Abstract
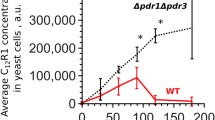
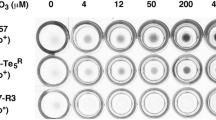
In yeast the resistance to kresoxim-methyl and azoxystrobin, like the resistance to strobilurin A (mucidin) is under the control of both mitochondrialcob gene and the PDR network of nuclear genes involved in multidrug resistance. The mucidin-resistantmucl (G137R) andmuc2 (L275S) mutants ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae containing point mutations in mtDNA were found to be cross-resistant to kresoximmethyl and azoxystrobin. Cross-resistance to all three strobilurin fungicides was also observed in yeast transformants containing gain-of-function mutations in the nuclearPDR3 gene. On the other hand, nuclear mutants containing disrupted chromosomal copies of thePDR1 andPDR3 genes or thePDR5 gene alone werehypersensitive to kresoxim-methyl, axoxystrobin and strobilurin A. The frequencies of spontaneous mutants selected for resistance either to kresoxim-methyl, azoxystrobin or strobilurin A were similar and resulted from mutations both in mitochondrial and nuclear genes. The results indicate that resistance to strobilurin fungicides, differing in chemical structure and specific activity, can be caused by the same molecular mechanism involving changes in the structure of apocytochromeb and/or increased efflux of strobilurins from fungal cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balzi E., Wang M., Leterme S., Van Dyck L., Goffeau A.:PDR5, a novel yeast multidrug resistance conferring transporter controlled by the transcription regulatorPDR1.J.Biol.Chem. 269, 2206–2214 (1994).
Barlett D.W., Clough J.M., Goldwin J.R., Hall A.A., Hamer M., Parr-Dobrzanski B.: The strobilurin fungicides.Pest.Manag.Sci. 58, 649–662 (2002).
Becker W.E., von Jagow G., Anke T., Steglich W.: Oudemansin, strobilurin A, strobilurin B and myxothiazol: new inhibitors of thebcl segment of the respiratory chain with anE-β-methoxyacrylate system as common structural element.FEBS Lett. 132, 329–333 (1981).
Bissinger P.H., Kuchler K.: Molecular cloning and expression of theS. cerevisiae STS1 gene product.J.Biol.Chem. 264, 4180–4186 (1994).
Chin K.M., Chavaillaz D., Kaesbohrer M., Staub T., Felsenstein F.G.: Characterizing resistance risk ofErysiphe graminis f.sp.tritici to strobilurins.Crop Protect. 20, 87–96 (2001).
Clough J.M., Godfrey C.R.A.: The strobilurin fungicides, pp. 109–148 in D.H. Hutson, J. Miyamoto (Eds):Fungicidal Activity. Wiley, Chichester (UK) 1998.
Delaveau T., Delahodde A., Carvajal E., Šubík J., Jacq C.:PDR3, a new yeast regulatory gene, is homologous toPDR1 and controls the multidrug resistance phenomenon.Mol.Gen.Genet. 178, 603–610 (1994).
De Risi J., van den Hazel B., Marc P., Balzi E., Brown P., Jacq C., Goffeau A.: Genome microarray analysis of transcriptional activation in multidrug resistance yeast mutants.FEBS Lett. 410, 156–160 (2000).
Di Rago J.P., Coppee J.Y., Colson A.M.: Molecular basis for resistance to myxothiazol, mucidin (strobilurin A) and stigmatellin. Cytochromeb inhibitors activity at the center of the mitochondrial ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase inSaccharomyces cerevisiae.J.Biol.Chem. 264, 14543–14548 (1989).
Espinel-Ingroff A., Barchiesi F., Hazen K.C., Martinez-Suarez J.V., Scalise G.: Standardization of antifungal susceptibility testing and clinical relevance.Med.Mycol. 36, 68–78 (1998).
Gisi U., Chin K.M., Knapova G., Kung Farberr R., Mohr U., Parisi S., Sierotzki H., Steinfeld U.: Recent developments in elucidated modes of resistance to phenylamide, DMI and strobilurin fungicides.Crop Protect. 19, 863–872 (2000).
Michalková-Papajová D., Obernauerová M., Šubík J.: Role of the PDR gene network in yeast susceptibility to the antifungal antibiotic mucidin.Antimicrob.Agents Chemother. 44, 418–420 (2000).
Morschhauser J.: The genetic basis of fluconazole resistance development inCandida albicans.Biochim.Biophys.Acta 1578, 240–248 (2002).
Nourani A., Papajová D., Delahodde A., Jacq C., Šubik J.: Clustered amino acid substitutions in the yeast transcription regulator Pdr3 increase pleiotropic drug resistance and identify a new central regulatory domain.Mol.Gen.Genet. 256, 397–405 (1997).
Sanglard D., Kuchler K., Ischer F., Pagani J.L., Monod M., Bille J.: Mechanisms of resistance to azole antifungal agents inCandida albicans isolates from AIDS patients involve specific multidrug transporters.Antimicrob.Agents Chemother. 39, 2378–2386 (1995).
Sanglard D., Ischer F., Monod M., Bille J.. Cloning ofCandida albicans genes conferring resistance to azole antifungal agents — characterization ofCDR2, a new multidrug ABC transporter gene.Microbiology 143, 405–416 (1997).
Sanglard D., Odds F.C.: Resistance ofCandida species to antifungal agents: molecular mechanisms and clinical consequences.Lancet Infect.Dis. 2, 73–85 (2002).
Sauter H., Steglich W., Anke T.: Strobilurins: evolution of a new class of active substances.Angew.Chem.Internat.Ed. 117, 1328–1349 (1999).
Šubík J., Behúň M., Musílek V.: Antibiotic mucidin, a new antimycin A-like inhibitor of electron transport in rat liver mitochondria.Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun. 57, 17–22 (1974).
Šubík J., Kováčová V., Takácsová G.: Mucidin resistance in yeast. Isolation, characterization and genetic analysis of nuclear and mitochondrial mucidin-resistant mutants ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae.Eur.J.Biochem. 73, 275–286 (1977).
Šubík J., Takácsová G.: Genetic determination of ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase. Mitochondrial locusmuc3 specifying resistance ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae to mucidin.Mol.Gen.Genet. 161, 99–108 (1978).
Šubík J., Ulaszewski S., Goffeau A.: Genetic mapping of nuclear mucidin resistance mutations inSaccharomyces cerevisiae. A newpdr locus on chromosome II.Curr.Genet. 10, 665–670 (1986).
Takácsová G., Šubík J., Kotylak Z.: Localization of mucidin-resistant locusmuc3 on mitochondrial DNA with respect to ubiquinolcytochrome-c reductase deficientbox loci. Locusmuc3 is allelic tobox2.Mol.Gen.Genet. 179, 141–146 (1980).
Thompson J.R., Register E., Curotto J., Kurtz M., Kelly R.: An improved protocol for the preparation of yeast cells for transformation by electroporation.Yeast 14, 565–571 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was partially supported by grants from theSlovak Grant Agency VEGA (1/0019/03), agency APVT (51-000502), andEuropean Union (QLK2-CT-2001-002377).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hnátová, M., Gbelská, Y., Obernauerová, M. et al. Cross-resistance to strobilurin fungicides in mitochondrial and nuclear mutants ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae . Folia Microbiol 48, 496–500 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931331
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931331