Abstract
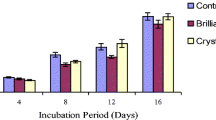
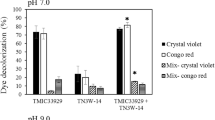
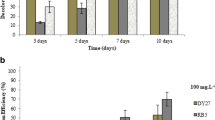
Dye decolorization capacity of two white-rot fungi,Irpex lacteus andPhanerochaete chrysosporium, was compared in N-limited liquid cultures. The agitated cultures showed lower ability to decolorize azo dyes Reactive Orange 16 and Naphthol Blue Black than static cultures. Similar effect was also observed with other structurally different synthetic dyes. The effect of surfactants on the decolorization process is discussed. A significant increase in the Reactive Orange 16 decolorization by the agitatedI. lacteus cultures was observed after adding 0.1% Tween 80, following a higher Mn-dependent peroxidase production. Thein vitro dye decolorization using the purified enzyme proved its decolorization ability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BPB:
-
Bromophenol Blue
- CSB:
-
Chicago Sky Blue
- CuP:
-
copper(II) phthalocyanine
- DB3:
-
Disperse Blue 3
- DMAB:
-
dimethylamine-borane
- LiP:
-
lignin peroxidases
- MB:
-
Methylene Blue
- MBTH:
-
3-methyl-2-benzothiazolinone hydrazone
- MnP:
-
Mn-dependent peroxidases
- NBB:
-
Naphthol Blue Black
- RBBR:
-
Remazol Brilliant Blue R
- RO16:
-
Reactive Orange 16
References
Bourbonnais R., Paice M.G.: Substrate range of veratryl alcohol oxidase and phenol oxidase from white rot fungi.Abstr.Pap.Amer.Chem.Soc. 199, 38 (1990).
Campos R., Kandelbauer A., Robra K.H., Cavaco-Paulo A., Gubitz G.M.: Indigo degradation with purified laccases fromTrametes hirsuta andSelerotium rolfsii.J.Biotechnol. 89, 131–139 (2001).
Chivukula M., Spadaro J.T., Renganathan V.: Lignin peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of sulfonated azo dyes generates novel sulfophenyl hydroperoxides.Biochemistry 34, 7765–7772 (1995).
Claus H., Faber G., König H.: Redox-mediated decolorization of synthetic dyes by fungal laccases.Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol. 59, 672–678 (2002).
Couto S.R., Rivela I., Muñoz M.R., Sanroman A.: Stimulation of ligninolytic enzyme production and the ability to decolourise Poly R-478 in semi-solid state cultures ofPhancrochaete chrysosporium.Biores.Technol. 74, 159–164 (2000).
Hammel K.E., Kapich A.N., Jensen K.A., Ryan Z.C.: Reactive oxygen species as agents of wood decay by fungi.Enzyme Microb.Technol. 30, 445–453 (2002).
Harazono K., Watanabe Y., Nakamura K.: Decolorization of azo dye by the white-rot basidiomycetePhanerochaete sordida and by its manganese peroxidase.J.Biosci.Bioeng. 95, 455–459 (2003).
Heinfling A., Martinez M.J., Martinez A.T., Bergbauer M., Szewzyk U.: Transformation of industrial dyes by manganese peroxidases fromBjerkandera adusta andPleurotus eryngii in a manganese-independent reaction.Appl.Environ.Microbiol. 64, 2788–2793 (1998).
Kasinath A., Novotný Č., Svobodová K., Patel K.C., Šašek V.: Decolorization of synthetic dyes byIrpex lacteus in liquid cultures and packed-bed bioreactor.Enzyme Microb.Technol. 32, 167–173 (2003).
Kim H.Y., Song H.G.: Transformation and mineralization of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene by the white rot fungusIrpex lacteus.Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol. 61, 150–156 (2003).
Maximo C., Costa-Ferreira M.: Decolourisation of reactive textile dyes byIrpex lacteus and lignin modifying enzymes.Process Biochem. 39, 1475–1479 (2004).
Mielgo I., Lopez C., Moreira M.T., Feijoo G., Lema J.M.: Oxidative degradation of azo dyes by manganese peroxidase under optimized conditions.Biotechnol.Progr. 19, 325–331 (2003).
Moen M.A., Hammel K.E.: Lipid-peroxidation by the manganese peroxidase ofPhanerochaete chrysosporium is the basis for phenanthrene oxidation by the intact fungus.Appl.Environ.Microbiol. 60, 1956–1961 (1994).
