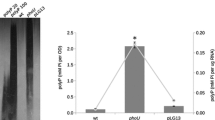
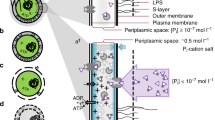
Abstract
Phosphorus (P) is an essential constituent in all types of living organisms. Bacteria, which use inorganic phosphate (Pi), as the preferred P source, have evolved complex systems to survive during Pi starvation conditions. Recently, we found thatPseudomonas aeruginosa, a monoflagellated, obligately aerobic bacterium, is attracted to Pi. The evidence that the chemotactic response to Pi (Pi taxis) was observed only with cells grown in Pi-limiting medium suggests that Pi taxis plays an important role in scavenging Pi residues under conditions of Pi starvation. Many bacteria also exhibit rapid and extensive accumulation of polyphosphate (polyP), when Pi is added to cells previously subjected to Pi starvation stress. Since polyP can serve as a P source during Pi starvation conditions, it is likely that polyP accumulation is a protective mechanism for survival during Pi starvation. In the present review, we summarize our current knowledge on regulation of bacterial Pi taxis and polyP accumulation in response to Pi starvation stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama M, Crooke E and Kornberg A 1992 The polyphosphate kinase gene ofEscherichia coli;J. Biol. Chem. 267 22556–22561
Armitage J P 1993 Methylation-independent behavioral responses in bacteria; inSignal transduction (eds) J Kurjan and B L Taylor. (San Diego: Academic Press) pp 43–65
Chet I and Mitchell R 1976 Ecological aspects of microbial chemotactic behavior;Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 30 221–239
Geissdorfer W, Frosch S C, Haspel G, Ehrt S and Hillen W 1995 Two genes encoding proteins with similarities to rubredoxin and rubredoxin reductase are required for conversion of dodecane to lauric acid inAcinetobacter calcoaceticus;Microbiology 141 1425–1432
Goldberg J B and Ohman D E 1987 Construction and characterization ofPseudomonas aeruginosa algB mutants: role of AlgB in high-level production of alginate;J. Bacteriol. 169 1593–1602
Griffin J B, Davidian N M and Penniall R 1965 Studies of phosphorus metabolism by isolated nucleic VII Identification of polyphosphate as a product;J. Biol. Chem. 240 4427–4434
Hammond A E 1971 Phosphate replacements: problems with the washday miracles;Science 172 361–364
Hancock R E W, Poole K and Benz R 1982 Outer membrane protein P ofPseudomonas aeruginosa: regulation by phosphate deficiency and formation of small anion-specific channels in lipid bilayer membranes;J. Bacteriol. 150 730–738
Hardoyo K Yamada, Muramatsu A, Anbe Y, Kato J and Ohtake H 1994a Genetic engineering of polyphosphate accumulation inEscherichia coli; inPhosphate in microorganisms: Cellular and molecular biology (eds) A Torriani-Gorni, E Yagil and S Silver (Washington DC: American Society for Microbiology) pp 209–214
Hardoyo K Yamada, Shinjo H, Kato J and Ohtake H 1994b Production and release of polyphosphate by a genetically engineered strain ofEscherichia coli;Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60 3468–3490
Harold F M 1963 Accumulation of inorganic polyphosphate inAerobacter aerogenes. I. Relationship to growth and nucleic acid synthesis;J. Bacteriol. 86 216–221
Harold F M 1966 Inorganic polyphosphates in biology: Structure, metabolism, and function;Bacteriol. Rev. 30 772–794
Harold F M and Harold R L 1965 Degradation of inorganic polyphosphate in mutants ofAerobacter aerogenes;J. Bacteriol. 89 1262–1270
Harwood C, Rivelli M and Ornston L N 1984 Aromatic acids and chemoattractants forPseudomonas putida;J. Bacteriol. 160 622–628
Holloway B W, Krishnapillai V and Morgan A F 1979 Chromosomal genetics ofPseudomonas;Microbiol. Rev. 43 73–102
Higgins C F 1992 ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man;Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 8 67–113
Kaneko T, Sato S, Kotani h, Tanaka A, Asamizu E, Nakamura Y, Miyajima N, Hirosawa M, Sugiura M, Sasamoto S, Kimura T, Hosouchi T, Matsuno A, Muraki A, Nakazaki N, Naruo K, Okumura S, Shimpo S, Takeuchi C, Wada T, Watanabe A, Yamada M, Yasuda M and Tabata S 1996 Sequence analysis of the genome of the unicellular cyanobacteriumSynechocystis sp strain PCC6803. II. Sequence determination of the entire genome and assignment of potential protein-coding regions (supplement);DNA Res. 30 185–209
Kato J, Ito A, Nikata T and Ohtake H 1992 Phosphate taxis inPseudomonas aeruginosa;J. Bacteriol. 174 5149–5151
Kato J, Yamada K, Muramatsu A, Hardoyo and Ohtake H 1993a Genetic improvement ofEscherichia coli for the enhanced biological removal of phhosphate;Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59 3744–3749
Kato J, Yamamoto T, Yamada Y and Ohtake H 1993b Cloning, sequence and characterization of the polyphosphate kinase-encoding gene (ppk) ofKlebsiella aerogenes;Gene 137 237–242
