Abstract
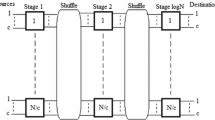
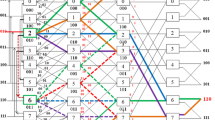
Multistage Interconnection Networks (MINs) are often used to provide interconnections in multiprocessor systems. A unique path MIN usually has lower hardware complexity and a simple control algorithm, but it lacks fault tolerance. This paper proposes a kind of multipath MINs, which are obtained by adding auxiliary links at the final stage in Quad Tree (QT) networks so that they can provide more paths between each source-destination pair, and presents their routing algorithm which is both destination tag based and adaptive. Starting with the routing tag for the minimum path between a given source-destination pair, the routing algorithm uses a set of rules to select switches and modify routing tag. In addition to trying the auxiliary link whenlink 0 andlink 1 are unavailable,link 1 will be tried whenlink 0 is unavailable. This feature distinguishing the proposed routing algorithm from that for QT networks makes better use of all the possible paths between the given source-destination pair. In the end, this paper introduces a performance index, which is calledcapacity, to compare different kinds of MINs. Comparison shows that the proposed MINs have bettercapacity than QT networks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar V P, Reddy S M. Design and analysis of fault tolerant multistage interconnection networks with low link complexity. InProc. of the 12th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, June 17–19, 1985 pp.376–386.
Goke L R, Lipovski G J. Banyan networks for partitioning multiprocessor systems. InProc. of the 1st Annual Symposium on Computer Architecture, December, 1971, pp.21–28.
Batcher K E. The flip network in STARAN. InProc. of 1980 International Conference on Parallel Processing, Aug., 1980, pp.79–80.
Crowther W, Goodhue Jet al., Performance measurements on a 128-node butterfly parallel processing. InProc. of 1985 International Conference on Parallel Processing, Aug., 1985, pp.531–540.
Pfister G F, Brantley W Cet al. The IBM research parallel processor prototype (RP3): Introduction and architecture. InProc of 1985 International Conference on Parallel Processing, Aug., 1985, pp.764–771.
Siegel H J, Siegel L Jet al. ASM: A partitionable SIMD/MIMD system for image processing and pattern recognition.IEEE Trans. on Computer, 1981, C-30: 934–947.
Gottlieb A, Grishman Ret al. The NYU ultracomputer—Designing an, MIMD shared memory parallel computer.IEEE Trans. on Computer, 1983, C-32:175–189.
Siegel H J, McMillen R J. The multistage cube: A versatile interconnection network.Computers, 1981, 14: 65–76.
Dennis J B, Boughton G Aet al. Building blocks for data flow prototypes. InProc. of the 7th Symposium on Computer Architecture, May, 1980, pp.1–8.
Sibai F N, Abonamah A. C2SC: A four-path fault-tolerant interconnection network. InProc. of the 20th International Conference on Parallel Processing, Aug., 1991, pp.698–699.
Reddy S M, Kumar V P. On fault-tolerant multistage interconnection networks. InProc. of the 1984 International Conference on Parallel Processing, Aug., 1984, pp.155–164.
Sharma N K, Sibai F N. A simulation analysis of fault and conflicts in a multicast-connected multi-path cube-based network. InProc of the 12nd International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems, June 9–12, 1992 pp.226–233.
Bansal P K, Singh Ket al. Quad tree: A cost-effective fault-tolerant multistage interconnection network. InIEEE INFOCOM’92, pp.860–866.
Tzeng N, Yew Pet al. A fault-tolerant scheme for multistage interconnection networks. InProc. of the 12nd Symposium on Computer Architecture, June 1985, pp.368–375.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant No. 69473024.
Zhou Yingquan received his B.S. degree and M.S. degree from Xiangtan University in 1983 and Chongqing University in 1988 respectively, both in computer science. In July of 1995, he obtained his Ph.D. degree in computer science from the Chinese Academy of Sciences. From 1994 to 1996, he did researches in the, Department of Electronic Engineering at the Hong Kong Polytechnic University. Before being admitted as a Ph.D. student by the Chinese Academy of Sciences in September of 1992, he worked as a lecturer in the Department of Computer Science at Xiangtan University for several years. His research interests are in the fields of computer algorithm, deisgn automation, communication software, and various aspects in fault-tolerant computing.
Min Yinghua is a Professor of computer science at Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China. He is the Chairman of the Technical Committee of Fault-Tolerant Computing, Chinese Computer Federation, and a senior member of IEEE. He serves on the editorial boards of several international journals and program committees of IEEE conferences. His research interests include circuit design and test, fault-tolerant computing, and computer system reliability.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Min, Y. A kind of Multistage Interconnection Networks with multiple paths. J. of Comput. Sci. & Technol. 11, 395–404 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02948483
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02948483