Abstract
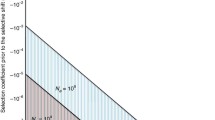
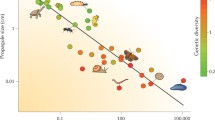
Selection at linked sites has important consequences for the properties of neutral variation and for tests of the predictions of the neutral theory of molecular evolution. We review the theory of the effect of adaptive gene substitutions on neutral variability at linked sites (hitchhiking or selective sweeps) and discuss theoretical results on the effect of selection against deleterious alleles on variation at linked sites (background selection). InDrosophila melanogaster there is a clear relation between the frequency of recombination in a given region of the chromosome and the amount of natural variability in that region. Attempts to predict this relation have given rise to models of selective sweeps and background selection. We describe possible methods of discriminating between these models, and also discuss the probable strong influence of selective sweeps on variation in largely nonrecombining genomes, with particular reference toEscherichia coll. Finally we present some unresolved questions and possible directions for future research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguade M., Miyashita N. and Langley C. H. 1989 Reduced variation in theyellow-achaete-scute region in natural populations ofDrosophila melanogaster.Genetics 122: 607–615
Akashi H. 1995 Inferring weak selection from patterns of polymorphism and divergence at “silent” sites inDrosophila DNA.Genetics 139: 1067–1076
Aquadro C. F., Begun D. J. and Kindahl E. C. 1994 Selection, recombination, and DNA polymorphism inDrosophila. InNon-neutral evolution: theories and molecular data (ed.) B. Golding (London: Chapman and Hall) pp. 46–56
Ashburner M. 1989Drosophila: a laboratory handbook (Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press)
Atwood K. C., Schneider L. K. and Ryan F. J. 1951a Selective mechanisms in bacteria.Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 16: 345–355
Atwood K. C., Schneider L. K. and Ryan F. J. 1951b Periodic selection inEscherichia coli.Proc. Natl, Acad. Sci. USA 37:146–155
Barton N. H. 1995 Linkage and the limits to natural selection.Genetics 140: 82–84
Begun D. J. and Aquadro C. F. 1992 Levels of naturally occurring DNA polymorphism correlate with recombination rate inDrosophila melanogaster.Nature 356: 519–520
Berg O. G. 1995 Periodic selection and hitchhiking in a bacterial population.J. Theor. Biol 173: 307–320
Berg O. G. 1996 Selection intensity for codon bias and the effective population size ofEscherichia coli Genetics 142: 1379–1382
Berry A. J., Ajioka J. W. and Kreitman M. 1991 Lack of polymorphism on theDrosophila fourth chromosome resulting from selection.Genetics 129: 1111–1117
Bird A. P. 1995 Gene number, noise reduction and biological complexity.Trends Genet. 11: 94–100
Birky C. W. and Walsh J. B. 1988 Effects of linkage on rates of molecular evolution.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 6414–6418
Braverman J. M., Hudson R. R., Kaplan N. L., Langley C. H. and Stephan W. 1995 The hitchhiking effect on the site frequency spectrum of DNA polymorphism.Genetics 140: 783–796
Charlesworth B. 1992 New genes sweep clean.Nature 356: 475–476
Charlesworth B. 1994a The effect of background selection against deleterious alleles on weakly selected, linked variants.Genet. Res. 63: 213–228
Charlesworth B. 1994b Patterns in the genome.Curr. Biol. 4: 182–184
Charlesworth B. 1996 Background selection and patterns of genetic diversity inDrosophila melanogaster. Genet. Res. (in press)
Charlesworth B., Morgan M. T. and Charlesworth D. 1993 The effect of deleterious mutations on neutral molecular variation.Genetics 34: 1289–1303
Charlesworth D., Charlesworth B. and Morgan M. T. 1995 The pattern of neutral molecular variation under the background selection model.Genetics 141: 1619–1632
Crow J. F. 1993 How much do we know about spontaneous human mutation rates?Environ. Mol. Mut. 21: 122–129
