Abstract
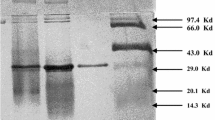
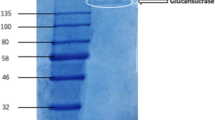
Differential centrifugation, precipitation with ammonium sulphate and chromatography on DEAE-cellulose led to a twenty-fold purification of glucosyltransferase fromStreptomyces aureofaciens B 96. The Michaelis constants for glucosyluridyl diphosphate (UDP-glucose) was 10.8 μm, for 1,2-dihydroxy-9, 10-anthraquinone (alizarin) 110 μm; the maximum rate of glucosylation reaction was 5.32 μmol per s per mg protein. The pH optimum was at 7.1; the flat temperature optimum was at 30 °C. Using some hydroxy derivatives of 9,10-anthraquinone it was found that the production of glucosides from aglycones with α-hydroxyl groups was about 1/8 of the values obtained with β-hydroxyl substrates. In both types of aglycones the presence of another hydroxyl group led to a higher glucoside production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blumauerová M., Mraček M., Vondráčková J., Podojil M., Hošťálek Z., Vaněk Z.: Regulation of biosynthesis of secondary metabolites. IX. The biosynthetic activity of blocked mutants ofStreptomyces aureofaciens.Folia Microbiol. 14, 215 (1969).
Cudlín J., Steinebová N., Matějů J., Blumauerová M., Vaněk Z.: Microbial transformation of 1,8-dihydroxy-9,10-anthraquinone.Coll. Czech. Chem. Commun. 43, 1803 (1978).
Florini J. R., Vestling C. S.: Graphical determination of the dissociation constants for two substrate enzyme systems.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 25, 575 (1957).
Hopkinson S. M.: The chemistry and biochemistry of phenolic glycosides.Quart. Rev. 23, 98 (1969).
Hovorková N., Cudlín J., Matějů J., Blumauerová M., Vaněk Z.: Microbial glucosidation of alizarin and anthraflavin.Coll. Czech. Chem. Commun. 39, 662 (1974a).
Hovorková N., Cudlín J., Matějů J., Blumauerová M., Vaněk Z.: Microbial glucosidation of monohydroxyanthraquinones.Coll. Czech. Chem. Commun. 39, 3568 (1974b).
Jermyn M. A.: Mechanism of oarbohydrase action.Science 125, 12 (1957).
Kotyk A., Horák J.:Enzyme Kinetics (in Czech). Academia, Prague 1977.
Linkweaver H., Burk D.: The determination of enzyme dissociation constants.J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 56, 658 (1934).
Lowby O. H., Rosenbrough N. J., Farr A. L., Randall R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265 (1951).
Matějů J., Cudlín J., Hovorková N., Blumauerová M., Vaněk Z.: Microbial glueosidation of dihydroxy-anthraquinones. General properties of the glucosidation system.Folia Microbiol. 19, 307 (1974).
Matějů J., Cudlín J., Steinerová N., Blumauerová M., Vaněk Z.: Isolation of glucosyltransferase fromStreptomyces aureofaciens.Folia Microbiol. 23, 337 (1978).
Seuberlich C.: Einwirkung der Schwefelsäure auf ein Gemenge von Gallus- und Benzoesäure.Ber. 10, 38 (1877).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matějů, J., Cudlín, J., Steinerová, N. et al. Partial purification and properties of glucosyltransferase fromStreptomyces aureofaciens . Folia Microbiol 24, 205–210 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02926449
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02926449