Abstract
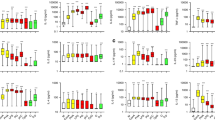
Testing of cytokine levels in colostrum, cord blood and amniotic fluid of healthy and allergic mothers and their newborns (using protein microarrays and quantitative analysis by ELISA) revealed differences in the levels of IL-5, IL-10, TGF-β, TNF-α, EGF and eotaxin between healthy and allergic groups. Significantly higher concentration of IL-5 and IL-10 in the colostrum of allergic mothers and cord blood of their children and also tendency to a higher level of IL-4 found at allergic mothers and their children (but without statistical significance) indicate a bias to TH2 response in this group. The higher level of TGF-β in the colostrum of healthy mothers should be involved in beneficial immunological tuning of their children including enhanced IgA formation and better intestine maturation. In amniotic fluid, concentration of TGF-β was higher in children of allergic mothers. A significantly higher level of EGF was proved in the colostrum of healthy mothers and in cord blood of their children in comparison with allergic group. EGF deficiency in the allergic group could impair or delay intestine maturation and support thus allergy development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGF:
-
epidermal growth factor
- ELISA:
-
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- GIT:
-
gastrointestinal tract
- GRO-α:
-
growth related oncoprotein α
- IL:
-
interleukin
- IFN-γ:
-
interferon γ
- MCP-1:
-
monocyte chemotactic protein-1
- MIP-1δ:
-
macrophage inflammatory protein 1δ
- PDGF-BB:
-
platelet-derived growth factor BB
- RANTES:
-
regulated upon activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted
- SEM:
-
standard error of the mean
- TGF-β:
-
transforming growth factor β
- TH :
-
helper T-lymphocyte
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor α
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Amoudruz P., Holmlund U., Malmstrom V., Trollmo C., Bremme K., Scheynius A., Sverremark-Ekstrom E.: Neonatal immune responses to microbial stimuli: is there an influence of maternal allergy?J.Allergy Clin.Immunol. 115, 1304–1310 (2005).
Bottcher M.F., Jenmalm M.C., Bjorksten B., Garofalo R.P.: Chemoattractant factors in breast milk from allergic and nonallergic mothers.Pediatr.Res. 47, 592–597 (2000a).
Bottcher M.F., Jenmalm M.C., Garofalo R.P., Bjorksten B.: Cytokines in breast milk from allergic and nonallergic mothers.Pediatr.Res. 47, 157–162 (2000b).
Cummins A.G., Thompson F.M.: Effect of breast milk and weaning on epithelial growth of the small intestine in humans.Gut 51, 748–754 (2002).
Duchen K., Thorell L.: Nucleotide and polyamine levels in colostrum and mature milk in relation to maternal atopy and atopic development in the children.Acta Paediatr. 88, 1338–1343 (1999).
Duchén K., Casas R., Fageras-Bottcher M., Yu G., Bjorksten B.: Human milk polyunsaturated long-chain fatty acids and secretory immunoglobulin A antibodies and early childhood allergy.Pediatr.Allergy Immunol. 11, 29–39 (2000).
Field C.J.: The immunological components of human milk and their effect on immune development in infants.J.Nutr. 135, 1–4 (2005).
Friedman N.J., Zeiger R.S.: The role of breast-feeding in the development of allergies and asthma.J.Allergy Clin.Immunol. 115, 1238–1248 (2005).
Hanson L.A., Korotkova M., Lundin S., Haversen L., Silfverdal S.A., Mattsby-Baltzer I., Strandvik B., Telemo E.: The transfer of immunity from mother to child.Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci. 987, 199–206 (2003).
Hauer A.C., Riederer M., Griessl A., Rosegger H., MacDonald T.T.: Cytokine production by cord blood mononuclear cells stimulated with cows milk proteinsin vitro: interleukin-4 and transforming growth factor β-secreting cells detected in the CD45RO T cell population in children of atopic mothers.Clin.Exp.Allergy 33, 615–623 (2003).
Kelleher S.L., Lonnerdal B.: Immunological activities associated with milk.Adv.Nutr.Res. 10, 39–65 (2001).
