Abstract
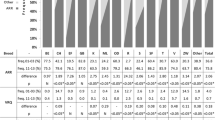
In a worldwide majority of sheep breeds an excessive susceptibility to scrapie associated with thePrP gene alleles coding for valine (V; at the 136 codon) and glutamine (Q; at the 171 codon) (e.g., VRQ/VRQ, VRQ/ARQ, or ARQ/ARQ) was demonstrated. Particularly thePrP VRQ allele is closely associated with the high-risk development of the disease; thePrP ARQ allele can also fulfil this function but under certain limited conditions. Polymorphism in thePrP gene sequences (conclusively related to the increased susceptibility of sheep to scrapie) of improved Valachian sheep from two Slovak regions, Orava and Spiš, was determined. Examination of 735 sheep showed that ARR/ARQ was the most frequent genotype (45.2 %). High-risk genotypes were determined in 32.4 % of sheep (ARQ/ARQ 19.3, ARR/VRQ 9.0, ARR/VRQ 3.5, VRQ/VRQ 0.3, ARR/VRR 0.3). Low-risk genotypes were found in 67.7 % of sheep (ARR/ARQ 45.2, ARR/ARR 10.9, ARR/AHQ 5.7, ARQ/ARQ 4.9, AHQ/AHQ 0.7, ARR/AHR 0.3). Despite the geographically distant flocks of improved Valachian sheep investigated no difference in the occurrence of individual PrP genotypes was observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belt P.B.G.M., Muileman I.H., Schreuder B.E.C., Bos-de Ruiter J., Gielkens A.L.J., Smits M.A.: Identification of five allelic variants of sheepPrP gene and their association with natural scrapie.J.Gen.Virol. 76, 509–517 (1995).
Bossers A., Schreuder B.E.C., Muileman I.H., Belt P.B.G.M., Smits M.A.: PrP genotype contributes to determining survival times of sheep with natural scrapie.J.Gen.Virol. 77, 2669–2673 (1996).
Bossers A., Belt P.B.G.M., Raymond G.J., Caughey B., de Vries R., Smits M.A.: Scrapie susceptibility-linked polymorphisms modulate thein vitro conversion of sheep prion protein to protease-resistant forms.Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.USA 94, 4931–4936 (1997).
Bossers A., Harders F.L., Smits M.A.: PrP genotype frequencies of the most dominant sheep breed in a country free from scrapie.Arch.Virol. 144, 829–834 (1999).
Braig H.R., Diringer H.: Scrapie: concept of a virus-induced amyloidosis of the brain.EMBO J. 4, 2309–2312 (1985).
Clouscard C., Beaudry P., Elsen J.M., Milan D., Dussaucy M., Bounneau C., Schelcher R., Chatelain J., Launay V., Laplanche J.L.: Different allelic effects of the codons 136 and 171 of the prion protein gene in sheep with natural scrapie.J.Gen.Virol. 76, 2097–2101 (1995).
Cuillé J., Chelle P.L.: La maladie dite tremblante du mouton ets-elle inoculable?C.R.Acad.Sci. 203, 1552–1554 (1936).
Dawson M., Hoinvilla L.J., Hosie B.D., Hunter N.: Guidnace on the use of genotyping as an aid to the control of clinical scrapie.Vet.Rec. 6, 623–625 (1998).
Dickinson A.G., Outram G.W.: Genetic aspects of unconventional virus infections: the basis of the virino hypothesis, pp. 63–83 in G. Bock, J. Marsh (Eds):Ciba Foundation Symp., Vol. 135. Novel Infectious Agents and the Central Nervous System. Wiley Interscience, London 1988.
Distl O.: Züchterische Kontrolle der Empfänglichkeit für die Traberkrankheit (Scrapie) beim Schaf über molekulargenetische Testverfahren.Tierärztl. Umschau 55, 609–613 (2000).
Ikeda T., Horiuchi M., Ishiguro N., Muramatsu Y., Kai-Une G.D., Shinagawa M.: Amino acid polymorphisms of PrP with reference to onset of scrapie in Suffolk and Corriedale sheep in Japan.J.Gen.Virol. 76, 2577–2581 (1995).
Elsen J.M., Amigues Y., Schelcher F., Ducrocq V., Andreoletti O., Eychenne F., Khang Tien J.V., Poivey J.P., Lantier F., Laplanche J.L.: Genetic susceptibility and transmission factors in scrapie: detailed analysis of an epidemic in a closed flock of Romanov.Arch.Virol. 144, 431–445 (1999).
Ferenčík M., Novák M., Mikula I.: Prions, prionoses and immunity system. (In Slovak)Klin.Imunol.Alergol. 11, 9–16 (2001).
