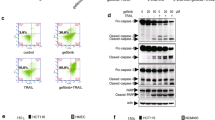
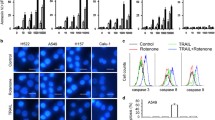
Abstract
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) has great potential for cancer treatment since it provokes cell death in most tumor cells while leaving most normal cells unscathed. Some cancers, however, show resistance to TRAIL, indicating that TRAIL alone may be insufficient for cancer therapy. Here we studied whether the apoptotic susceptibility of A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells could be modulated by inhibiting protein kinase C (PKC). We show that an inhibitor with preference for novel PKC isozymes, NPC 15437, significantly augmented TRAIL sensitivity of A549 cells, as judged by assessing cell death and mitochondrial membrane potential. Likewise, NPC 15437 also significantly potentiated the responsiveness of DAOY medulloblastoma cells to TRAIL. In contrast, an inhibitor with preference for conventional PKC isozymes, Gö6976, did not augment TRAIL sensitivity of A549 cells. To further specify the PKC isozyme responsible for TRAIL sensitization, we used a peptide inhibitor with selectivity for the novel PKC isozyme ɛ, myr-PKCɛ V1-2. The inhibition of PKCɛ resulted in a significant amplification of the cytotoxic activity of TRAIL in A549 cells. Altogether, our study provides evidence for a considerable role of PKCɛ in the apoptotic responsiveness of A549 lung cancer cells, and possibly other malignancies, to TRAIL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baader E, Toloczko A, Fuchs U, et al: Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated proliferation of tumor cells with receptor-proximal apoptosis defects. Cancer Res 65: 7888–7895, 2005.
Basu A, Lu D, Sun B, et al: Proteolytic activation of protein kinase C-epsilon by caspase-mediated processing and transduction of antiapoptotic signals. J Biol Chem 277: 41850–41856, 2002.
Basu A, Weixel KM: Comparison of protein kinase C activity and isoform expression in cisplatin-sensitive and -resistant ovarian carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 62: 457–460, 1995.
Carney DN: Lung cancer—time to move on from chemotherapy. N Engl J Med 346: 126–128, 2002.
Courage C, Budworth J, Gescher A: Comparison of ability of protein kinase C inhibitors to arrest cell growth and to alter cellular protein kinase C localisation. Br J Cancer 71: 697–704, 1995.
Ding L, Wang H, Lang W, et al: Protein kinase C-epsilon promotes survival of lung cancer cells by suppressing apoptosis through dysregulation of the mitochondrial caspase pathway. J Biol Chem 277: 35305–35313, 2002.
Fan QL, Zou WY, Song LH, et al: Synergistic antitumor activity of TRAIL combined with chemotherapeutic agents in A549 cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 55: 189–196, 2005.
Fesik SW: Promoting apoptosis as a strategy for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer 5: 876–885, 2005.
Frese S, Brunner T, Gugger M, et al: Enhancement of Apo2L/TRAIL (tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand)-induced apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines by chemotherapeutic agents without correlation to the expression level of cellular protease caspase-8 inhibitory protein. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 123: 168–174, 2002.
Fulda S, Debatin KM: Exploiting death receptor signaling pathways for tumor therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1705: 27–41, 2004.
Ganten TM, Koschny R, Sykora J, et al: Preclinical differentiation between apparently safe and potentially hepatotoxic applications of TRAIL either alone or in combination with chemotherapeutic drugs. Clin Cancer Res 12: 2640–2646, 2006.
Gillespie S, Zhang XD, Hersey P: Variable expression of protein kinase C epsilon in human melanoma cells regulates sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther 4: 668–676, 2005.
Harper N, Hughes MA, Farrow SN, et al: Protein kinase C modulates TRAIL-induced apoptosis by targeting the apical events of death receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 278: 44338–44347, 2003.
Held J, Schulze-Osthoff K: Potential and caveats of TRAIL in cancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat 4: 243–252, 2001.
Hofmann J: Protein kinase C isozymes as potential targets for anticancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4: 125–146, 2004.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin 56: 106–130, 2006.
Jin H, Yang R, Fong S, et al: Apo2 ligand/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand cooperates with chemotherapy to inhibit orthotopic lung tumor growth and improve survival. Cancer Res 64: 4900–4905, 2004.
Johnson JA, Gray MO, Chen CH, et al: A protein kinase C translocation inhibitor as an isozyme-selective antagonist of cardiac function. J Biol Chem 271: 24962–24966, 1996.
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA, Lowe SW: Apoptosis: a link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell 108: 153–164, 2002.
Kim CY, Giaccia AJ, Strulovici B, et al: Differential expression of protein kinase C epsilon protein in lung cancer cell lines by ionising radiation. Br J Cancer 66: 844–849, 1992.
Laack E, Dickgreber N, Muller T, et al: Randomized phase III study of gemcitabine and vinorelbine versus gemcitabine, vinorelbine, and cisplatin in the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: from the German and Swiss Lung Cancer Study Group. J Clin Oncol 22: 2348–2356, 2004.
LeBlanc HN, Ashkenazi A: Apo2L/TRAIL and its death and decoy receptors. Cell Death Differ 10: 66–75, 2003.
Manna SK, Aggarwal BB: All-trans-retinoic acid upregulates TNF receptors and potentiates TNF-induced activation of nuclear factors-kappaB, activated protein-1 and apoptosis in human lung cancer cells. Oncogene 19: 2110–2119, 2000.
