Abstract
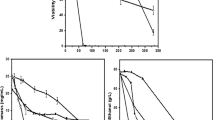
The retention of whole-cell bioactivity is essential to the biocatalysis in reaction mixture containing organic compounds for the preparation of products in the pharmaceutical fine chemicals and food industries. A Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship (QSAR) toxicity model for determination of whole-cell bioactivity was developed on the basis of receptor theory. And the glycolysis activity retention of baker's yeast in the presence of organic compounds was investigated in this study. Based on the fitting of the QSAR model to experimental data obtained in this study and in previous literatures, the regression analysis indicated that calculated values with this model were consistent with experimental data. Comparison of experimental data to the modeled curves suggests good predictive capabilities of the model for determination of whole-cell bioactivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cruz, A., P. Fernandes, J. M. S. Cabral, and H. M. Pinheiro (2001) Whole-cell bioconversion of β-sitosterol in aqueous-organie two-phase systems.J. Mol. Catal. B 11: 579–585.
Cruz, A., P. Fernandes, J. M. S. Cabral, and H. M. Pinheiro (2004) Solvent partitioning and whole-cell sitosterol bioconversion activity in aqueous-organic twophase systems.Enzyme Microb. Technol. 34: 342–353.
León, R., P. Fernandes, H. M. Pinheiro, and J. M. S. Cabral (1998): Whole-cell biocatalysis in organic media.Enzyme Microb. Technol. 23: 483–500.
Luo, D. H., M. H. Zong, and J. H. Xu (2003) Biocatalytic synthesis of (−)-1-trimethylsilylethanol by asymmetric reduction of acetyltrimethylsilane with a new isolateRhohotorula sp. AS2.2241.J. Mol. Catal. B 24–25: 83–88.
Park, O.-J., H. L. Holland, J. A. Khan, and E. N. Vulfson (2000) Production of flavour ketones in aqueousorganic two-phase systems by using free and microencapsulated fungal spores as biocatalysts.Enzyme Microb. Technol. 26: 235–242.
Salter, G. J. and D. B. Kell (1995) Solvent selection for whole cell biotransformations in organic media.Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 15: 139–177.
Laane, C., S. Boeren, K. Vos, and C. Veeger (1987) Rules for optimization of biocatalysis in organic solvents.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 30: 81–87.
León, R., I. Garbayo, R. Hernández, J. Vigara, and C. Vilchez (2001) Organic solvent toxicity in photoautotrophic unicellular microorganisms.Enzyme Microb. Technol. 29: 173–180.
Tong, Y. P., M. Hirata, H. Takanashi, T. Hano, M. Matsumoto, and S. Miura (1998) Solvent screening for production of lactic acid by extractive fermentation.Sep. Sci. Technol. 33: 1439–1453.
Vermuë, M., J. Sikkema, A. Verheul, R. Bakker, and J. Tramper (1993) Toxicity of homologous series of organic solvents for the Gram-positive bacteriaArthrobacter andNocardia sp. and the Gram-negative bacteiraAcinetobacter andPseudomonas sp.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 42: 747–758.
Cruz, A., P. Fernandes, J. M. S. Cabral, and H. M. Pinheiro (2002) Effect of phase composition on the whole-cell bionconversion of β-sitosterol in biphasic media.J. Mol. Catal. B 19–20: 371–375.
Rajagopal, A. N. (1996) Growth of Gram-negative bacteria in the presence of organic solvents.Enzyme Microb. Technol. 19: 606–613.
Cronin, M. T. and T. W. Schultz (1996) Structuretoxicity relationships for phenols toTetrahymena pyriformis.Chemosphere 32: 1453–1468.
Kurup, A., R. Garg, D. J. Carini, and C. Hansch (2001) Comparative QSAR: Angiotensin II antagonists.Chem. Rev. 101: 2727–2750.
Wang, X. D., C. S. Yin, and L. S. Wang (2002) Structure-activity relationships and response-surface analysis of nitroaromatics toxicity to the yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae).Chemosphere 46: 1045–1051.
Wang, L. S. and S. K. Han (1997)Molecular Structure. Property and Activity. Chemical Engineering Press, Beijing, China.
Hansch, C. (1973)Structure-activity Relationships, Pergmon Press Inc., Elmsford, NY, USA.
Wang, L. S. and S. K. Han (1993)Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships of Organic Compounds, China Environment Science Press, Beijing, China.
Osborne, S. J., J. Leaver, M. K. Turner, and P. Dunnill (1990) Correlation of biocatalytic activity in an organicaqueous two-liquid phase system with solvent concentration in the cell membrane.Enzyme Microb. Technol. 12: 281–291.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Q., Yao, S. Predictive modeling of whole-cell bioactivity retention data in the presence of organic compounds. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 12, 228–234 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931097
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931097