Abstract
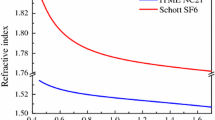
We propose a simple, highly sensitive fiber-optic autocollimation method for refractive-index dispersion measurement of solid-state and liquid bulk optical materials using a double-pass fiber Raman laser with Littrow-prism-tuned emission. The optical fiber is a key element of the scheme and serves simultaneously as a point laser source for the test, as a highly sensitive point receiver (or spatial filter) of the autocollimation backreflectance signal and as a medium for nonlinear frequency conversion and generation of a broadband continuum spectrum. When the Raman medium is a graded-index multimode fiber with powerful pumping (over 100 kW) using the second harmonic of a Q-switched Nd:YAG laser (λp=532nm), we obtain widely tunable (0.54-1.01 μm) generation in both the visible and near-IR ranges. The results obtained in the refractive-index dispersion measurements are fitted to the Sellmeier dispersion equation and the standard deviation of the experimental data from the analytical curve does not exceed 5x10-5.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Tropf, M. Thomas and T. Harris:Handbook of Optics, ed. M. Bass (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1995) Vol. 2, Chap. 33, p. 33. 1.
P. Shaffer: Appl. Opt.10 (1971) 1034.
S. Mitachi and T. Miyashita: Appl. Opt.22 (1983) 2419.
C. Carniglia, K. Schrader, P. O’Connell and S. Tuenge: Appl. Opt.28 (1989) 2902.
O. Stavroudis and L. Sutton: J. Opt. Soc. Am.51 (1961) 368.
B. Tatian: Appl. Opt.23 (1984) 4477.
G. Ghosh, M. Endo and T. Iwasaki: J. Lightwave Technol.12 (1994) 1338.
J. Dakin and B. Culshaw eds.:Optical Fiber Sensors: Principles and Components (Artech House, Dedham, MA, 1988) Chap. 1, p. 1.
E. Udd: Rev. Sci. Instrum.66 (1995) 4015.
Z. Zhou and F. Liu: J. Opt. Soc. Am. A8 (1991) 322.
I. Ilev: Appl. Opt.34 (1995) 1741.
I. Ilev: Opt. Commun.119 (1995) 513.
G. Agrawal:Nonlinear Fiber Optics (Academic Press, London, 1989) Chap. 8, p. 218.
C. Lin: J. Lightwave Technol.LT-4 (1986) 1103.
L. Cohen and C. Lin: IEEE I. Quantum Electron.QE-14 (1978) 855.
I. Ilev, H. Kumagai, K. Toyoda and I. Koprinkov: Appl. Opt.35 (1996) 2548.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ilev, I.K., Kumagai, H. & Toyoda, K. Refractive-index dispersion measurement of bulk optical materials using a fiber raman laser widely tunable in the visible and near-infrared. Optical Review 4, A61–A64 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02935993
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02935993