Martiny-Baron G, Kazanietz MG, Mischak H, et al: Selective inhibition of protein kinase C isozymes by the indolocarbazole Go 6976. J Biol Chem 268: 9194–9197, 1993.
McJilton MA, Van Sikes C, Wescott GG, et al: Protein kinase Cepsilon interacts with Bax and promotes survival of human prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 22: 7958–7968, 2003.
Mitsiades N, Mitsiades CS, Poulaki V, et al: Intracellular regulation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis in human multiple myeloma cells. Blood 99: 2162–2171, 2002.
Monick M, Staber J, Thomas K, et al: Respiratory syncytial virus infection results in activation of multiple protein kinase C isoforms leading to activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Immunol 166: 2681–2687, 2001.
Odoux C, Albers A, Amoscato AA, et al: TRAIL, FasL and a blocking anti-DR5 antibody augment paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in human non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 97: 458–465, 2002.
Okhrimenko H, Lu W, Xiang C, et al: Protein kinase C-epsilon regulates the apoptosis and survival of glioma cells. Cancer Res 65: 7301–7309, 2005.
Okhrimenko H, Lu W, Xiang C, et al: Roles of tyrosine phosphorylation and cleavage of protein kinase Cdelta in its protective effect against tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 280: 23643–23652, 2005.
Pardo OE, Wellbrock C, Khanzada UK, et al: FGF-2 protects small cell lung cancer cells from apoptosis through a complex involving PKCepsilon, B-Raf and S6K2. EMBO J 25: 3078–3088, 2006.
Platzbecker U, Ward JL, Deeg HJ: Chelerythrin activates caspase-8, downregulates FLIP long and short, and overcomes resistance to tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in KG1a cells. Br J Haematol 122: 489–497, 2003.
Reed JC: Drug insight: Cancer therapy strategies based on restoration of endogenous cell death mechanisms. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 3: 388–398, 2006.
Saraiva L, Fresco P, Pinto E, et al: Isoform-selectivity of PKC inhibitors acting at the regulatory and catalytic domain of mammalian PKC-alpha, -betaI, -delta,-eta and -zeta. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 18: 475–483, 2003.
Sarker M, Ruiz-Ruiz C, Lopez-Rivas A: Activation of protein kinase C inhibits TRAIL-induced caspases activation, mitochondrial events and apoptosis in a human leukemic T cell line. Cell Death Differ 8: 172–181, 2001.
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, et al: Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 346: 92–98, 2002.
Shi RX, Ong CN, Shen HM: Protein kinase C inhibition and x-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein degradation contribute to the sensitization effect of luteolin on tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis in cancer cells. Cancer Res 65: 7815–7823, 2005.
Shimomoto H, Hasegawa Y, Nozaki Y, et al: Expression of tumor necrosis factor receptors in human lung cancer cells and normal lung tissues. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 13: 271–278, 1995.
Shinohara H, Kayagaki N, Yagita H, et al: A protective role of PKCepsilon against TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in glioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284: 1162–1167, 2001.
Sivaprasad U, Shankar E, Basu A: Downregulation of Bid is associated with PKCepsilon-mediated TRAIL resistance. Cell Death Differ 14: 851–860, 2007.
Sonnemann J, Gange J, Kumar KS, et al: Histone deacetylase inhibitors interact synergistically with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) to induce apoptosis in carcinoma cell lines. Invest New Drugs 23: 99–109, 2005.
Sonnemann J, Gekeler V, Sagrauske A, et al: Down-regulation of protein kinase Ceta potentiates the cytotoxic effects of exogenous tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 3: 773–781, 2004.
Spierings DC, de Vries EG, Timens W, et al: Expression of TRAIL and TRAIL death receptors in stage III non-small cell lung cancer tumors. Clin Cancer Res 9: 3397–3405, 2003.
Sullivan JP, Connor JR, Shearer BG, et al: 2,6-Diamino-N-([1-(1-oxotridecyl)-2-piperidinyl] methyl)hexanamide (NPC 15437): a novel inhibitor of protein kinase C interacting at the regulatory domain. Mol Pharmacol 41: 38–44, 1992.
Tillman DM, Izeradjene K, Szucs KS, et al: Rottlerin sensitizes colon carcinoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis via uncoupling of the mitochondria independent of protein kinase C. Cancer Res 63: 5118–5125, 2003.
Trauzold A, Wermann H, Arlt A, et al: CD95 and TRAIL receptor-mediated activation of protein kinase C and NF-kappaB contributes to apoptosis resistance in ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Oncogene 20: 4258–4269, 2001.
van Valen F, Fulda S, Schafer KL, et al: Selective and nonselective toxicity of TRAIL/Apo2L combined with chemotherapy in human bone tumour cells vs. normal human cells. Int J Cancer 107: 929–940, 2003.
Wu D, Thakore CU, Wescott GG, et al: Integrin signaling links protein kinase Cepsilon to the protein kinase B/Akt survival pathway in recurrent prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 23: 8659–8672, 2004.
Zhang J, Liu N, Zhang J, et al: PKCdelta protects human breast tumor MCF-7 cells against tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis. J Cell Biochem 96: 522–532, 2005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from the “Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung, Neustadt/Donau”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Felber, M., Sonnemann, J. & Beck, J.F. Inhibition of novel protein kinase Cɛ augments TRAIL-induced cell death in A549 lung cancer cells. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 13, 295–301 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02940308
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02940308