Crow J. F. and Simmons M. J. 1983 The mutation load inDrosophila. InThe genetics and biology of Drosophila (eds.) M. Ashburner, H. L. Carson and J. N. Thompson (London: Academic Press) vol. 3c, pp. 1–35
Drake J. W. 1992 Mutation rates.Bioessays 14: 137–140
Dykhuizen D. E. 1992 Periodic selection. InEncyclopedia of microbiology (San Diego: Academic Press) pp. 351–355
Dykhuizen D. E. and Hartl D. L. 1983 Selection in chemostats.Microbiol. Rev. 47: 150–168
Fu Y. -X. and Li W. -H. 1993 Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations.Genetics 133: 693–709
Gillespie J. H. 1994 Alternatives to the neutral theory. InNon-neutral evolution: theories and molecular data (ed.) B. Golding (London: Chapman and Hall) pp. 1–17
Guttman D. S. and Dykhuizen D. E. 1994a Detecting selective sweeps in naturally occurringEscherichia coli.Genetics 138: 993–1003
Guttman D. S. and Dykhuizen D. E. 1994b Clonal divergence inEscherichia coli as a result of recombination, not mutation.Science 266: 1380–1383
Haldane J. B. S. 1927 A mathematical theory of natural and artificial selection. Part V. Selection and mutation.Proc. Cambridge Philos. Soc. 23: 838–844
Hartl D. L., Moriyama E. N. and Sawyer S. A. 1994 Selection intensity for codon bias.Genetics 138: 227–234
Hudson R. R. 1994 How can the low levels of DNA sequence variation in regions of theDrosophila genome with low recombination rates be explained?Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 91: 6815–6818
Hudson R. R. and Kaplan N. L. 1994 Gene trees with background selection. InNon-neutral evolution: theories and molecular data (ed.) B. Golding (London: Chapman and Hall) pp. 140–153
Hudson R. R. and Kaplan N. L. 1995 Deleterious background selection with recombination.Genetics 141: 1605–1617
Hudson R. R., Kreitman M. and Aguade M. 1987 A test of neutral molecular evolution based on nucleotide data.Genetics 116: 153–159
Jarne P. 1995 Mating system, bottlenecks and polymorphism in hermaphroditic animals.Genet. Res. 65: 193–207
Kaplan N. L., Hudson R. R. and Langley C. H. 1989 The “hitch-hiking“ effect revisited.Genetics 123: 887–899
Keightley P. D. 1994 The distribution of mutation effects on viability inDrosophila melanogaster.Genetics 138: 1–8
Kimura M. 1971 Theoretical foundations of population genetics at the molecular level.Theor. Popul. Biol. 2: 174–208
Kimura M. 1983The neutral theory of molecular evolution (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press)
Kimura M. and Crow J. F. 1964 The number of alleles that can be maintained in a finite population.Genetics 49: 725–738
Kimura M. and Maruyama T. 1966 The mutational load with epistatic gene interactions in fitness.Genetics 54: 1303–1312
Kimura M. and Ohta T. 1969 The average number of generations until extinction of an individual mutant gene in a population.Genetics 63: 701–709
Kliman R. M. and Hey J. 1993 Reduced natural selection associated with low recombination inDrosophila melanogaster.Mol. Biol Evol. 10: 1239–1258
Kreitman M. 1983 Nucleotide polymorphism at the alcohol dehydrogenase locus ofDrosophila melanogaster.Nature 304: 412–417
Kreitman M. 1991 Detecting selection at the level of DNA. InEvolution at the molecular level (eds.) R. K. Selander, A. G. Clark and T. S. Whittam (Sunderland, Mass., USA: Sinauer) pp. 202–221
Kreitman M. and Wayne M. L. 1994 Organization of genetic variation at the molecular level: lessons fromDrosophila. InMolecular ecology and evolution: approaches and applications (eds.) B. Schierwater, B. Streit, G. P. Wagner and R. DeSalle (Basel: Birkhauser) pp. 157–184
Levin B. R. 1981 Periodic selection, infectious gene exchange and the genetic structure ofE. coli populations.Genetics 99: 1–23
Levin B. R. 1988 The evolution of sex in bacteria. InThe evolution of sex (eds.) R. E. Michod and B. R. Levin (Sunderland, Mass., USA: Sinauer) pp. 194–211
Lindsley D. L. and Zimm G. G. 1992The genome of Drosophila melanogaster (San Diego: Academic Press)
Maynard Smith J. 1991 The population genetics of bacteria.Proc. R. Soc. London B245: 37–41
