Abstract
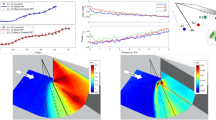
An experimental research program establishing a database of the surface pressure in swept shock wave/boundary-layer interactions is described. An equilibrium turbulent boundary-layer on a flat plate is subjected to impingement by swept planar shock waves genterated by a sharp fin. Various fin angles at 4 different freestream Mach numbers produce a variety of interaction strengths from weak to very strong. For each of different interaction cases, the surface flow patterns are obtained by a kerosene-lampblack-adhesive transparent tape technique. Surface pressures within the interactions are also measured from several streamwise row of taps connected to a computer-controlled Scanivalve system. An extensive error analysis is carried out for the experiments yielding an uncertainty of about ±3%. From these measurements, high spatial resolution surface pressure distributions for different interaction cases are obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- M :
-
Mach number
- p :
-
Surface static pressure
- R :
-
Radial distance from fin leading-edge
- VCO:
-
Virtual conical origin
- α:
-
Angle-of-attack of the fin
- β:
-
Angle with respect to incoming free-stream direction, measured from fin leading-edge
- pa :
-
Primary attachment
- peak :
-
Peak value
- ps :
-
Primary separation
- ss :
-
Secondary separation
- ui :
-
Upstream influence
- ∞:
-
Incoming freestream
- n :
-
Normal component
References
Alvi, F. S. and Settles G. S., 1990, “Structure of Swept Shock Wave/Boundary-Layer Interactions Using Conical Shadowgraphy,”AIAA Paper 90-1644.
Alvi, F. S. and Settles, G. S., 1991, “Physical Flowfield Model of the Swept Shock/Boundary-Layer Interaction Flowfield,”AIAA Paper 91-1768.
Coleman, H. W. and Steel W. G., 1989,Experimentation and Uncertainty Analysis for Engineers, John Wile & Sons.
Dolling, D. S., 1993, “Fluctuating Loads in Shock Wave/Turbulent Boundary-Layer Interactions: Tutorial and Update,”AIAA paper 93-0284.
Garg, S. and Settles, G. S., 1993, “Wall Pressure Fluctuations Beneath Swept Shock Wave/Boundary Layer Interactions,”AIAA paper 93-0384.
Gibson, B. and Dolling, D. S., “Wall Pressure Fluctuations Near Separation in a Mach 5, Sharp Fin-Induced Turbulent Interaction,”AIAA Paper 91-0646.
Hayes, J. R., 1977, “Prediction Techniques for the Characteristics of Fin Generated Three Dimensional Shock Wave Turbulent Boundary Layer Interactions,” AFFDL-TR-77-10.
Kim, K-S., Lee, Y., Alvi, F. S., Settles, G. S. and Horstman, C. C., 1991, “Laser Skin Friction Measurements and CFD Comparison of Weak-to-Strong Swept Shock/Boundary Layer Interactions,”AIAA Journal, Vol. 29, No. 10, pp. 1643–1650.
Knigit, D. and Badekas, D., 1991, “On the Quasi-Conical Flowfield Structure of the Swept Shock Wave-Turbulent Boundary-Layer Interaction,”AIAA Paper 91-1759.
Lee, Y., Settles, G. S. and Horstmann, C. C., 1994, “Heat Transfer Measurements and Computations of Swept-Shock-Wave/Boundary-Layer Interactions,”AIAA Journal, Vol. 32, No. 4, pp. 726–734.
Lu, F. K. and Settles, G. S., 1983, “Conical Similarity of Shock/Boundary-Layer Interactions Generated by Swept Fins,”AIAA Paper 83-756.
Oskam, B., Bogdonoff, S. M. and Vas, I. E., 1975, “Study of Three-Dimensional Flow Fields Generated by the Interaction of a Skewed Shock Wave with a Turbulent Boundary-Layer,” AFFDL-TR-75-21, (also seeAIAA Paper 76-336, 1976).
Settles, G. S. and Dolling, D. S., 1986, “Swept Shock Wave Boundary-Layer Interactions,” inAIAA Progress in Astronautics and Aeronautics: Tactical Missile Aerodynamics, edited by M. Hemsch and J. Nielsen, Vol. 104, pp. 297–379, AIAA, New York.
Settles, G. S. and Dollign, D. S., 1990, “Swept Shock/Boundary-Layer Interactions-Tutorial and Update,”AIAA paper 90-0375.
Token, K. H., 1974, “Heat Transfer Due to Shock Wave Turbulent Boundary Layer Interactions on High Speed Weapon System,” AFFDL-TR-74-77, Air Force Flight Dynamics Laboratory, WPAFB, Ohio.
Zheltovodov, A. A., Maksimov, A. I. and Shilein, E. K., 1987, “Development of Turbulent Separated Flows in the Vicinity of Swept Shock Waves,” edited by Kharitonov, A. M.,Institute of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics; USSR Academy of Sciences, Novosibrisk, pp. 67–91.
Zubin, M. A. and Ostapenko, N. A., 1979, “Structure of Flow in the Separation Region Resulting from Interaction of a Normal Shock Wave with a Boundary Layer in a Corner,”Izvest. Akad. Nauk S. S. S. R., Mekh. Zhid. i Gaza, No. 3, 51–58, (English translation).
Zukoski, E. E., 1967, “Turbulent Boundary layer Separation in Front of a Forward Facing Step,”AIAA Journal, Vol. 5, No. 10, pp. 1746–1753.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y., Garg, S. & Settles, G.S. Surface pressure measurements in shock wave/boundary-layer interactions. KSME International Journal 11, 164–172 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02944890
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02944890