Abstract
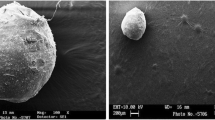
We studied the pH-sensitive indomethacin (IND) delivery system using pullulan. Hydrophobic pullulan acetate was prepared by chemical modification of hydrophilic pullulan and pullulan acetate microsphere was made by a solvent evaporation method. The size of microspheres was below 5 μm, and the drug loading efficiencies of microspheres were approximately 78 and 65% at the initial amount of drug 40 and 80 mg, respectively. The microsphere showed pH-sensitive swelling behavior in PBS buffer. After 15 hrs, the swelling of the microsphere at pH 7.4 was approximately 20 times greater than that at pH1.2. The pH of the medium significantly influenced on thein vitro release rate. The released amount of drug at pH 7.2 was approximately 90 times greater than that at pH 1.2. The shape of microspheres at pH 1.2 were maintained sphere forms, but at pH 7.4 were disintegrated. The pH-sensitive IND release pattern was due both to the pH-sensitive diffusion of IND from the microspheres and to the release of the drug from the surface which underwent disintegration after swelling, due to the chemical composition of the microspheres and the pH of the release media.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Langer, R. (1990) New methods of drug delivery,Science, 249: 1527–1533.
Hoffman, A. S., A. Afrassiabi, and A. C. Dong (1986) Thermally reversible hydrogels: II. Delivery and selective release of substances from aqueous solution.J. Control. Release 4: 213–222.
Siegel, R. A. and B. A. Firestone (1988) pH-dependent equilibrium swelling properties of hydrophobic polyelectrolyte copolymer gels.Macromolecules 21: 3254–3259.
Kwon, I. G., Y. H. Bae, T. Okano, B. Berner, and S. W. Kim (1990) Stimuli sensitive polymers for drug dolivery systems,Macromol. Chem. Macro. Symp. 33: 265–277.
Kuhn, W., B. Haritary, A. Katchalsky, and H. Eisenberg (1950) Reversible dilation and contraction by changing the state of ionization of high-polymer acid network.Nature 165: 414–418.
Dong, L., Q. Yan, and A. S. Hoffman (1994) Controlled release of amylase from thermal and pH-sensitive, macroporous hydrogel,J. Control. Release 28: 143–152.
Sugawara, S., T. Imai, and M. Otagiri (1994) The controlled release of prednisolone using alginate gel.Pharm. Res. 11: 272–277.
Yuk, S. H., S. H. Cho, and H. B. Lee (1995) pH-sensitive drug delivery system using O/W emulsion.J. Control. Release 37: 69–74.
Laakso, R. and K. Paulamaki (1984) Release of IND from ethyl cellulose film- coating granules and multiple unit tablets.Acta Pharm. Fenn. 93: 193–200.
Santucci, E., F. Alhaique, M. Carafa, T. Coviello, E. Murtas, and F. M. Riccieri (1996) Gellan for the formulation of sustained delivery beads.J. Control. Release 42: 157–164.
Catley, B. J. (1972) Pullulan elaboration, an inducible system ofPullularia pullulans, FEBS Lett. 20: 174–176.
Zajic J. E. and A. LeDuy (1973) Flocculant and chemical properties of a polysaccharide fromPullularia pullulans.Appl. Microbial. 25: 628–635.
LeDuy, A. and J. J. Yarmoff (1983) Enhanced production of pullulan from lactose by adaptation and by mixed culture techniques.Biotechnol. Lett. 5: 49–54.
Motozato, Y., H. Ihara, T. Tomoda, and C. Hirayama (1986) Preperation and gel permeation chromatographic properties of pullulan sphere.J. Chromatography 355: 434–437.
Conn, E. E. and P. K. Stumpf (1979) Outlines of Biochemistry.John Wiley and Sons IND 4: 79.
La, S. B., Okano, T. and K. Kataoka (1996) Preparation and characterization of the micelle-forming polymeric drug indomethacin-incorporated poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(β-benzyl L-aspartate) block copolymer micelles.J. Pharm. Sci. 85: 85–90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Na, K., Jeong, YI. & Lee, KY. Release of indomethacin from pH-sensitive pullulan acetate microsphere. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2, 48–52 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932463
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932463