Abstract
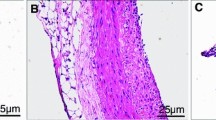
Objective: To evaluate the possibility of Salvia Miltiorrhiza (SM) on the prevention of restenosis, the authors investigated the effects of SM on the intimal thickening of air-injured carotid artery of rats, and examined the effects of SM on the proliferation of rabbit aortic median smooth muscle cells (SMC) cultivated in vitro.Methods: Artery injury model of 17 rats about 4 months old was established by Fishman air-dry method. Fourteen days after operation, the maximal artery intimal and medial thickness of the control and SM group were measured on the image analysis system. Using cell counting and thymidine (3H-TdR) up-take method, the authors also examined the effects of SM on the proliferation of aortic median SMC from 4 rabbits.Results: SM inhibited the proliferation and3H-TdR up-take of SMC in a dose-dependent manner in vitro (P < 0.05 or 0.01 vs. control). It also inhibited the intimal thickening of rat arteries after deendothelialization. The maximal intimal thickness of the SM group was much thinner than that of the control (15.22 ± 2.19 μm vs. 80.17 ± 23.49 μm,P < 0.01).Conclusions: The study raises the possibility that SM can be used to prevent clinical restenosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gruentzig AR, Senning A, Siegenthaler WE. Nonoperative dilation of coronary artery stenosis: Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. N Engl Med 1979; 301: 61–68.
Holmes DR Jr, Viliestra RE, Smith HC, et al. Restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PT-CA): A report from the PTCA registry of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Am J Cardiol 1984; 53 (Suppl.):71c-81c.
Fishman JA, Ryan GB, Karnovsky MJ. Endothelial regeneration in the rat carotid artery and the significance of endothelial denudation in the pathogenesis of myointimal thickening. Lab Invest 1975; 32: 339–351.
Ohnishi H, Yamaguchi K, Shimada S, et al. An evidence for “response to injury” hypothesis. Life Sci 1982; 31: 2595–2602.
Lungergan C, Foegh ML, Vargas R, et al. Inhibiting of myointimal proliferation of the rat carotid artery by the peptide, angiopeptin and BIM 23034. Atherosclerosis 1989; 80: 49–55.
Muller DWM, Ellis SG, Topol EJ. Experimental models of coronary artery restenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 1991; 19: 418–432.
Liu, MW. Roubin GS, King SB. Restenosis after coronary angioplasty: Potential biologic determinants and role of intimal hyperplasia. Circulation 1989; 79: 1374–1387.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, XM., Lu, ZY. & Wang, DW. Experimental study of Salvia Miltiorrhiza on the prevention of restenosis after angioplasty. CJIM 3, 131–134 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02935372
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02935372