Kato J, Sakai Y, Nikata T and Ohtake H 1994a Cloning and characterization of aPseudomonas aeruginosa gene involved in the negative regulation of phosphate taxis;J. Bacteriol. 176 5874–5877
Kato J, Sakai Y, Nikata T, Masduki A and Ohtake H 1994b Phosphate taxis and its regulation inPseudomonas aeruginosa; inPhosphate in microorganisms: cellular and molecular biology (eds) A Torriani-Gorini, E Yagil and S Silver (Washington DC: American Society for Microbiology) pp 315–317
Kornberg A 1995 Inorganic polyphosphate: A molecular fossil come to life;J. Bacteriol. 177 498–505
Kulaev I S 1975 Biochemistry of inorganic polyphosphates;Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 73 131–158
Kuroda A, Kumano T, Taguchi K, Nikata T, Kato J and Ohtake H 1995 Molecular cloning and characterization of a chemotactic transducer gene inPseudomonas aeruginosa;J. Bacteriol. 177 7019–7025
Kuroda A and Kornberg A 1997 Guanosine tetra- and pentaphosphate promote accumulation of inorganic polyphosphate inEscherichia coli;J. Biol. Chem. 272 21240–21243
Kusaka K, Shibata K, Kuroda A, Kato J and Ohtake H 1997 Isolation and characterization ofEnterobacter cloacae mutants which are defective in chemotaxis toward inorganic phosphate;J. Bacteriol. 179 6192–6195
Macnab R M 1996 Flagella and motility, inEscherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: cellular and molecular biology, (eds) F C Neidhardt, R Curtiss III, J L Ingraham, E C C Lin, K B Low, B Magasanik, W S Reznikoff, M Riley, M Schaechter and H E Umbarger (Washington DC: American Society for Microbiology) 2nd edition, pp 123–145
Makino K, Shinagawa H, Amemura M and Nakata A 1986 Nucleotide sequence of thephoB gene, the positive regulatory gene for the phosphate regulon ofEscherichia coli K12;J. Mol. Biol. 190 37–44
Masduki A, Nakamura J, Ohga T, Umezaki R, Kato J and Ohtake H 1995 Isolation and characterization of chemotaxis mutants and genes ofPseudomonas aeruginosa;J. Bacteriol. 177 948–952
Nikata T, Sumida K, Kato J and Ohtake H 1992 Rapid method for analyzing bacterial behavioral responses to chemical stimuli;Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58 2250–2254
Nikata T, Sakai Y, Shibata K, Kato J, Kuroda A and Ohtake H 1996 Molecular analysis of the phosphate-specific transport (pst) operon ofPseudomonas aeruginosa;Mol. Gen. Genet. 250 692–698
Ohtake H, Takahashi K, Tsuzuki Y and Toda K 1985 Uptake and release of phosphate by a pure culture ofAcinetobacter calcoaceticus;Water Res. 19 1587–1594
Ohtake H, Kato J, Kuroda A, Taguchi K and Sakai Y 1996 Chemotactic signal transduction network inPseudomonas aeruginosa inPseudomonas: Molecular biology and biotechnology (eds) T Nakazawa, K Furukawa, D Haas and S Silver (Washington DC: American Society for Microbiology) pp 188–194
Stewart R C and Dahlquist F W 1987 Molecular components of bacterial chemotaxis;Chem. Rev. 87 997–1025
Stinson M W, Cohen M A and Merrick J M 1977 Purification and properties of the periplasmic glusose-binding protein ofPseudomanas aeruginosa;J. Bacteriol. 131 672–681
Stock J B and Surette M G 1996 Chemotaxis; inEscherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: cellular and molecular biology (eds) F C Neidhardt, R Curtiss III, J L Ingraham, E C C Lin, K B Low, B Magasanik, W S Reznikoff, M Riley, M Schaechter and H E Umbarger (Washington DC: American Society for Microbiology) 2nd edition, pp 1103–1129
Taguchi K, Fukutomi H, Kuroda A, Kato J and Ohtake H 1997 Genetic identification of chemotactic transducers for amino acids inPseudomonas aeruginosa;Microbiology 143 3223–3229
Tinsley C R and Gotschlich E C 1995 Cloning and characterization of the meingococcal polyphosphate kinase gene: production of polyphosphate synthesis mutants;Infect. Immun. 63 1624–1630
Tsuda M, Miyazaki H and Nakazawa T 1995 Genetic mapping of genes involved in pyoverdin production inPseudomonas aeruginosa;J. Bacteriol. 177 423–431
Vieira J and Messing J 1987. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA;Methods Enzymol. 153 3–11
Wanner B L 1996 Phosphorus assimilation and control of the phosphate regulon; inEscherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: cellullar and molecular biology (eds) F C Neidhardt, R Curtiss III, J L Ingraham, E C C Lin, K B Low, B Magasanik, W S Reznikoff, M Riley, M Schaechter and H E Umbarger (Washington DC: American Society for Microbiology) 2nd edition, pp 1357–1381
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohtake, H., Kato, J., Kuroda, A. et al. Regulation of bacterial phosphate taxis and polyphosphate accumulation in response to phosphate starvation stress. J. Biosci. 23, 491–499 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02936143
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02936143