Moldes D., Couto S.R., Cameselle C., Sanroman M.A.: Study of the degradation of dyes by MnP ofPhanerochaete chrysosporium produced in a fixed-bed bioreactor.Chemosphere 51, 295–303 (2003).
Novotný Č., Svobodová K., Erbanová P., Cajthaml T., Kasinath A., Lang E., Šašek V.: Ligninolytic fungi in bioremediation: extracellular enzyme production and degradation rate.Soil Biol.Biochem. 36, 1545–1551 (2004).
Ollikka P., Harjunpaa T., Palmu K., Mantsala P., Suominen I.: Oxidation of Crocein Orange G by lignin peroxidase isoenzymes kinetics and effect of H2O2.Appl.Biochem.Biotechnol. 75, 307–321 (1998).
Paszczyński A., Crawford R.L.: Potential for bioremediation of xenobiotic compounds by the white rot fungusPhanerochaete chrysosporium.Biotechnol.Progr. 11, 368–379 (1995).
Pease E.A., Tien M.: Heterogeneity and regulation of manganese peroxidases fromPhanerochaete chrysosporium.J.Bacteriol. 174, 3532–3540 (1992).
Pointing S.B.: Feasibility of bioremediation by white-rot fungi.Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol. 57, 20–33 (2001).
Rabinovich M.L., Bolobova A.V., Vasil’chenko L.G.: Fungal decomposition of natural aromatic structures and xenobiotics: a review.Appl.Biochem.Microbiol. 40, 1–17 (2004).
Rothschild N., Novotný Č., Šašek V., Dosoretz C.G.: Ligninolytic enzymes of the fungusIrpex lacteus (Polyporus tulipiferae): isolation and characterization of lignin peroxidase.Enzyme Microb.Technol. 31, 627–633 (2002).
Saparrat M.C.N., Guillén F.: Ligninolytic ability and potential biotechnology applications of the South American fungusPleurotus laciniatocrenatus.Folia Microbiol. 50, 155–160 (2005).
Schliephake K., Mainwaring D.E., Lonergan G.T., Jones I.K., Baker W.L.: Transformation and degradation of the bisazo dye Chicago Sky Blue by a purified laccase fromPycnoporus cinnabarinus.Enzyme Microb.Technol. 27, 100–107 (2000).
Selvam K., Swaminathan K., Chae K.S.: Decolourization of azo dyes and a dye industry effluent by a white rot fungusThelephora sp.Biores.Technol. 88, 115–119 (2003).
Shin K.W.: The role of enzymes produced by white-rot fungusIrpex lacteus in the decolorization of the textile industry effluent.J.Microbiol. 42, 37–41 (2004).
Shin K.S., Kim Y.H., Lim J.S.: Purification and characterization of manganese peroxidase of the white-rot fungusIrpex lacteus.J.Microbiol. 43, 503–509 (2005).
Soares G.M.B., Costa-Ferreira M., de Amorim M.T.P.: Decolorization of an anthraquinone-type dye using a laccase formulation.Biores.Technol. 79, 171–177 (2001).
Swamy J., Ramsay J.A.: The evaluation of white rot fungi in the decoloration of textile dyes.Enzyme Microb.Technol. 24, 130–137 (1999).
Tien M., Kirk T.K.: Lignin peroxidase fromPhanerochaete chrysosporium.Meth.Enzymol. 161, 238–248 (1988).
Urek R.O., Pazarlioglu N.K.: Production and stimulation of manganese peroxidase by immobilizedPhanerochaete chrysosporium.Process Biochem. 40, 83–87 (2005).
Vyas B.R.M., Bakowski S., Šašek V., Matucha M.: Degradation of anthracene by selected white-rot fungi.FEMS Microbiol.Ecol. 14, 65–70 (1994).
Wang Y.X., Yu J.: Adsorption and degradation of synthetic dyes on the mycelium ofTrametes versicolor.Water Sci.Technol. 38, 233–238 (1998).
Young L., Yu J.: Ligninase-catalyzed decolorization of synthetic dyes.Water Res. 31, 1187–1193 (1997).
Zheng Z.M., Obbard J.P.: Effect of non-ionic surfactants on elimination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soil-slurry byPhanerochaete chrysosporium.J.Chem.Technol.Biotechnol. 76, 423–429 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The work was supported by the projects no. IAA 602 0411 of theGrant Agency of the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, COST no. 1P 04O C8 47.002 and by theInstitutional Research Concept no. AV 0Z 5020 0510.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Svobodová, K., Erbanová, P., Sklenář, J. et al. The role of Mn-dependent peroxidase in dye decolorization by static and agitated cultures ofIrpex lacteus . Folia Microbiol 51, 573–578 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931622
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931622