Abstract
A study was performed on the effect of various concentrations of IAA, 2,3,6-triiodobenzoic acid, and maleic hydrazide, supplied to Richter’s nutrient solution, on growth of pea plants in water cultures. After a 18-day cultivation growth was evaluated and in the plants gathered the content of total N, P, K, and Ca was estimated.
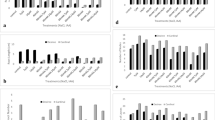
Growth of experimental plants (as evaluated from fresh and dry weight) was affected by all three regulators in dependence on the concentration used. It was stimulated by lower concentrations and inhibited by higher, the production of both fresh and dry weight of the root system being stimulated by all IAA concentrations used.
The ratio of root dry weight to that of the entire plant was markedly increased after application of IAA and 2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid, whereas when applying maleic hydrazide it was only slightly increased in comparison with control.
Stimulation or inhibition of growth induced by IAA treatment was accompanied by an accordingly increased or decreased accumulation of N, P, K, and Ca. Thus their utilization did not change in comparison with control. On the other hand, both inhibitory and stimulatory effects of 2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid and maleic hydrazide on growth were associated with a relatively lower accumulation of the elements in question, resulting in an increased utilization.
The distribution index of N, P, K, and Ca decreased with increasing concentrations of IAA, 2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid and maleic hydrazide. Only the highest 2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid and maleic hydrazide concentrations used brought about a more marked increase in the distribution index of potassium, simultaneously with a marked decrease in the distribution index of calcium.
Abstract
Sledovali jsme ve vodních kulturách vliv různých koncentrací IAA, TIBA a MH přidávanych do Richterova živného roztoku na růst hrachu. Po 18 dneoh kultivace jsme hodnotili růst a ve sklizených rostlinách jsme stanovili obsah celkového N, P, K a Ca.
Růst pokusných rostlin (hodnoceno vahou svěží a suché hmoty) byl všemi třemi regulátory ovlivňován v závislosti na použité konoentraci. Nižší koncentrace růst stimulovaly, vyšší inhibovaly, přičemž všeohny použité koncentrace IAA stimulovaly tvorbu svěží hmoty i sušiny kořenového systému.
Poměr váhy sušiny kořenů váze sušiny celé rostliny (RWR) byl aplikací IAA a TIBA zvýšen, zatímco MH jej oproti kontrole neměnil. Stimulace příp. inhibice růstu vyvolaná aplikací IAA byla provázena úměrně zvýšenou nebo sníženou akumulací N, P, a Ca. Proto se také utilizace oproti kontrole neměnila.
Naproti tomu inhibiční i stimulační působení TIBA a MH na růst bylo provázeno relativně nižší akumulací zmíněných prvků, což se projevilo ve zvýšené utilizaci.
DistribuČní index N, P, K a Ca se stoupajícími koncentracemi IAA, TIBA i MH klesal. Pouze nejvyšší použité koncentrace TIBA a MH vyvolaly výraznější zvýšení DI draslíku se současně výrazným snížením DI vápníku.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Booth, A., Moorby, J., Davies, R., Jokes, H., Wakeing, P. F.: Effects of indolyl-3-acetic acid on the movement of nutrients within plants. — Nature194: 204–205, 1962.
Commoner, B., Mazia, D.: The mechanism of auxin action. — Plant Physiol.17: 682–685, 1942.
Davies, C. R., Wareing, P. W.: Auxin-directed transport of radiophosphorus in stems. — Planta65: 139–156, 1965.
Fryee, H. C.: Elements of Statistic — New York, 1954.
Hay, J. R.: The effect of 2,3-dichlorphenoxyacetic acid and 2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid on the transport of indolacetic acid. — Plant Physiol.31: 118–120, 1956.
Higinbouthman, N., Latimer, H., Eppleym, R.: Stimulation of rubidium absorption by auxins. — Science118: 243–245, 1954.
Heubý, K., Konvička, O.: Polní pokusy, jejich zakládání a hodnocení [Field experiments, their foundation and evaluation. — Olomouc, 1954.
Ilan, I.: A specific stimulatory action of indolyl-3-aeetic acid on potasium uptake by plant cells, with concomitant inhibition of ammonium uptake —. Nature194: 203–204, 1962.
Ilan, I., Reinhold, L.: Analysis of the effects of indole-3-acetic acid on the uptake of monovalent cations. — Physiol. Plant.16: 696–603, 1963.
Kentzer, T., Libbert, E.: Blockade des Gibberellinsäuretransports in Hypocotylsegmenten durch Trijodbenzoesäure. Zugleich ein Agarblocktest auf Gibberelline. — Planta56: 23–27, 1961.
Libbert, E.: Trijodbenzoesäure und die Stoffleitung bei höheren Pflanzen — Planta53: 612–627, 1969.
Lindner, R. C.: Rapid methods for some of the more common inorganic constituents of plant tissues. — Plant Physiol.19: 76–89, 1944.
MináУ, J., Laštůvka, Z.: Gegenseitige Beeinflussung von Gerste(Hordeum vulgare L.) und Hafer(Avena sativa L.) in Wasserkulturen bei ergänzter Ernährung. — Biol. Plant.8: 305–315, 1966.
Mitschel, J. W., Martin, W. E.: Effect of indoleacetic acid on growth and chemical com, position of etiolated bean plants. — Bot. Gaz.99: 171–183, 1937.
Nakamuba, E.: Effect of decapitation and indole-3-acetic acid on the distribution of radioactive phosphorus in the stem ofPisum sativum. — Plant Cell Physiol.5: 521–524, 1964.
Riebartsch, K.: Flammenphotometrische Calcium-Bestimmung in Pflanzen ohne Abtrennung von Begleitelementen. — Z. Pflanz. Düngung Bodenkunde103: 39–43, 1963.
Stuart, N. W.: Nitrogen and carbohydrate of kidney bean cuttings as affected by treatment with indolacetic acid. — Bot. Gaz.100: 298–311, 1939.
Ţebánek, J.: O korelativní stimulaci zeleniny směsí kyseliny β-indolylmásehiè a nikotinove. [On correlative Stimulation in vegetables by a mixture of β-indolylbutiric acid and nicotinic acid.] — Sborník VSZ, Brno, A, (1): 15–21, 1956.
Ţebánek, J.: Effect of the amputation of the cotyledon and of the application of growth regulators on the transport32P in decapitated pea seedlings. — Biol. Plant.7: 380–386, 1965.
Ţebánek, J.: Interaction of indoleacetic acid with synthetic and native growth regulators during transfer32P into epicotyls of etiolated pea seedlings. — Biol. Plant.8: 213–219, 1966.
Ţebánek, J.: Einfluss von Pasten mit verschiedenen Indolylessigsäure-Konzentrationen auf den Transport von32P dekapitierten Erbsenepikotylen. — Planta15: 283–285, 1967.
Udvardy, J.: The effect of naphthalene acetic acid and maleic hydrazide on nitrogen metabolism of apricot-buds. — Acta bot. Acad. Sci. hung.9: 348–358, 1963.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raková, A., Minar, J. Effect of β-indoleacetic acid, maleic hydrazide, and 2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid on N, P, K, and Ca accumulation by pea plants. Biol Plant 12, 348–358 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02922189
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02922189