Summary
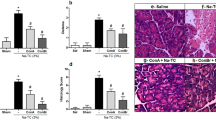
We examined the ability of a highly potent synthetic protease inhibitor, nafamostat mesilate (FUT-175), to protect the rat pancreas against AP induced by a supramaximal dose of caerulein (CR). Rats received a 6-h, continuous intravenous (iv) infusion of either CR alone or CR + a 6-h infusion of either 2.5, 5.0, 10.0, 25.0, or 50.0 mg of FUT-175/kg/h. Pancreas weights and serum chymotrypsinogen concentrations were significantly elevated by approximately 85 and 75%, respectively, over values in saline infused rats. Pancreas weights in rats treated with CR+ FUT-175 at doses from 2.5–25.0 mg/kg/h were significantly reduced by approximately 20% compared to rats given CR along, and histology showed a reduction in the extent and size of acinar cell vacuolization and reduced interstitial edema compared to rats treated with CR alone. Serum chymotrypsinogen concentrations in rats treated with CR and either 5.0 or 10.0 mg of FUT-175/kg/h were significantly lower than in rats given CR alone. Significant mortality occurred in rats infused with FUT-175 at doses of either 25.0 or 50.0 mg of FUT-175/kg/h. These data indicate that serine proteases appear to be involved in the pathogenesis of CR induced AP in rats and that FUT-175 administered in low doses (2.5–10.0 mg/kg/h) provides significant protection against this form of pancreatitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scheele G. Biochemical concepts and markers in acute pancreatitis. Gyr K, Singer M, Singer M, Sarles H. eds., Pancreatitis: concepts and classification. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1984: 119–125.
Adler G, Kern HF, Scheele GA. Experimental models and concepts in acute pancreatitis. Go VLW, Gardner JD, Brooks FP, Lebenthal E, DiMagno EP, Scheele GA. eds., The exocrine pancreas: biology, pathobiology, and diseases. Raven Press, New York, 1986: 407–421.
Adler G, Hupp T, Kern HF. Alteration of membrane fusion as a cause of acute pancreatitis in the rat. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1982; 27: 993–1002.
Watanabe O, Baccino FM, Steer ML, Meldolesi J. Effects of supramaximal caerulein stimulation on the ultrastructure of the rat pancreatic acinar cell: early morphological changes during development of experimental pancreatitis. Amer. J. Physiol. 1984; 246; G457-G467.
Steer ML, Meldolesi J, Figarella. C. Pancreatitis: the role of lysosomes. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1984; 29; 934–938.
Adler G, Hahn C, Kern HF, Rao KN. Cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in rats: increased lysosomal enzyme activity and autophagocytosis. Digestion 1985; 32: 10–18.
Steer ML, Meldolesi J. The cell biology of experimental pancreatitis. New EngL J. Med. 1987; 316: 144–150.
Wisner JR Jr., Renner IG, Grendell JH, Niederau C, Ferrell LD. Gabexate mesilate (FOY) protects against ceruletide-induced acute pancreatitis in the rat. Pancreas 1987; 2: 181–186.
Iwaki M, Ozeki M, Sato T, Suzuki K, Motoyoshi A, Suzuki S, Fujita S, Aoyama T. Pharmacological studies of FUT-175, nafamstat mesilate. II. Effects on experimental acute pancreatitis. Folia Pharmacol. Japon. 1984; 84: 363–372.
Iwaki M, Ino Y, Motoyoshi A, Ozeki M, Sato T, Kurumi M, Aoyama Y. Pharmacological studies of FUT-175, nafamostat mesilate. V. Effects on the pancreatic enzymes and experimental acute pancreatitis in rats. Japan. J. Pharmacol. 1986; 41: 155–162.
Hummel BC. A modified spectrophotometric determination of chymotrypsin, trypsin and thrombin. Can. J. Biochem. 1959; 37: 1393–1399.
Wisner JR Jr., McLaughlin RE, Rich KA, Ozawa S, Renner IG. Effects of L-364,718, a new cholecystokinin receptor antagonist, on camostate-induced growth of the rate pancreas. Gastroenterol. 1988; 94: 109–113.
Adler HL, Roessler EB. Introduction to probability and statistics. 4th ed., W. H. Freeman, San Francisco, 1968.
Steele RGD, Torie JH. Principles and procedures of statistics. McGraw-Hill, New York, 1960.
Nakahara H. Inhibitory effects of aprotinin and gabexate mesilate on human plasma kallikrein. Arzneimittelforsch. 1983; 33: 969–971.
Aoyama T, Ino Y, Ozeki M, Oda M, Sato T, Koshiyama Y, Suzuki S, Fujita M. Pharmacological studies of FUT-175, nafamstat mesilate. I. Inhibition of protease activity ofin vitro andin vivo experiments. Japan. J. Pharmacol. 1984; 35: 203–227.
Fujii S, Hitomi Y. New synthetic inhibitors of C1r, C1-esterase, thrombin, kallikrein and trypsin. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1981; 661: 342–345.
Fishbein R, Murphy GP, Wilder RJ. The pleuropulmonary manifestations of pancreatitis. Dis. Chest 1962; 41: 392–397.
Carey LC. Extra-abdominal manifestations of acute pancreatitis. Surgery 1979; 86: 337–342.
Onstad GR, Bubrick M P. Pathophysiology. Toledo-Pereya LH. ed., The pancreas: principles and medical and surgical practice. Wiley, New York, 1985: 97–116.
Renner IG, Savage WT, Pantoja JL, Renner VJ. Death due to acute pancreatitis: a retrospective analysis of 405 autopsy cases. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1985; 30: 1005–1018.
Sato K, Watanabe K, Terasawa K, Yokomoto Y, Nagai N, Otani K. Acute toxicity studies of FUT-175 (Nafamstat mesilate) in mice and rats. Principle and Clinics (Japan.) 1984; 18: 227–234.
Goke B, Stockmann, Muller R, Lankisch PG, Creutzfeldt W. Effect of a specific serine protease inhibitor on the rat pancreas: systemic administration of camostate and exocrine pancreatic secretion. Digestion 1984; 30: 171–178.
Adler G, Rausch U, Weidenbach F, Arnold R, Kern HF. General and selective inhibition of pancreatic enzyme discharge using a proteinase inhibitor (FOY-305). Klin. Wochenschr. 1984; 62: 406–411.
Muramatu M, Fujii S. Inhibitory effects of omega-guanidino acid esters on trypsin, plasmin, plasma kallikrein and thrombin. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1972; 268: 221–224.
Tamura Y, Hirado M, Okamura K, Minato Y, Fujii S. Synthetic inhibitors of trypsin, plasmin, kallikrein, thrombin, C(1r)and C(1)-esterase. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1977; 484: 417–422.
Takasugi S, Toki N. Inhibitory effects of native and synthetic protease inhibitors on plasma proteases in acute pancreatitis. Hiroshima J. Med. Sci. 1980; 29: 189–194.
Guice KS, Miller DE, Oldham KT, Townsend CM, Thompson JC. Superoxide dismutase and catalase: a possible role in established pancreatitis. Amer. J. Surg. 1986; 151: 163–169.
Wisner JR Jr., Renner IG. Allopurinol attenuates caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in the rat. Gut 1988; 29: 926–929.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wisner, J.R., Ozawa, S. & Renner, I.G. The effects of nafamostat mesilate (FUT-175) on caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in the rat. Int J Pancreatol 4, 383–390 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02938474
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02938474