituents of the bark.Yakugaku Zasshi, 103, 279–292 (1983).
Jo, Y. S., Huong, D. T., Bae, K. H., Lee, M. K., and Kim, Y. H., Monoamine oxidase inhibitory coumarin fromZanthoxylum schinifolium.Planta Med., 68, 84–85 (2002).
Jung, B. S. and Shin, M. K., Encyclopedia of illustrated Korean natural drugs. Young Lim Sa, Seoul, pp 785–786 (1990).
Jung, H. J., Sok, D. E., Kim, Y. H., Min, B. S., Lee, J. P., and Bae, K. H., Potentiating effect of obacunone fromDictamnus dasycarpus on cytotoxicity of microtuble inhibitors, vincristine, vinblastine and taxol.Planta Med., 66, 74–76 (2000).
Kanamori, H., Sakamoto, I., and Mizuta M. Further study on mutagenic furoquinoline alkaloids of Dictamni Radicis Cortex: isolation of skimmianine and high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 34, 1826–1829 (1986).
Kraml, M., A rapid microfluorimetric determination of monoamine oxidase.Biochem. Pharmacol., 14, 1684–1686 (1965).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J., Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem., 193, 265–275 (1951).
Masuda, T., Muroya, Y., and Nakatani, N., 7-Hydroxycoumarin derivatives from the juice oil ofCitrus hassaku.Phytochemistry, 31, 1363–1366 (1992).
Nam, K. W., Je, K. H., Shin, Y. J., Kang, S. S., and Ma, W., Inhibitory effects of furoquinoline alkaloids fromMelicope confusa andDictamnus albus against human phosphodiesterase 5 (hPDE5A) in vitro.Arch. Pharm. Res., 28, 675–679 (2005).
Naoi, M, Matsuura, S, Parvez, H, Takahashi, T, Hirata, Y, Minami, M., and Nagatsu, T., Oxidation of N-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline into the N-methyl-isoquinolinium ion by monoamine oxidase.J. Neurochem., 52, 653–655 (1989).
Patkar, A. A., Pae, C. U., and Masand, P. S., Transdermal selegiline: the new generation of monoamine oxidase inhibitors.CNS Spectr. 11, 363–375 (2006).
Ro, J. S., Lee, S. S., Lee, K. S., and Lee, M. K., Inhibition of type A monoamine oxidase by coptisine in mouse brain.Life Sci., 70, 639–645 (2001).
Souleles, C., Flavonoids glycoside fromDictamnus albus.Planta Med., 55, 402 (1989).
Stevenson, P. C., Simmonds, M. S., Yule, M. A., Veitch, N. C., Kite, G. C., Irwin, D., and Legg, M., Insect antifeedant furanocoumarins fromTetradium daniellii.Phytochemistry, 63, 41–46 (2003).
Takeuchi, N., Fujita, T., Goto, K., Morisaki, N., Osone, N., and Tobinaga, S., Dictamnol, A new trinor-guaiane type sesquiterpene, from the roots ofDictamnus dasycarpus.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 41, 923–925 (1993).
Thanh, P. N., Jin, W. Y., Song, G. Y., Bae, K. H., and kang, S. S., Cytotoxic coumarins from the root ofAngelica dahurica.Arch. Pharm. Res., 27, 1211–1215 (2004).
Woo, W. S. and Kang, S. S., Furoquinoline alkaloids inDictamnus albus root bark.Kor. J. Pharmacog., 16, 125–128 (1985).
Woo, W. S., Lee, E. B., Kang, S. S., Shin, K. H., and Chi, H. J., Antifertility principle ofDictamnus albus root bark.Planta Med., 53, 399–401 (1987).
Yamada, M. and Yasuhara, H., Clinical pharmacology of MAO inhibitors: Safety and future.Neurotoxicology, 25, 215–221 (2004).
Youdim, M. B. and Bakhle, Y. S., Monoamine oxidase: isoforms and inhibitors in Parkinson's disease and depressive illness.Br. J. Pharmacol., 147, S287-S296 (2006).
Youdim, M. B., Edmondson, D., and Tipton, K. F., The therapeutic potential of monoamine oxidase inhibitors.Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 7, 295–309 (2006).
Zhao, W., Wolfender, J. L., Hostettmann, K., Xu, R., and Qin, Q., Antifungal alkaloids and limonoid derivatives fromDictamnus dasycarpus.Phytochemistry, 47, 7–11 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, S.H., Han, X.H., Hong, S.S. et al. Monoamine oxidase inhibitory coumarins from the aerial parts ofDictamnus albus . Arch Pharm Res 29, 1119–1124 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02969302
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02969302