Abstract
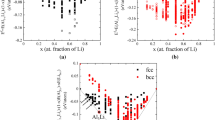
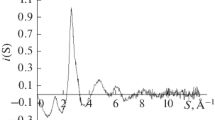
Using X-ray diffraction, the structure factors of molten Al−Fe alloys were determined as a function of composition at a constant 1 550°C. The nearest neighbour distance and coordination number are given. Both structure factors and total density functions could be well reproduced by a micro-inhomogeneous model. The entire concentration region can be divided into four intervals with Al, Al7Fe, Al5Fe2, Fe3Al and Fe acting as borders. Alloys situated at the borders of the concentration intervals contain clusters of one type whose composition represents that of the alloy in question. The alloys between the borders contain clusters of the two border types.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mckamey, C. C., Devan, J. H., Tortorelli, P. F., et al., A review of recent developments in Fe3Al-based alloys,J. Mater. Res, 1991, 6(8): 1779.
Mondolfo, L. F.,Aluminum Alloys: Structure and Properties, London: Butterworths, 1976, 244–245.
Black, P. J., Cundall, J. A., The structure of aluminum-iron alloys,Acta Cryst., 1966, 20: 417.
Emelganov, A. V., Bazin, Yu. A., Klimenkov, E. A., An X-ray study of melts of the Fe−Al system,Fiz Svoistva Met: Splavov, 1983, 4: 88.
Homtova, E. V., Sluhofskii, Romanova, A. V., Structure of aluminum-iron melts,J. Phys. (in Russian), 1986, 31 (7): 1045.
Kirchhoff, F., Holender, J. M., Gillan, M. J., The liquid Ag−Se system studied byab initio simulations,J. Non-cryst. Solids, 1996, 205–207: 79.
Kita, V., Zeze, M., Morita, Z., Structural analysis of molten Fe−Si alloys by X-ray diffraction.Transactions ISIJ, 1982, 22: 571.
Wasada, Y.,The Structure of Non-crystalline Materials, New York: McGraw-Hill, 1980, 27–36.
Wagner, C. N. J., Halder, N. C., Atomic distribution and electronic transport properties in liquid alloys studied by X-ray diffraction,Advances in Physics, 1967, 16(62–64): 241.
Ilinskii, A. G., Sliusarenko, S. I., Hoyer, W., et al., Liquid atomic structure of Bi-Ga system,Tam Zhie, 1992, 14(12): 35.
Buhalenko, V. V., Ilinskii, A. G., Romanova, A. V., et al., X-ray diffraction study on the liquid structure of Zn-Ga alloy system,Metallofizika, 1991, 13(10): 92.
Gebhardt, B., Halm, Th., Hoyer, W., The structure of liquid Ca-In alloys,J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 1995, 192&193: 306.
Gilgien, P., Zryd, A., Kurz, W., Microstructure selection maps for Al−Fe alloys,Acta Metall. Mater., 1995, 43(9): 3477.
Hsieh, H. Y., Egami, T., He, Y., et al., Short range ordering in amorphous Al90FexCe10−x,J. Non-cryst. Solids, 1991, 135: 248,
Robertson, J. L., Moss, S. C., Kreider, K. G., Comparison of amorphous and quasicrystalline films of sputtered Al0.72Mn0.22Si0.06,Phys. Rev. Lett., 1988, 60(2): 2062.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 59671046).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, J., Bian, X., Wang, W. et al. Micro-inhomogeneous structure of liquid Al−Fe alloys. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 41, 182–187 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919681
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919681