Abstract
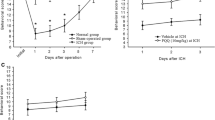
Objective: To observe the effect of Qingkailing (QKL) on brain damage induced by glutamate, in order to seek for effective drugs for antagonizing neurotoxicity of glutamate.Methods:The number and morphological metrology of neurocytes in cerebral cortex and hippocampus were detected by MIAS-300 image analyser, electron microscope and immunohistochemical methods.Results: QKL could alleviate the glutamate induced accumulation of water and sodium in brain tissue, relieve the metrological and structural damage of cerebral cells in cortex and hippocampus, reduce the percentage of c-fos positive cell in brain.Conclusion: QKL could protect brain damage induced by glutamate, which might be related to the inhibition of QKL on the enhancement of cfos gene expression induced by glutamate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yeu Sj. The excitatory neurotoxicity induced by glutamate and the damage of central nerve system. Foreign Medical Sciences 1994;21(4):205–208.
Yue Sj, Luo Zq, Yu Pl, et al. The protective effect of QKL on the excitatory neurotoxicity of glutamate. J Beijing Uni of TCM 1998;21(4):32–33.
Cheung Ns, Pascoe Cj, Giardina Sf, et al. Micromolar Lglutamate induces extensive apoptosis in an apoptotic-necrotic continuum of insult-dependent, excitotoxic injury in cultured cortical neurons. Neuropharmacology, 1998; (10)37:10–11, 1419-1429.
Yang Jh. Clinical application of QKL injection. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine. 1994;16(12):20–21.
Jiang Yf, Zhu Lq, Li Kl, et al. The protective effect of Xingnao Jianshen capsule, Zhongfeng Naodeping, Qingkailing on hippocampal neurocytes in hemorrhagic apoplexy. J Beijing Uni of TCM 1996; 19(3):33–35.
Liu T, Meng Pj, Shen Fg, et al. The effect of Angong Niuhuang pills on glutamate neurotoxicity induced by cerebrospinal lactic dehydrogenase, lactic dehydrogenase of the cerebral tissue in rabbits. Jiangsu J TCM. 1987;6:33–35.
Tanaka S, Kiuchi Y, Numazawa S, et al. Changes in glutamate receptors, c-fos mRNA expression and activator protein-1 (AP-l)DNA binding activity in the brain of phenobarbital-dependent and -withdrawn rats. Brain Research 1997,756: 35–45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, SJ., Yu, PL., Luo, ZQ. et al. Experimental study of protective effect of Qingkailing ( )on brain damage induced by glutamate)on brain damage induced by glutamate.
CJIM 7, 112–116 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02935016
)on brain damage induced by glutamate)on brain damage induced by glutamate.
CJIM 7, 112–116 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02935016
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02935016