Abstract
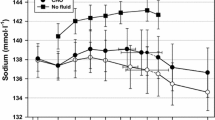
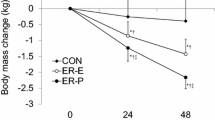
The objective of this investigation was to determine the effect of daily intake of fluid and salt supplementation (FSS) on increased urinary losses of microelements that developed during hypokinesia (decreased number of walking steps/d). The studies were performed on 30 endurance-trained male volunteers aged 23–26 yr, with an averaged maximum oxygen uptake of 65 mL/kg/min during 364 d of hypokinesia (HK). All volunteers were divided into three equal groups: Ten volunteers were placed continuously under an average of 10,000 running steps/d (14.2 km/d) (control subjects), ten volunteers subjected continuously to HK without the use of FSS (hypokinetic subjects), and ten volunteers were continuously submitted to HK and consumed daily FSS (hyperhydrated subjects). For the simulation of the hypokinetic effect the hypokinetic and hyperhydrated volunteers were kept under an average of 3,000 walking steps/d (2.7 km/d) for 364 d. Prior to their exposure to HK the volunteers were on an average of 10,000 running steps/d (14.2 km/d). During the prehypokinetic period of 60 d and during the hypokinetic period of 364 d were determined renal excretion of microelements responses of endurance-trained volunteers. In the hyperhydrated volunteers urinary excretion of iron, zinc, copper, manganese, cobalt, nickel, lead, tin, chromium, aluminum, molybdenum, and vanadium decreased, whereas in the hypokinetic volunteers it increased significantly. It was concluded that chronic hyperhydration may be used to attenuate urinary excretion of microelements in endurance-trained volunteers during prolonged restriction of muscular activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. P. Krotov,Kinetics and Regulation of Fluid-Electrolyte Metabolism in Animals and Humans During Hypokinesia, “Interkosmos” Council, Academy of Sciences USSR and Directorate of Cosmic Biology and Medicine, Ministry of Health USSR, Moscow, 1978, p. 233.
A. V. Volozhin,Pathogenesis of Disturbances of Calcium Metabolism in Mineralized Tissues During Long-Term Hypokinesia, “Interkosmos” Council, Academy of Sciences USSR and Directorate of Cosmic Biology and Medicine, Ministry of Health USSR, Moscow, 1978, p. 189.
Y. G. Zorbas, N. I. Abratov, and C. B. Stoikolescu,Urologia 3, 229–238 (1988).
Y. G. Zorbas, Y. F. Federenko, and M. N. Togawa,J. Environ. Geochem. Health 22, 333–339 (1989).
Y. G. Zorbas, Y. F. Federenko, and K. A. Naexu,Biol. Trace Element Res. (1993) (in press).
J. Durnin and M. Rahaman,Br. J. Nutr. 21, 681–689 (1967).
Y. G. Zorbas, K. A. Naexu, and Y. F. Federenko,Clin. Experimen. Pharmacol. Physiol. 19, 137–145 (1992).
Ye. A. Kovalenko and N. N. Gurovskiy,Hypokinesia, Meditsina, Moscow, 1980, p. 319.
I. V. Fedorov,Metabolism Under Hypodynamic Conditions, Izdatel'stvo Nauka Moscow, 1982, p. 254.
Y. G. Zorbas, V. R. Bobylev, and A. N. Marketi,Int. J. Rehab. Res. 12(3), 326–330 (1989).
Y. G. Zorbas, Y. F. Federenko, and M. N. Togawa,Acta Astronautica 21(8), 599–605 (1990).
Yu. M. Bala and V. M. Lifshifts,Trace Elements in the Practice of Internal Medicine, Meditsina, Voronezh, 1973, p. 240.
L. P. Bushmeleva,Biological Role of Trace Elements and Electrolytes, and Their Significance in Medicine, Meditsina, Tomsk, 1977, p. 255.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zorbas, Y.G., Federenko, Y.F. & Naexu, K.A. Urinary excretion of microelements in endurance-trained volunteers during restriction of muscular activity and chronic rehydration. Biol Trace Elem Res 40, 189–202 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02950792
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02950792