Abstract
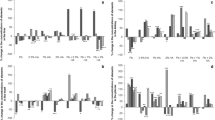
The effect of tin and lead on the levels of essential metals (Zn, Cu, Ca, Fe) in rabbit tissues was compared in relation to the route of administration. Animals received intraperitoneally, or per os, SnCl2 (2 mg Sn/kg) or Pb(CH3COO)2 (3.5 mg Pb/kg) every day for 5 d or for 1 mo. Copper, zinc, iron, and calcium were determined by AAS in the liver, kidneys, spleen, brain, bone marrow, and blood; lead and tin concentration were measured in the blood of animals. Tin and lead administered per os caused either no changes or the decreased concentration of endogenous metals in several tissues. The other route of administration (ip) of both metals generally contributed to the increased storage of essential elements. Blood tin levels of tin treated animals were only about ≲1/10 of blood lead concentrations of rabbits exposed to lead.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. R. Flanagan, D. L. Hamilton, J. Haist, and L. S. Valberg,Gastroenterology 77, 1074 (1979).
P. R. Flanagan, J. Haist, and L. S. Valberg,J. Nutr. 110, 1754 (1980).
R. M. El-Gazzar, V. N. Finelli, J. Boiano, and H. G. Petering,Toxicol. Lett. 1, 227 (1978).
H. G. Petering,Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 298, (1980).
D. S. Klauder and H. G. Petering,J. Nutr. 107, 1779 (1977).
G. J. Brewer, G. M. Hill, R. D. Dick, A. S. Prasad, and Z. T. Cossack,J. Amer. Coll. Nutr. 4, 33 (1985).
C. L. Keen, N. H. Reistein, J. Goudey-Lefevre, M. Lefevre, B. Lonnerdal, B. O. Schneeman, and L. S. Hurley,Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 8, 123 (1985).
M. Abdulla, S. Svensson, and B. Haeger-Aronsen,Arch. Environ. Health 34, 464 (1979).
P. Meredith and M. Moore,Int. Arch. Occup. Environm. Health 45, 163 (1980).
G. D. Miller, T. F. Massaro, and E. Koperek,Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 6, 519 (1984).
F. L. Cerklewski,J. Nutr. 114, 550 (1984).
A. A. Mylroie, H. Collins, C. Umbles, and J. Kyle,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 82, 512 (1986).
W. Victery, C. R. Miller, and R. A. Goyer,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 107, 129 (1986).
M. Chiba and M. Kikuchi,Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 82, 1057, (1978).
G. Zaręba and J. Chmielnicka,Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 9, 40 (1985).
G. Zaręba, J. Chmielnicka, and G. Kustra,Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 11, 144 (1986).
R. A. Hiles,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 27, 366 (1974).
M. Yamaguchi, R. Saito, and S. Okada,Toxicol. 16, 267 (1980).
J. Chmielnicka, J. A. Szymańska, and J. Snieć,Arch. Toxicol. 47, 263, (1981).
J. L. Greger and M. A. Johnson,Fd Cosmet. Toxicol. 19, 163 (1981).
M. A. Johnson and J. L. Greger,J. Nutr. 114, 1843 (1984).
M. Chiba, K. Ogihara, Y. Inaba, and T. Nishima,Toxicol. 31, 23 (1984).
J. Chmielnicka, E. A. Brzeźnicka, B. Barański, and K. Sitarek,Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 8, 191 (1985).
F. L. Cerklewski and R. M. Forbes,J. Nutr. 106, 689 (1976).
K. B. Mahaffey, S. C. Capell, B. C. Gladen, and B. A. Fowler,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 98, 463 (1981).
W. Victery, D. Thomas, P. Schoeps, and A. J. Vander,Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 4, 211 (1982).
E. Hietanen, A. Aito, U. Koivusaari, J. Kilpio, T. Nevalainen, M. Narhi, H. Savolainen, and H. Vainio,Toxicol. 25, 113 (1982).
M. A. Johnson, M. J. Baier, and J. L. Greger,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 35, 1332 (1982).
K. R. Mahaffey, In H. L. Needleman, ed.,Low Level Lead Exposure New York, 1980, Raven, p. 172.
K. R. Mahaffey, In R. L. Singhal, J. A. Thomas, eds.Lead Toxicity, Baltimore, 1980, Urban and Schwarzenberg, p. 425.
E. Weigand and M. Kirchgessner,J. Nutr. 110, 469 (1980).
T. Maitani, A. Watahiki, and K. T. Suzuki,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 83, 211 (1986).
Y. Suzuki and H. Yoshikawa,Ind. Health 14, 25 (1976).
K. Arizono, J. Toshihoko, S. Ota, and T. Ariyoshi,Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 35, 143 (1985).
N. Sugawara, Ch. Sugawara, and H. Miyako.Arch. Toxicol. 56, 25 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaręba, G., Chmielnicka, J. Effects of tin and lead on organ levels of essential minerals in rabbits. Biol Trace Elem Res 20, 233–242 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02917438
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02917438