Abstract
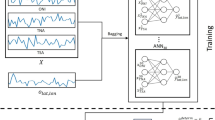
In terms of the modular fuzzy neural network (MFNN) combining fuzzy c-mean (FCM) cluster and single-layer neural network, a short-term climate prediction model is developed. It is found from modeling results that the MFNN model for short-term climate prediction has advantages of simple structure, no hidden layer and stable network parameters because of the assembling of sound functions of the selfadaptive learning, association and fuzzy information processing of fuzzy mathematics and neural network methods. The case computational results of Guangxi flood season (JJA) rainfall show that the mean absolute error (MAE) and mean relative error (MRE) of the prediction during 1998–2002 are 68.8 mm and 9.78%, and in comparison with the regression method, under the conditions of the same predictors and period they are 97.8 mm and 12.28% respectively. Furthermore, it is also found from the stability analysis of the modular model that the change of the prediction results of independent samples with training times in the stably convergent interval of the model is less than 1.3 mm. The obvious oscillation phenomenon of prediction results with training times, such as in the common back-propagation neural network (BPNN) model, does not occur, indicating a better practical application potential of the MFNN model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baik, J. J., and H. S. Hwang, 1998: Tropical cyclone intensity prediction using a regression method and a neural network.J. Meteor. Soc. Japan,76, 711–717.
Cao Hongxing, and Chen Guofan, 1988:Fuzzy Set Methods with Meteorological Applications. China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 215–343. (in Chinese)
Dean, A. R., and B. H. Fiedler, 2002: Forecasting warmseason burnoff of low clouds at the San Francisco International Airport using linear regression and a neural network.J. Appl. Meteor.,41, 629–639.
Jin Long, Luo Ying, and Lin Zhenshan, 1997: Comparison of long-term forecasting of June–August rainfall over Changjiang-Huaihe valleys.Adv. Atmos. Sci.,14, 87–92.
Jin Long, Qin Weiliang, and Yao Huadong, 2000: A multistep prediction wavelet neural network model.Chinese J. Atmos. Sci.,24, 79–86. (in Chinese)
Kim, G., and A. P. Barros, 2001: Quantitative flood dorecasting using multisensor data and neural neworks.J. Hydrol.,246, 45–62.
Kim, H., and K. Nan, 1995: Object recognition of one-DOF tools by back-propagation neural network.IEEE Transactions on Neural Network,6, 484–487.
Kuligowski, R. J., and A. P. Brros, 1998: Experiments in short-term precipitation forecasting using artificial neural networks.Mon. Wea. Rev.,126, 470–482.
Langari, R., and L. Wang, 1996: Fuzzy models, modular networks and hybrid learning.Fuzzy Sets and Systems,79, 141–150.
Luo Xueshan, and Wang Zhenlei, 1998: Application of fuzzy neural networks to the blending of data.Fuzzy System and Mathematics,12, 11–19. (in Chinese)
Marzban, C., and A. Witt, 2001: A Bayesian neural network for severe-hail size prediction.Wea. Forecasting,16, 600–610.
Mavrovouniotis, M. L., and S. Chang, 1992: Hierarchical neural networks.Computers and Chemical Engineering,16, 347–369.
McBratney, A. B., and A. W. Moore, 1985: Application of fuzzy sets to climatic classification.Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,35, 165–185.
Rajeevan, M., P. Guhathakurta, and V. Thapliyal, 2000: New models for long range forecast of summer monsoon rainfall over north west and peninsular India.Meteorology and Atmosphere Physics,73, 211–225.
Wang Yutao, Xia Jinbo, Zhou Jianchang, and Wang Shi, 1999: The fuzzy neural network expert system for learning of blast furnaces.J. Iron and Steel Research,11, 72–76. (in Chinese)
Yu Dongjun, and Wang Shitong, 1998: A new Fuzzy neural network model and its use in modeling.J. East China Institute of Ship-Building Industry,12, 22–28. (in Chinese)
Zhao Xiang, and Xiao Deyun, 2001: Fault diagnosis of nonlinear systems based on modular fuzzy neural networks.Cybernetics Theories and Applications,18, 395–400. (in Chinese)
Zhang Liming, 1992:Artificial Neural Network Models and Applications. Fudan University Press, Shanghai, 43–47. (in Chinese)
Zhou Jiabin, and Huang Jiayou, 1997: Recent advances in statistical meteorology in China.Acta Meteorologica Sinica,55, 297–304. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, J., Jian, J. & Cai, Y. A short-term climate prediction model based on a modular fuzzy neural network. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 22, 428–435 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02918756
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02918756