Maynard Smith J. and Haigh J. 1974 The hitch-hiking effect of a favourable gene.Genet. Res. 23: 23–35
Maynard Smith J., Smith N. H., O’Rourke M. and Spratt B. G. 1993 How clonal are bacteria?Proc. Natl. Acad. Sri. USA 90: 4384–4388
Milkman R. 1973 Electrophoretic variation inEscherichia coli from natural sources.Science 182: 1024–1026
Milkman R. 1975 Allozyme variation ofE. coli of diverse natural origins. InIsozymes (ed.) C. L. Markert (New York: Academic Press) vol. 4, pp. 273–285
Milkman R. and Bridges M. M. 1990 Molecular evolution of theEscherichia coli chromosome. III. Clonal frames.Genetics 126: 505–517
Moriyama E. N. and Powell J. R. 1996 Intraspecific nuclear DN A variation inDrosophila.Mol. Biol. Evol. 13: 261–277
Mukai T., Chigusa S. I., Mettler L. E. and Crow J. F. 1972 Mutation rate and dominance of genes affecting viability inDrosophila melanogaster.Genetics 72: 335–355
Nordborg M., Charlesworth B. and Charlesworth D. 1996 The effect of recombination on background selection.Genet. Res. 67: 159–174
Ohnishi O. 1977 Spontaneous and ethyl methanesulfonate-induced mutations controlling viability inDrosophila melanogaster. II. Homozygous effects of polygenic mutations.Genetics 87: 529–545
Ohta T. 1971 Associative overdominance caused by linked detrimental mutations.Genet. Res. 18: 277–286
Ohta T. 1973 Effect of linkage on behaviour of mutant genes in finite populations.Theor. Popul. Biol. 4: 145–172
Ohta T. and Kimura M. 1975 The effect of a selected locus on heterozygosity of neutral alleles (the hitch-hiking effect).Genet. Res. 25: 313–326
Peck J. 1994 A ruby in the rubbish: beneficial mutations, deleterious mutations, and the evolution of sex.Genetics 137: 597–606
Reeves P. R. 1992 Variation in O-antigens, niche-specific selection, and bacterial populations.FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 100: 509–516
Selander R. K. and Levin B. R. 1980 Genetic diversity and structure inEscherichia coli populations.Science 210: 545–547
Simonsen K. L., Churchill G. A. and Aquadro C. F. 1995 Properties of statistical tests of neutrality for DNA polymorphism data.Genetics 141: 413–429
Slatkin M. 1995 Hitchhiking and associative overdominance at a microsatellite locus.Mol. Biol. Evol. 12: 473–480
Stephan W. 1995 An improved method for estimating the rate of fixation of favorable mutations based on DNA polymorphism data.Mol. Biol. Evol 12: 959–962
Stephan W. and Langley C. H. 1989 Molecular genetic variation in the centromeric region of the X chromosome in threeDrosophila ananassae populations. I. Contrasts between thevermilion andforked loci.Genetics 121: 89–99
Stephan W., Wiehe T. H. E. and Lenz M. W. 1992 The effect of strongly selected substitutions on neutral polymorphism: analytical results based on diffusion theory.Theor. Popul. Biol. 41: 237–254
Sturtevant A. H. 1929 The genetics ofDrosophila simulans.Carnegie Inst. Wash. Publ. 399: 1–62
Sved J. A. 1972 Heterosis at the level of the chromosome and at the level of the gene.Theor. Popul. Biol 3: 491–506
Tajima F. 1989 Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis.Genetics 123: 585–595
Thomson G. 1977 The effect of a selected locus on linked neutral loci.Genetics 85: 753–788
True J. R., Mercer J. M. and Laurie C. C. 1996 Differences in crossover frequency and distribution among three sibling species ofDrosophila.Genetics 142: 507–523
Whittam T. S. and Ake S. E. 1993 Genetic polymorphisms and recombination in natural populations ofE. coli. InMechanisms of molecular evolution (eds.) N. Takahata and A. G. Clark (Sunderland, Mass., USA: Sinauer) pp. 223–245
Wiehe T. H. E. and Stephan W. 1993 Analysis of a genetic hitchhiking model and its application to DNA polymorphism data.Mol. Biol. Evol. 10: 842–854
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charlesworth, B., Guttman, D.S. Reductions in genetic variation inDrosophila andE. coli caused by selection at linked sites. J. Genet. 75, 49–61 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931751
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931751