Abstract
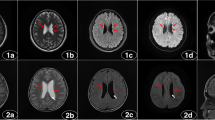
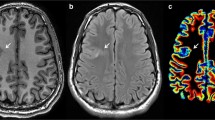
Heterotopic grey matter is an abnormality of neuronal migration that has been reported in association with refractory epilepsy. In this study we reviewed the magnetic resonance (MR) imaging records of all patients undergoing MR scanning for evaluation of intractable epilepsy and identified sixteen patients who had grey matter heterotopia. The distribution of the grey matter heterotopia was periventricular in 9 patients, laminar in 3 and was in a “band” form in 4 patients. Congenital anomalies associated with grey matter heterotopia in this study included polymicrogyria in one patient and absence of the corpus callosum in 2 patients. Grey matter heterotopia is an important MR finding in patients with intractable epilepsy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bronen, R. Epilepsy: the role of MR imaging. AJR 1992; 159: 1165–74.
Bergeron, R. T. Radiographic demonstration of cortical heterotopia. Acta Radiologica. 1969; 9: 135–39.
Mikhael, M. A., Mattar, A. G. Malformation of the cerebral cortex with heterotopia of the grey matter. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1978; 2: 291–96.
Bairaman, B., Di Chiro, G., Theodore, W. H., Holmes, M. D., Bouvart, R. H., Larsen, S. M. MR imaging and positron emission tomography of cortical heterotopias. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1985; 9(6): 1137–39.
Barkovich, A., Chuang, S., Norman, D. MR of neuronal migrational anomalies. AJNR 1987; 8: 1009–17.
Raymond, A., Fish, D. R., Stevens, J. M., Sisodiya, S. M., Alsanjari, N., Shorvon, S. D. Subependymal heterotopia: a distinct neuronal migration disorder associated with epilepsy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994; 57: 1195–1202.
Barkovitch, J., Jackson, D., Boyer, R. Band heterotopias: a newly recognized neuronal migration anomaly. Radiology 1989; 171: 455–458.
Kunziecky, R. I. Magnetic resonance imaging in developmental disorders of the cerebral cortex. Epilepsia 1994; 35.(S)6: S44–56.
Kamuro, K., Tenokuchi, Y. Familial periventricular nodular heterotopia. Brain and Development 1993; 15(3): 237–41.
Oda, T., Nagai, Y., Fujimoto, S., Sobajima, H., Kobayashai, M., Togari, H., Wada, Y. Hereditary nodular heterotopia accompanied by mega cisterna. American Journal of Genetics 1993; 47(2): 268–71.
Huttenlocher, P. R., Taravath, S., Mojtahedi, S. Periventricular heterotopia and epilepsy. Neurology 1994; 44(1): 51–55.
Smith, S., Weinstein, M., Quencer, R., Muroff, L., Stonesifer, K., Chaney, F. et al. Association of heterotopic grey matter with seizures: MR imaging. Radiology 1988; 168: 195–98.
Palmini, A., Gambardella, A., Andermann, F., Dubeau, F., DaCosta, J. C., Olivier, A. et al. Operative strategies for patients with cortical dysplastic lesions and intractable epilepsy. Epilepsia 1994; 35 (Suppl 6): S57–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, D.B.S., Brennan, P., Dwyer, A.J.O. et al. Grey matter heterotopia: An unusual association of intractable epilepsy. I.J.M.S. 166, 135–138 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02943590
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02943590