Abstract
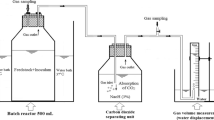
Pretreatment under mild conditions in the presence of water (solvolysis) or aqueous orthophosphoric acid (phosphorolysis) was used to increase the nutritional value of sugar cane bagasse for cattle feeding. The best pretreatment conditions were defined as those in which the highestin situ degradability rates (ruminal digestion) were achieved with the least energy consumption and/or production of inhibitory products. Heating sugar cane bagasse up to 197°C (13.5 atm) at a 4∶1 (w/w) water ratio was shown to be a compromised condition for solvolysis, as higher temperatures would require more energy consumption without adding too much to the already high 60% ruminal degradability of the residue in relation to its dry weight. These rates of degradability were shown to be further enhanced to almost 70% by adding 2.9% (w/w) orthophosphoric acid as an acid catalyst. A mathematical treatment of the kinetic data describing ruminal digestion of each of the pretreated residues was also developed in this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramos, L. P. and Saddler, J. N. (1994), ACS Symp, Series (in press).
Castro, F. B., Hotten, P. M., and Orskov, E. R. (1993)Animal Feed Sci. Technol. 42, 39–53.
Castro, F. B., Hotten, P. M., and Orskov, E. R. (1993)Animal Feed Sci. Technol. 42, 55–67.
Parisi, F. (1989), inAdvances in Biochemical Engineering and Biotechnology, vol. 38, Fiechter, A., ed., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 53–87.
Walseth, C. S. (1952)Tappi 35, 228–233.
Fontana, J. D., Correa, J. B. C., Duarte, J. H., Barbosa, A. M., and Blumel, M. (1984)Biotechnol. Bioeng. Symp. 14, 175–184.
Goering, H. K. and Van Soest P. J. (1970)USDA Agric. Handbook 379. US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC.
Krampton, E. W. and Maynard, L. A. (1938),J. Nutr. 15, 383–395.
Ramos, L. P., Breuil, C., and Saddler, J. N. (1992),Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 34/35, 37–48.
Fontana, J. D., Gebara, M., Blumel, M., and Schneider, H. (1988)Methods Enzymol. 160, 560–571.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Ribers, P. A., and Smith, F. (1956),Anal. Chem. 28, 350–356.
Nelson, N. A. (1944),J. Biol. Chem. 153, 375–380.
Somogyi, M. (1945),J. Biol. Chem. 160, 61–68.
Mehrez, A. Z. and Orskov, E. R. (1977),J. Agric. Sci. 88, 645–650.
Nocek, J. E. (1988),J. Animal Sci. 71, 2051–2069.
Orskov, E. R. and MacDonald, I. (1979),J. Agric. Sci. 92, 499–503.
Baumgardt, B. R., Taylor, M. W., and Cason, J. L. (1962),J. Dairy Sci.,45, 62–68.
Dekker, R. F. H. and Wallis, A. F. A. (1983),Biotechnol. Bioeng. 25, 3027–3048.
Saddler, J. N., Ramos, L. P., and Breuil, C. (1993) inBioconversion of Forest and Agricultural Plant Wastes, Saddler, J. N., ed. C. A. B. International, London, pp. 73–92.
Hart, M. R., Walker, H. G., Graham, R. P. Jr, Graham, P. J., Hanni, P. J., Brown, H., and Kohler, G. O. (1981)J. Animal Sci. 51, 402–408.
Saddler, J. N., Brownell, H. H., Clermont, L. P., and Levitin, N. (1982),Biotechnol. Bioeng. 24, 1389–1402.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fontana, J.D., Ramos, L.P. & Deschamps, F.C. Pretreated sugar cane bagasse as a model for cattle feeding. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 51, 105–116 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02933415
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02933415