Abstract
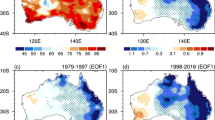
The influences of the wintertime AO (Arctic Oscillation) on the interdecadal variation of summer monsoon rainfall in East Asia were examined. An interdecadal abrupt change was found by the end of the 1970s in the variation of the AO index and the leading principal component time series of the summer rainfall in East Asia. The rainfall anomaly changed from below normal to above normal in central China, the southern part of northeastern China and the Korean peninsula around 1978. However, the opposite interdecadal variation was found in the rainfall anomaly in North China and South China. The interdecadal variation of summer rainfall is associated with the weakening of the East Asia summer monsoon circulation. It is indicated that the interdecadal variation of the AO exerts an influence on the weakening of the monsoon circulation. The recent trend in the AO toward its high-index polarity during the past two decades plays important roles in the land-sea contrast anomalies and wintertime precipitation anomaly. The mid- and high-latitude regions of the Asian continent are warming, while the low-latitude regions are cooling in winter and spring along with the AO entering its high-index polarity after the late 1970s. In the meantime, the precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau and South China is excessive, implying an increase of soil moisture. The cooling tendency of the land in the southern part of Asia will persist until summer because of the memory of soil moisture. So the warming of the Asian continent is relatively slow in summer. Moreover, the Indian Ocean and Pacific Ocean, which are located southward and eastward of the Asian land, are warming from winter to summer. This suggests that the contrast between the land and sea is decreased in summer. The interdecadal decrease of the land-sea heat contrast finally leads to the weakening of the East Asia summer monsoon circulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, M., P. Xie, J. E. Janowiak, and P. A. Arkin, 2002: Global land precipitation: A 50-yr monthly analysis based on gauge observations.Journal of Hydrometeorology,3, 249–266.
Gong, D., S. Wang, and J. Zhu, 2001: East Asian winter monsoon and Arctic Oscillation.Geophys. Res. Lett.,28, 2073–2076.
Gong, D., and S. Wang, 2003: Influence of Arctic Oscillation on winter climate over China.J. Geophys Res.,13, 208–216.
Gong, D., and C. H. Ho, 2003: Arctic oscillation signals in the East Asian summer monsoon.J. Geophys. Res., doi:10.1029/2002JD002193.
Huang, R. H., 2001: Decadal variability of the summer monsoon rainfall in East Asia and its association with the SST anomalies in the tropical Pacific.CLIVAR Exchange,2, 7–8.
Hu, Z., 1997: Interdecadal variability of summer climate over East Asia and its association with 500hPa height and global sea surface temperature.J. Geophys. Res.,102(D12), 19403–19412.
Kalnay, E. M., and Coauthors, 1996: The NCEP/NCAR 40-year Reanalysis Project.Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc.,77, 437–471.
Kerr, R. A., 1999: A new force in high-latitude climate.Science,284, 241–242.
Li Chongyin, Li Guilong, and Long Zhenxia, 1999: Comparing analyses of atmospheric circulation for interdecadal climate variation in China. Quart.Journal of Applied Meteorology,10(Suppl.), 1–8. (in Chinese)
Li Chongyin, and Li Guilong, 2000: The NPO/ NAO and interdecadal climate variation in China.Adv. Atmos. Sci.,17, 555–561.
Overland, J. E., J. M. Adams, and N. A. Bond, 1999: Decadal Variability of the Aleutian Low and its Relation to High-Latitude Circulation.J. Climate,12, 1542–1548.
Reynolds, R. W., 1988: A real-time global sea surface temperature analysis.J. Climate,1, 75–86.
Thompson, D. W. J., and J. M. Wallace, 1998: The Arctic Oscillation signature in the wintertime geopotential height and temperature fields.Geophys. Res. Lett.,25, 1297–1300.
Thompson, D. W. J., and J. M. Wallace, 2000: Annular modes in the extratropical circulation, Part I: Monthto-month variability.J. Climate,13, 1000–1016.
Thompson, D. W. J., and J. M. Wallace, 2001: Regional climate impacts of the Northern Hemisphere Annular Mode and associated climate trends.Science,293, 85–89.
Wang Huijun, 2001a: The weakening of the Asian monsoon circulation after the end of 1970’s.Adv. Atmos. Sci.,18, 376–386.
Wang Shaowu, 2001b:Advances in the Study of Modern Climatology. China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 458pp. (in Chinese)
Wang Qiang, and Fu Congbin, 1992: The detection of climate abrupt change with Mann-Kendall Rank Statistics.Acta Meteorological Sinica,6, 254–260. (in Chinese)
Weng, H., K. M. Lau, and Y. Xue, 1999: Multi-Scale Summer Rainfall Variability over China and its Long-term Link to Global Sea Surface Temperature Variability.J. Meteor. Soc. Japan,77, 845–857.
Wu Bingyi, and Wang Jia, 2002: Possible impacts of Winter Arctic Oscillation on Siberian High, the East Asian Winter Monsoon and Sea-ice Extent.Adv. Atmos. Sci.,19, 297–320.
Xue Feng, 2001: Interannual to Interdecadal Variation of East Asian Summer Monsoon and its Association with the Global Atmospheric Circulation and Sea Surface Temperature.Adv. Atmos. Sci.,18, 567–575.
Yeh, T. C., R. T. Wetherald, and S. Manabe, 1984: The effect of soil moisture on the short-term climate and hydrology change—A numerical experiment.Mon. Wea. Rev.,112, 474–490.
Zhang, Y., T. Li, and B. Wang, 2004: Decadal Change of the Spring Snow Depth over the Tibetan Plateau: The Associated Circulation and Influence on the East Asian Summer Monsoon.J. Climate,17, 2780–2793.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jianhua, J., Junmei, L., Jie, C. et al. Possible impacts of the arctic oscillation on the interdecadal variation of summer monsoon rainfall in East Asia. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 22, 39–48 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02930868
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02930868