Goldmann W., Hunter N., Benson G., Foster J.D., Hope J.: Different scrapie associated fibril proteins (PrP) are encoded by lines of sheep selected for different alleles of theSip gene.J.Gen.Virol. 72, 2411–2417 (1991).
Goldmann W., Hunter N., Smith G., Foster J., Hope J.: PrP genotype and agent effects in scrapie: change in allelic interaction with different isolates of agent in sheep, a natural host of scrapie.J.Gen.Virol. 75, 989–995 (1994).
González L., Martin S., Begara-McGorum I., Hunter N., Houston F., Simmons M., Jeffrey M.: Effect of agent strains and host genotype on PrP accumulation in the brain of sheep naturally and experimentally affected with scrapie.J.Comp.Path. 126, 17–29 (2001).
Hunter N., Cairns D.: Scrapie-free Merino and Poll Dorset sheep from Australia and New Zeeland have normal frequencies of scrapie-susceptible PrP genotypes.J.Gen.Virol. 79, 2079–2082 (1998).
Hunter N., Goldmann W., Benson G., Foster J.D., Hope J.: Swale dale sheep affected by natural scrapie differ significantly in PrP genotype frequencies from healthy sheep and those selected for reduced incidence of scrapie.J.Gen.Virol. 74, 1025–1031 (1993).
Hunter N., Cairns D., Foster J.D., Smith G., Goldmann W., Donnelly K.: Is scrapie solely a genetic disease? Evidence from scrapie-free countries.Nature 386, 137 (1997).
Laplanche J.L., Chatelain J., Beaudry P., Dussaucy M., Launay J.L.: French autochthonous scrapied sheep without the 136 Val PrP polymorphism.Mamm.Genome 4, 463–464 (1993).
Mikula I., Novak M., Tkáčiková L’., Ferenčík M.: Prion devitalization. (In Slovak)Klin.Imunol.Alergol. 11, 18–21 (2001).
Mitrova E., Hunčaga S., Hocman G., Nyitrayová O., Tatara M.: “Clusters” of CJD in Slovakia: the first laboratory evidence of scrapie.Eur.J.Epidemiol. 5, 520–524 (1991).
Novák M., Vrtiak O.J., Mikula I., Tkáčikova L’.: Ovine scrapie: priorities and importance.Folia Microbiol. 45, 475–483 (2000).
O’Doherty E., Aherne M., Ennis S., Weavers E., Hunter N., Roche J.F., Sweeney T.: Detection of polymorphisms in the prion protein gene in a population of Irish Suffolk sheep.Vet.Rec. 146, 335–338 (2000).
Prusiner S.B.: Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie.Science 216, 136–144 (1982).
Prusiner S.B.: Prions.Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.USA 95, 13363–13383 (1998).
Race R., Jenny A., Sutton D.: Scrapie infectivity and proteinase K-resistant prion protein in sheep placenta, brain, spleen, and lymph node: implication for transmission andante mortem diagnosis.J.Infect.Dis. 178, 949–953 (1998).
Tkáčiková E., Novák M., Mikula I., Ferenčík M.: Genotypization of sheep and scrapie elimination.Klin.Imunol.Alergol. 11, 5–7 (2001).
Tranulis M.A.: Influence of the prion protein gene,Prnp, on scrapie succeptibility in sheep.APMIS 110, 33–43 (2002).
Tranulis M.A., Osland A., Bratberg B., Ulvund M.J.: Prion protein gene polymorphisms in sheep with natural scrapie and healthy controls in Norway.J.Gen.Virol. 80, 1073–1077 (1999).
Thorgeirsdottir S., Sigurdarson S., Thorison M., Georgsson G., Palsdottir A.:PrP gene polymorphism and natural scrapie in Icelandic sheep.J.Gen.Virol. 80, 2527–2534 (1997).
Vaccari G., Petraroli R., Agrimi U., Eleni C., Perfetti M.G., di Bari M.A., Morelli L., Ligios C., Busani L., Nonno R., di Guardo G.: PrP genotype in Sarda breed sheep and its relevance to scrapie.Arch.Virol. 146, 2029–2037 (2001).
Westeway D., Zuliain V., Cooper C.M., da Costa M., Newman S., Jenny A.L., Detwiler L., Prusiner S.B.: Homozygosity for prion protein alleles encoding glutamine-171 renders sheep susceptible to natural scrapie.Genes Develop.8, 959–969 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tkáčiková, L., Hanušovská, E., Novák, M. et al. The PrP genotype of sheep of the improved Valachian breed. Folia Microbiol 48, 269–276 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02930968
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02930968