Abstract
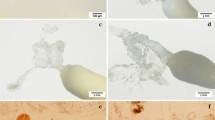
Embryogenic callus was initiated from immature zygotic embryos of black pine on medium DCR supplemented with 2 mg 1-1 2,4-D and 0.5 mg 1-1 BAP. The diploid number of chromosomes confirmed the origin of callus from zygotic embryos. The callus was white, glossy, mucilaginous and contained somatic embryos consisted of an embryonic region with densely cytoplasmic cells and suspensor region with long vacuolated cells. Although somatic embryos with green cotyledons were recognisable after ABA treatment and subsequent transfer to growth-regulator free media whole plants have not yet been obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- BAP:
-
6-benzylaminopurine
- NAA:
-
naphthylacelic acid
- KIN:
-
kinetin
- ABA:
-
abscisic acid
References
Becwar, M.R., Nagmani, R., Wann, S.R.: Initiation of embryogenic cultures and somatic embryo development in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda). - Can. J. Forest Res.20: 800–817, 1990.
Becwar, M.R., Noland, T.L., Wann, S.R.: Somatic embryo development and plant regeneration from embryonic Norway spruce callus. - TAPPI70: 155–160, 1987.
Finer, J.J., Kriebel, H.B., Becwar, M.R.: Initiation of embryogenic callus and suspension cultures of eastern white pine (Pinus strobus L.). - Plant Cell Rep.8: 203–206, 1989.
Gupta, P.K., Durzan, D.J.: Shoot multiplication for mature trees of Douglas-fir(Pseudotsuga menziesii) and sugarpine(Pinus lambertiana). - Plant Cell Rep.4: 177–179, 1985.
Gupta, P.K., Durzan, J.J.: Somatic polyembryogenesis from callus of mature sugar pine embryos. - Biotechnology4: 643–645, 1986.
Hakman, I., Fowke, L.C.: Somatic embryogenesis inPicea glauca (white spruce) andPicea mariana (black spruce). -Can. J. Bot.65: 656–659, 1987.
Hakman, I., Fowke, L.C., von Arnold, S., Ericksson, T.: The development of somatic embryos in tissue cultures initiated from immature embryos ofPicea abies (Norway spruce). - Plant Sci.38: 53–60, 1985.
Hakman, I., von Arnold, S.: Plantlet regeneration through somatic embryogenesis inPicea abies (Norway spruce). -J. Plant Physiol.121: 149–158, 1985.
Jain, S.M., Dong, N., Newton, R.J.: Somatic embryogenesis in slash pine(Pinus elliottii) from immature embryos culturedin vitro. - Plant Sci.65: 233–243, 1989.
Jain, S.M., Newton, R.J., Soltes, E.J.: Enhancement of somatic embryogenesis in Norway spruce(Picea abies L.). - Theor. Appl. Genet.76: 501–506, 1988.
Klimaszewska, K.: Plantlet development from immature zygotic embryos of hybrid larch through somatic embryogenesis. - Plant Sci.63: 95–103, 1989.
Kormut’ak, A., Lanáková, M.: Biochemistry of Reproductive Organs and Hybridological Relationships of Selected Pine Species(Pinus sp.). (Acta dendrologica) - Veda, Bratislava 1988, 119 pp.
Laine, E., David, H.: Somatic embryogenesis in immature embryos and protoplasts ofPinus caribae. - Plant Sci.69: 215–225, 1990.
Lelu, M.-A., Boulay, M., Arnaud, Y.: Obtention de cals embryogenes a partir de cotylédons dePicea abies (L.) Karst. prélevés sur de jeunes plantes agées de 3 a 7 après germination. Compt. rend. Acad. Sci. Paris, Sér. III305: 105–109, 1987.
Litvay, L.D., Johnson, M.A., Verma, D., Einspahr, D., Weyrauch, K.: Conifer suspension culture medium developmental using analytical data from developing seeds. - Tech. Paper Serv., Inst. Paper Chem. (Appleton, WI)115: 1–17, 1981.
Nagmani, R., Bonga, J.M.: Embryogenesis in subcultured callus ofLarix decidua. - Can. J. Forest Res.15: 1088–1091, 1985.
Salajová, T.: [Micropropagation of European black pine(Pinus nigra Arn.)]. - In: Vagera, J., Doležel J., Sokolová H. (ed.):In Vitro Manipulation in Higher Plants. (Proc. Conf. Olomouc 13–16 Nov. 1990.).] P. 130. ÚEB ČSAV, Olomouc 1990. [In Slovak.]
Schuller, A., Reuter, G., Geiger, T.: Somatic embryogenesis from seed explants ofAbies alba. - Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult.17: 53–59, 1989.
Tremblay, F.M.: Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration from embryos isolated from stored seedsof Picea glauca. - Can. J. Bot.68: 236–242, 1990.
von Arnold, S.: Improved efficiency of somatic embryogenesis in mature embryos ofPicea abies (L.) Karst. - J. Plant Physiol.128: 233–244, 1987.
von Arnold, S., Eriksson, T.:In vitro studies of adventitious shoot formation inPinus contorta. - Can. J. Bot.59: 870–874, 1981.
von Arnold, S., Hakman, I.: Regulation of somatic embryo development inPicea abies by abscisic acid (ABA). -J. Plant Physiol.132: 164–169, 1988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salajová, T., Salaj, J. Somatic embryogenesis in European black pine (Pinus nigra Arn.). Biol Plant 34, 213–218 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02925871
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02925871