Kopp M.V., Zehle C., Pichler J., Szepfalusi Z., Moseler M., Deichmann K., Forster J., Kuehr J.: Allergen-specific T cell reactivity in cord blood: the influence of maternal cytokine production.Clin.Exp.Allergy 31, 1536–1543 (2001).
Kverka M., Burianová J., Lodinová-Žádníková R., Kocourková I., Cínová J., Tučková L., Tlaskalová-Hogenová H.: Cytokine profiling in human colostrum and milk by protein array.Clin.Chem. 53, 955–962 (2007).
Laiho K., Lampi A.M., Hamalainen M., Moilanen E., Piironen V., Arvola T., Syrjanen S., Isolauri E.: Breast milk fatty acids, eicosanoids, and cytokines in mothers with and without allergic disease.Pediatr.Res. 53, 642–647 (2003).
Liebler-Tenorio E.M., Riedel-Caspari G., Pohlenz J.F.: Uptake of colostral leukocytes in the intestinal tract of newborn calves.Vet.Immunol.Immunopathol. 85, 33–40 (2002).
Meki A.R.M.A., Saleem T.H., Al-Ghazali M.H., Sayed A.A.: Interleukins-6,-8 and -10 and tumor necrosis factor-α and its soluble receptor I in human milk at different periods of lactation.Nutr.Res. 23, 845–855 (2003).
Newburg D.S., Walker W.A.: Protection of the neonate by the innate immune system of developing gut and of human milk.Pediatr.Res. 61, 2–8 (2007).
Nowicki S., Goldblum R.M.: Amniotic fluid and the fetal mucosal immune system, pp. 1747–1762 in P.L. Ogra, J. Mestecky, M.E. Lamm, W. Strober, J. Bienenstock, J.R. McGhee, L. Mayer (Eds):Mucosal Immunology, Vol. I., 3rd ed. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego 2005.
Peden D.B.: The epidemiology and genetics of asthma risk associated with air pollution.J.Allergy Clin.Immunol. 115, 213–219 (2005).
Prokešová L., Lodinová-Žádníková R., Žižka J., Kocourková I., Novotná O., Petrásková P., Šterzl I.: Cytokine levels in healthy and allergic mothers and their children during the first year of life.Pediatr.Allergy Immunol. 17, 175–183 (2006).
Schlesinger J.J., Covelli H.D.: Evidence for transmission of lymphocyte responses to tuberculin by breast-feeding.Lancet 2, 529–532 (1977).
Schnorr K.L., Pearson L.D.: Intestinal absorption of maternal leucocytes by newborn lambs.J.Reprod.Immunol. 6, 329–337 (1984).
Snijders B.E., Damoiseaux J.G., Penders J., Kummeling I., Stelma F.F., Van R.R., van den Brandt P.A., Thijs C.: Cytokines and soluble CD14 in breast milk in relation with atopic manifestations in mother and infant (Koala Study).Clin.Exp.Allergy 36, 1609–1615 (2006).
Takeda T., Sakata M., Minekawa R., Yamamoto T., Hayashi M., Tasaka K., Murata Y.: Human milk induces fetal small intestinal cell proliferation — involvement of a different tyrosine kinase signaling pathway from epidermal growth factor receptor.J.Endocrinol. 181, 449–457 (2004).
Tariq S.M., Matthews S.M., Hakim E.A., Stevens M., Arshad S.H., Hide D.W.: The prevalence of and risk factors for atopy in early childhood: a whole population birth cohort study.J.Allergy Clin.Immunol. 101, 587–593 (1998).
Warner J.A., Warner J.O.: Early life events in allergic sensitisation.Brit.Med.Bull. 56, 883–893 (2000).
Warner J.O.: The early life origins of asthma and related allergic disorders.Arch.Dis.Child 89, 97–102 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
1st part of this study:Pediatr.Allergy Immunol. 17, 175–183 (2006).
This work was supported by the grant no. IGA/MZ NR/8040-3 of theMinistry of Public Health of the Czech Republic.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Žižka, J., Kverka, M., Novotná, O. et al. Perinatal period cytokines related to increased risk of future allergy development. Folia Microbiol 52, 549–555 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932118
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932118