Abstract
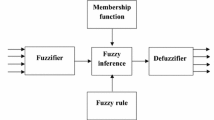
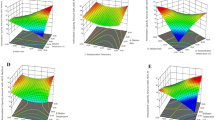
Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Fuzzy techniques are applied for the development of sugarcane juice based lime beverage. Both the techniques were compared for the adequacy of optimization and applicability in beverage industry. The vegetative clarified sugarcane juice (SCJ) was used as sugar replacer in the preparation of beverage. The specific proportions of sugarcane juice were utilized for beverage preparation using central composite rotatable design (CCRD) for the development of the process for utilization of sugarcane juice in the preparation of lime RTS beverages. It was found that sugarcane juice could replace sugar up to a level of 100% for lime beverage using RSM. The results of fuzzy technique in agreement with the RSM based experimentation results. Therefore, this technique could also be used for the optimization and development of beverage formulation. If the domain knowledge exists in the form of knowledge base, then first approximation using fuzzy modeling is suited, with the further possibility of design cycle for the development of the product using RSM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amerine, M. A., Pangborn, R. M. andRoessler, E. B. (1965). Principles of sensory evaluation of food. Academic Press Inc. New York.
AOAC (1980). Methods of Analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Washington DC.
Filmore, E. B., Kramer, A. andGerald, K. (1976). Response surface techniques In: System analysis for the food industry. Pp. 121–193. AVI Pub. Westport, Connecticut.
Jang, Roger andGulley, Ned. (1995). “Fuzzy Logic Toolbox for MATLAB, User’s Guide”, The Math Works, Inc., USA, January.
Joglckar, A. M. andMay, A. T. (1991). Product excellence through experimental design In: Food product development from concept to the market place (edited by E. Graf and I. S. Saguy). Pp. 211–230. AVI Pub. New York.
Klir George J. andYuan, Bo. (2000). “Fuzzy Sets Fuzzy Logic: Theory and Applications”, Prentice-Hall of India, New Delhi.
Kukreja, T. R., Kumar, D., Prasad, K., Chauhan, R. C. Choc, S. andKundu, P. P. (2002). Optimisation of physical and mechanical properties of rubber compounds by response surface methodology-Two component modeling using vegetable oil and carbon black.European Polymer Journal,38: 1417–1422.
Montgomery, D. C. (1984). Design and Analysis of Experiments; John Wiley. New York.
Patyra, J. andMlynek, D. M. (1996). “Fuzzy Logic: Implementation and Applications”. John Wiley & Sons Ltd. and B. G. Teubner.
Prasad, K. and Nath, N. (2002a). Mathematical modeling and optimisation of sugarcane juice level in grape beverage using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). International Journal of Food Science and Technology, Communicated for publication,
Prasad. K. andNath, N. (2002b). Effect of pre-treatments and clarificants on sugarcane juice characteristics.Asian J Chemistry. 14: 723–731.
Prasad, K. (2000). Effect of replacing sugar with sugarcane juice on quality of ready-to-serve beverage. PhD Thesis, G.B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology, Pantnagar. India.
Ranganna, S. (1986). Handbook of analysis and quality control for fruit and vegetable products. Tata McGraw - Hill Publishing Company Ltd., New Delhi.
Rcfai, M. K. (1979). Mannuals of food quality control 4. Microbiological analysis. FAO of United Nations, Rome.
Sharma, H. K., Prasad, K., Jindal, S., Sood, P. andPandey, H. (2002). Optimization of ingredients for the manufacture of soft serve ice cream (Softy) by Response Surface Methodology (RSM).International Journal of Dairy Technology. 55(4): 1–4.
Sridhar, V., Prasad, K., Choc, S. andKundu, P. P. (2001). Optimisation of physical and mechanical properties of rubber compounds by a response surface methodological approach.Journal of Applied Polymer Science. 82: 997–1005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, K., Nath, N. Comparison of sugarcane juice based beverage optimisation using response surface methodology with Fuzzy method. Sugar Tech 4, 109–115 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02942691
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02942691